
FLORIDA CIVIC LITERACY STUDY QUESTIONS WITH CORRECT ANSWERS GUARANTEED PASS | RATED A+
$ 10.5

The Early Industrial Revolution: The First Industrial Revolution. Best Study Notes.
$ 5.5

NR_327_POSTPARTUM_ISBAR NEWEST 2022.
$ 3

SCI 228 WEEK 6: WHAT IS A HEALTHY BODY WEIGHT?
$ 10

eBook [PDF] Community Pharmacy Practice Guidebook 1st Edition By Jessica Wooster, Frank Yu
$ 20

Information Technology Auditing 4th Edition Solution Manual
$ 24

GEN 216 Written Communications Exam | Q & A
$ 13

CONSTITUTIONAL LAW STUDY NOTES STUDY NOTES FOR CONSTITUTIONAL LAW WITH POSSIBLE QUESTIONS ASKED IN EXAM PAPERS
$ 11

Cash and Internal Controls: Management Notes
$ 4.5

CANCER OF THE ESOPHAGUS
$ 6.5
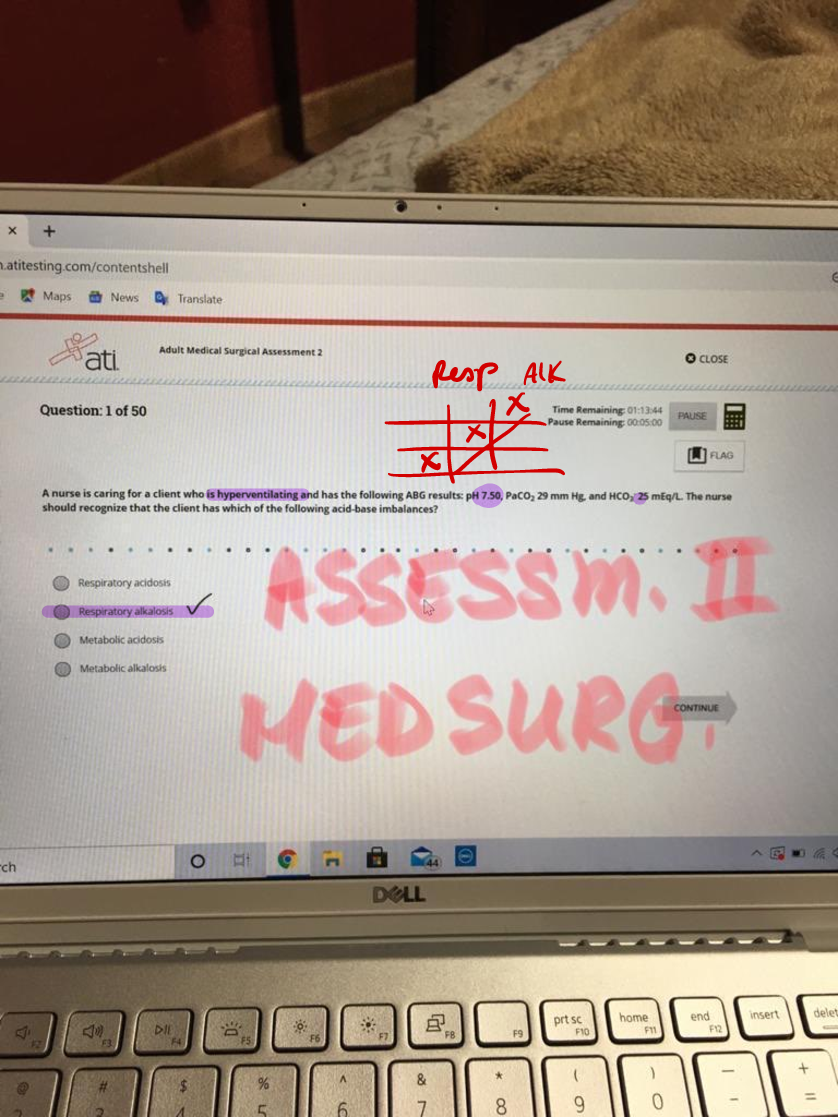
Capstone Adult Medical Surgical Assessment 2 Nursing Exams Questions and Answers (Screenshots of Actual Exam Questions and Correct Answers)
$ 41

EEC 104 MAE31012021.Working efficiently and effectively in advanced manufacturing and engineering
$ 10
.png)
University of south Africa-ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR AND MENTAL HEALTH
$ 10
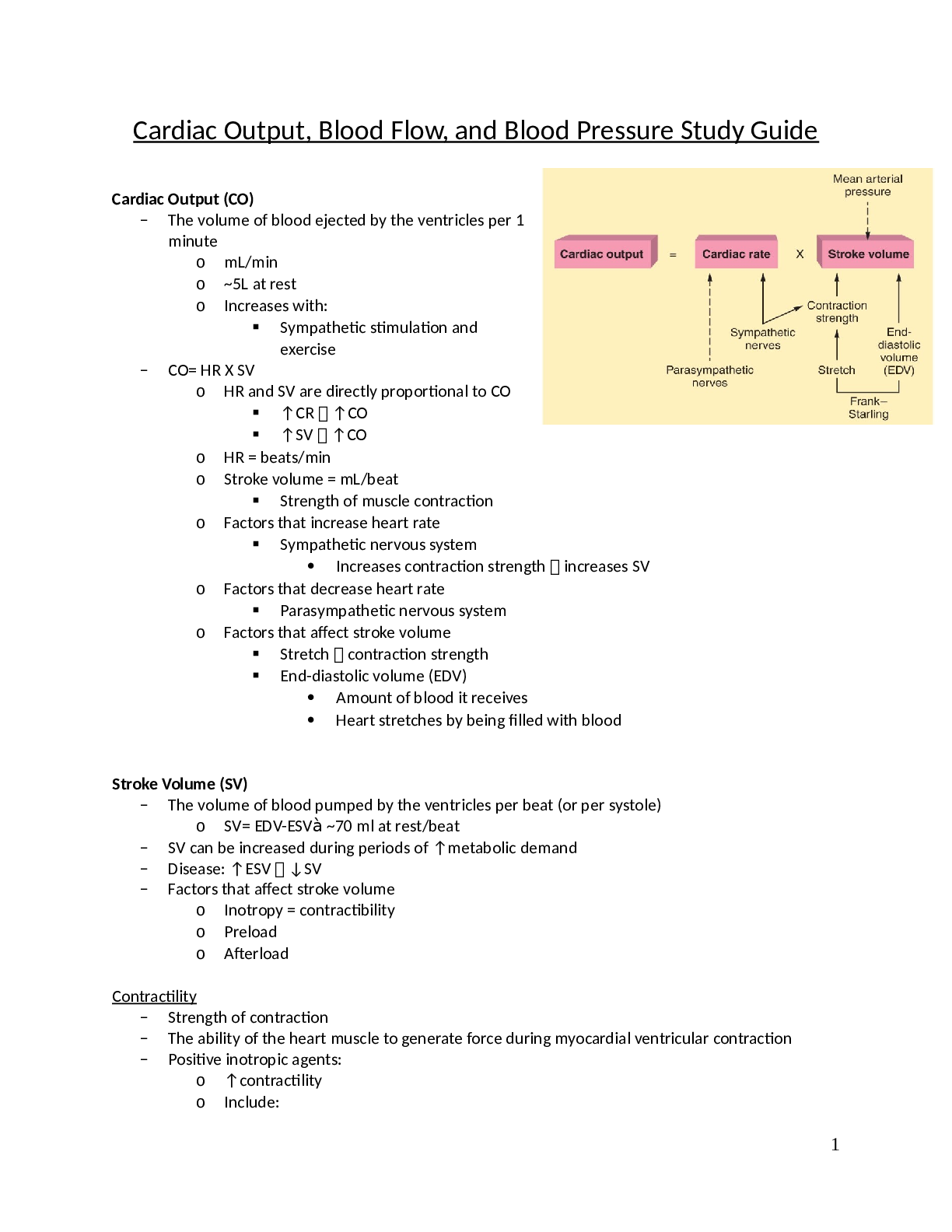
Cardiac Output, Blood Flow, and Blood Pressure Study Guide.
$ 12

Assignment 1 -Audit Risks and Going Concerns of Razor’s Edge Laser Cutting Inc. - Sheridan College FIN 4200D


























