
Death With Dignity Scenario And Reflection
$ 3

Aqa A-level COMPUTER SCIENCE 7517/2 Paper 2 Mark scheme June 2021 Version: Final 1.1
$ 11

HESI PN Practice (2025/2026) — Comprehensive Sample Questions With Verified Answers — Guaranteed Study Success — Updated & A+ Study Set
$ 38

[eBook] [PDF] Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Materials Fundamentals and Applications 1st Edition By Hongjing Wu, Jun Luo, Meiyin Yang
$ 25

UHC 2022 Ethics and Compliance Test
$ 11
A-level GEOGRAPHY Paper 2 Human Geography Time allowed: 2 hours 30 minutes Materials
$ 7

A Level Computer Science_H446/01 Mark Scheme Nov 2020 | Computer Systems
$ 7

NR 602 Midterm Study Guide
$ 7

eBook Agriculture through the Ages 1st Edition By Michael Woods, Mary B. Woods
$ 30
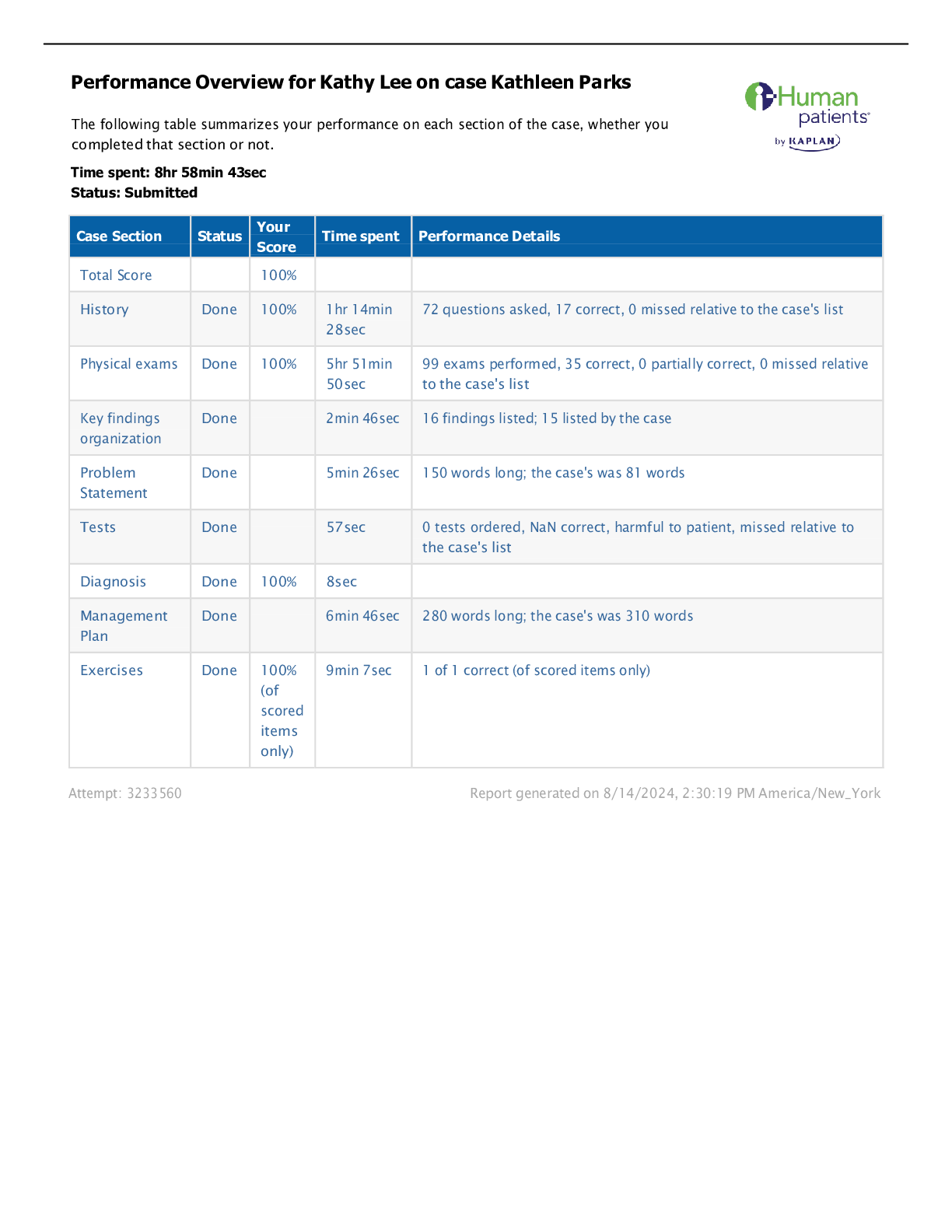
Kathleen Parks ihuman Complete Performance Overview
$ 14.5

Prominent Sociologists CASE STUDY
$ 5

eBook (EPUB) [PDF] Intermediate Microeconomics with Calculus A Modern Approach 2nd Edition By Hal R. Varian, Marc Melitz
$ 30

AF 4207 – L6 FINANCIAL REPORTING II
$ 7

2022 AHIP Final Exam Questions with Correct Answers Verified and Graded A+
$ 11

eBook [PDF] Person, Thing, Robot A Moral and Legal Ontology for the 21st Century and Beyond 1st Edition By David J. Gunke
$ 29

FIRE INSPECTOR 2023 SERIES ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 100% VERIFIED .
$ 13
Chapter 2 Bake 1 Study Guide / Score 100% / 2025 New Version


























