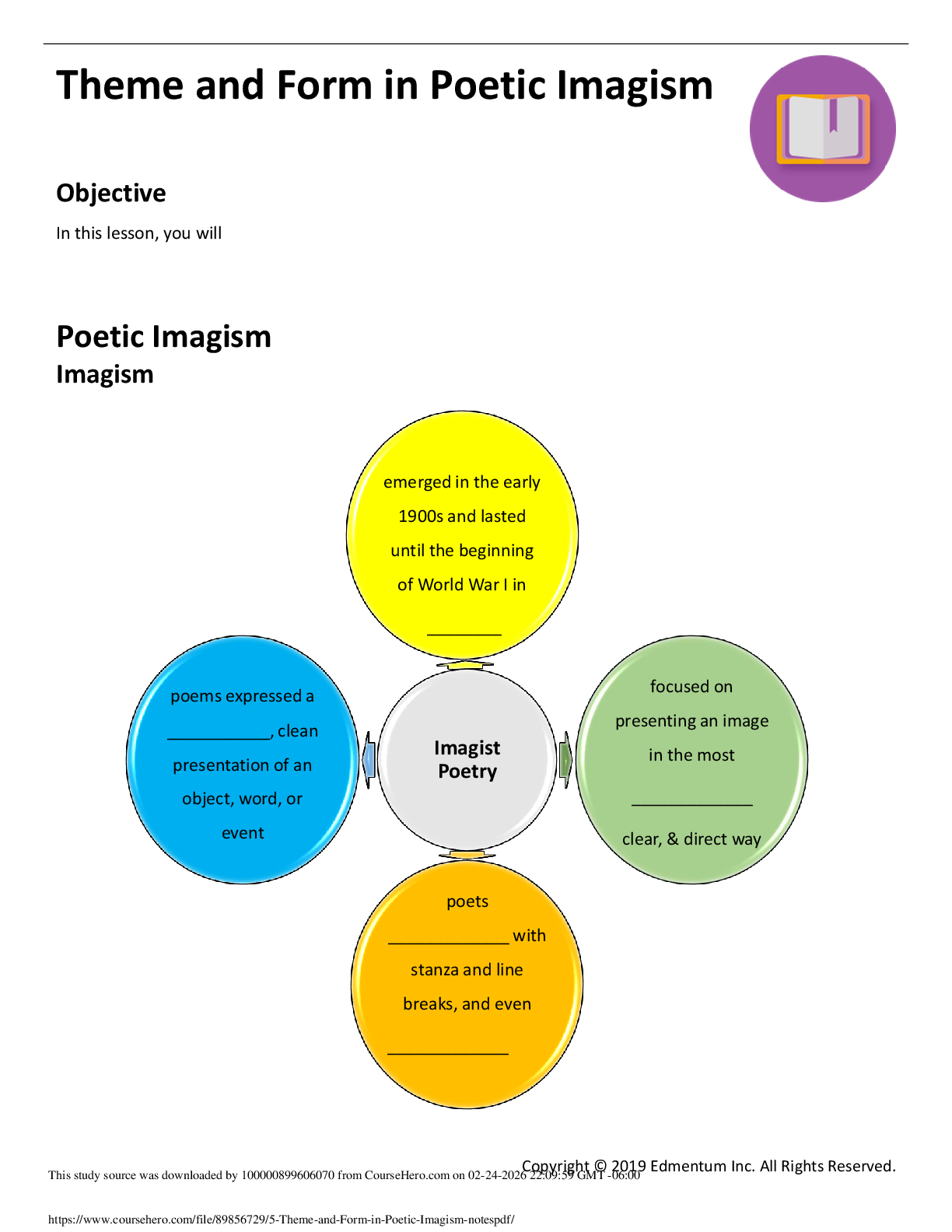
NR228: Nutrition
Health-is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, emotional, spiritually, socially.
Nut
? Formal Education-School
? Non-formal Education-American Heart Association or community
...
NR228: Nutrition
Health-is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, emotional, spiritually, socially.
Nut
? Formal Education-School
? Non-formal Education-American Heart Association or community wellness programs
? Informal Education- occurs through daily activities
? When a nurse chats with a patient regarding diet modification
Carbs= fuel—Simple (sugar) Complex (starch, fiber-provides no Kcals, no energy
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI)- How much experts recommend you eat of something, the goal to help prevent the chronic development of illness.
? Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
? Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
? Adequate Intake (AI)
? Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL)-how much of a nutrient you can have before you have negative effect.
? Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDRs)- counting macros (proteins, carbs)
? Fats 20-35%, Carbs 45-65%, Proteins 10-35%.
Kilocalorie know the table below
Males 2 drinks per is mod, 1 Food labels
-1st thing to do is to read the serving size.
o Free- Contains insignificant amount of fat (<0.5 grams)
o Reduced- 25% less calories
o Light/Lite- 1/3 fewer calories, or 50% less fat
o Organic vs Non-Organic-meat has to be no antibodies, no GMO, no synthesis fert., no pest control.
chooseMyplate.gov
✓ Requires 50% of grains should have whole grains.
✓ Vegs 2 ½ cups/ per day
✓ Fruit 2 cups/ day
✓ Dairy= skim/low fat Plant base diet is recommended
Best form of food is Fresh/ Raw vegs, then frozen, then canned foods. Exchange List
? Created by the American Diabetes and the American Dietetic Association
? Foods are divided into carbs, meats/meat subs, and fats.
? Serving size provides similar amount of carbs, protein, fat, and kcal.
Most effective way to evaluation a Pt’s diet is a FOOD JOURNAL. Carbs:
► Carbs are made up of: organic compounds of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen make up
simple carbs
► Simple: Monosaccharides (glucose, fructose) pass thought the GI easily.
► Simple: Disaccharides [Sucrose (fructose + glucose)] Table sugar
► Complex: Polysaccharides
► Many units of monosaccharides held together by a chemical bond
► Starch and fiber Lactose “milk Sugar” (glut galactose)
Maltose (glu + glu) + fermentation = alcohol gluconeogenesis-turning glycogen into glucose Glycogenosis-turning glucose into glycogen
► Primary job of Carb metabolism- Maintaining blood glucose (BG) levels
► Blood glucose levels can be maintained by metabolizing
► Carbs- easily broken down, and easily converted into glucose
► Lipids – Gluconeogenesis (ketosis)-turning fat into glucose, byproduct of ketones.
► Proteins- gluconeogenesis-turning glycogen into glucose, byproduct is ammonia, excess is turned into fat
► BG levels are maintained through:
► Carb metabolism
► Fat metabolism
► Ketones à Metabolic Acidosis
► Stored Carbs
► Glycogenosis-turning glucose into glycogen Nature Sources in the food supply
► Sugar cane and sugar beets
► Honey, dextrose, and molasses
► Other sources, such as corn syrup and high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS)
Sugar alcohols slower absorption effects:
► Provide 2-3 kcals of energy
► Occur naturally in fruits and berries
► Sorbitol, Mannitol, and Xylitol
Alternative sweeteners (artificial sweeteners) have no nutrient value:
► Aspartame- found in diet sodas, 160-220% sweeter than sucrose. Phenylketonuria PKU Pt are not to eat this. Cannot process/ absorb Phenylalanine
► Saccharin- Sweet N Low. 300x sweeter sucrose. Hx link to bladder cancer.
► Sucralose- Splenda. 600x sweeter sucrose. Poorly absorb be the body and excrete in the urine.
► Stevia- Stevia- 200 x sweeter sucrose.
Fiber
► 25-38 g/day
► Most Americans adults average 16 g/day
► Most Americans eat high protein & high fat diets & drink high sugared beverages
► Americans consume high amounts of refined grains
► Race/ethnicity
► Mexican-Americans: fiber consumption is the highest
► African Americans: fiber consumption is the lowest
► Fiber cannot be broken down by digestive juices
► Fiber adds no nutritional value
► Fiber creates bulk and eases the work of the GI muscles that regulate food movement
► GI flora uses fiber as a medium for microbial fermentation for vitamin synthesis & formation short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
► vitamin k, biotin, B12, folate, thiamin
► SCFAs: used by the colon mucosa for energy (maintains the health of the colon epithelial cells) & increase fecal matter bulk
Soluble Fiber: dissolves in fluids
► Thickens substances
► Pectin, mucilage, psyllium seed husk, guar gum, Insoluble Fiber: does not dissolve in fluids
► Cellulose, hemicellulose
► Foods are classified by type of fiber
► Less soluble: whole wheat, bran, fruits and mature veggies
► More soluble: oats, legumes, barley, apples, carrots
► Some are known to reduce cholesterol (oats, barley bran)
...........................................................................CONTINUED........................................................................................
[Show More]


















.png)