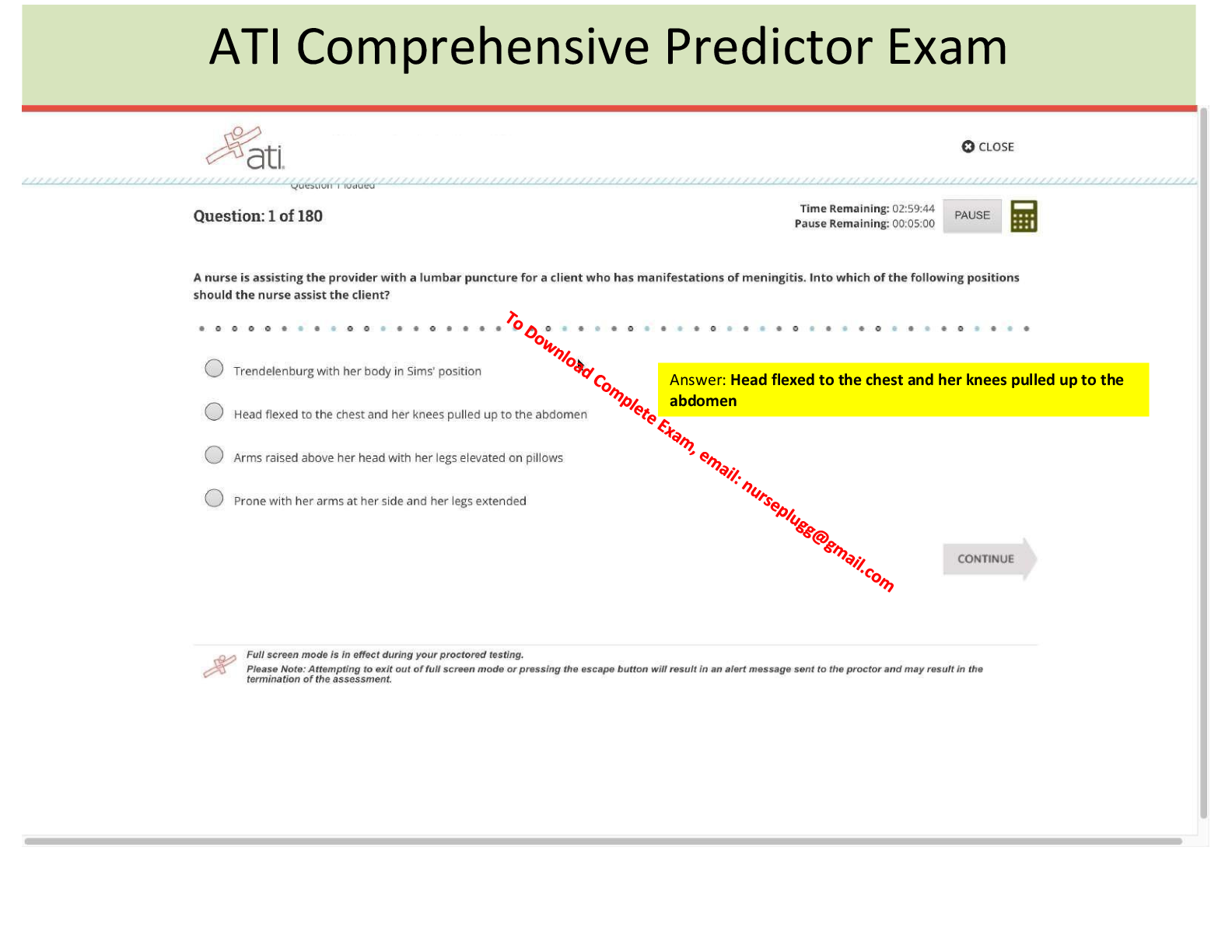
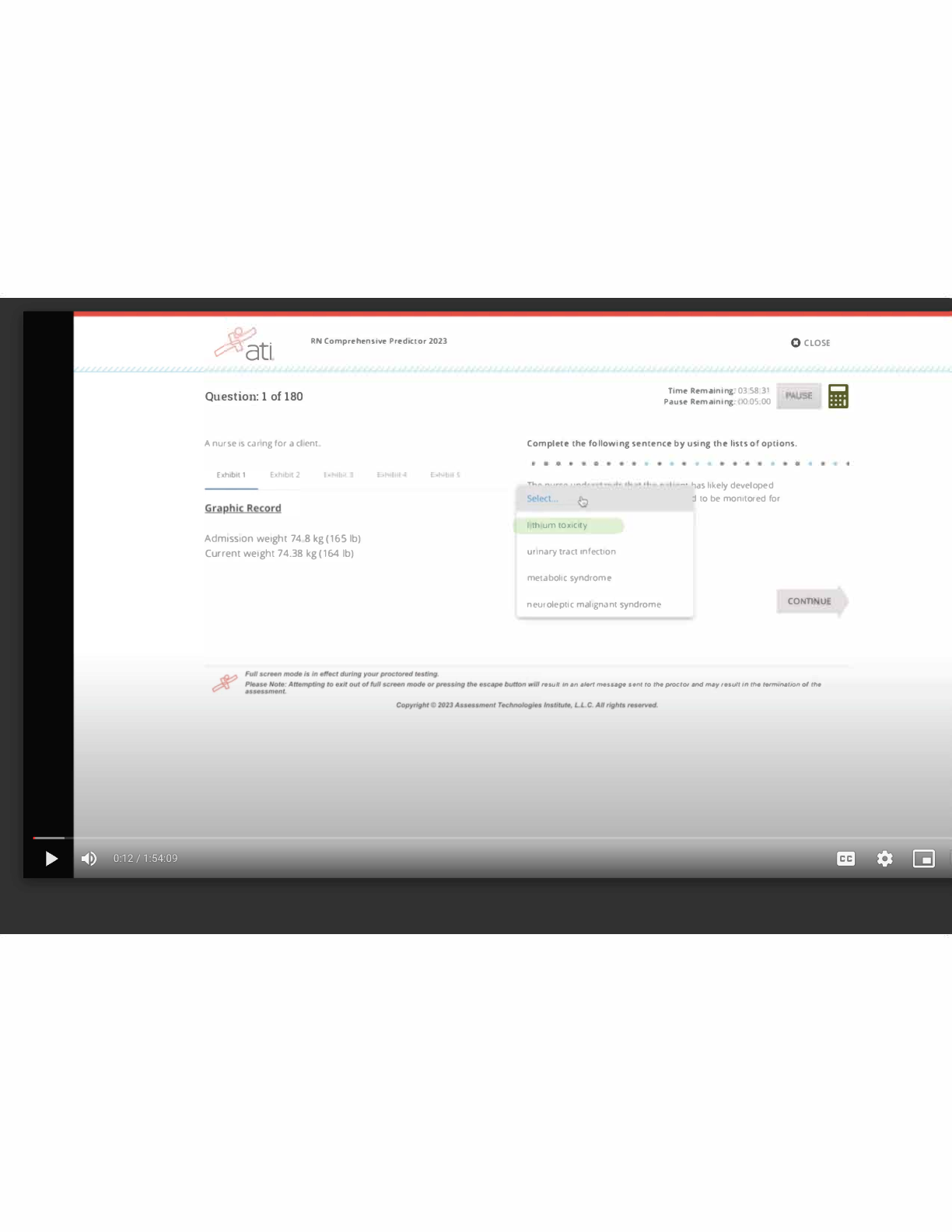
ATLS Practice Test 2
1. A 22yearold man sustains a gunshot wound to the left chest and is transported to a small
community hospital at which surgical capabilities are not available. In the emergency
department, a ch
...
ATLS Practice Test 2
1. A 22yearold man sustains a gunshot wound to the left chest and is transported to a small
community hospital at which surgical capabilities are not available. In the emergency
department, a chest tube is inserted and 700 mL of blood is evacuated. The trauma center
accepts the patient in transfer. Just before the patient is placed in the ambulance for
transfer, his blood pressure decreases to 80/68 mm Hg and his heart rate increases to 136
beats per minute. The next step should be to:
a. clamp the chest tube.
b. cancel the patient's transfer.
c. perform an emergency department thoracotomy.
d. repeat the primary survey and proceed with transfer.
e. delay the transfer until the referring doctor can contact a thoracic surgeon.
2. A young woman sustains a severe head injury as the result of a motor vehicle crash. In
the emergency department, her GCS is 6. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg and her
heart rate is 80 beats per minute. She is intubated and mechanically ventilated. Her pupils
are 3 mm in size and equally reactive to light. There is no other apparent injury. The most
important principle to follow in the early management of her head injury is to:
a. avoid hypotension.
b. administer an osmotic diuretic.
c. aggressively treat systemic hypertension.
d. reduce metabolic requirements of the brain.
e. distinguish between intracranial hematoma and cerebral edema.
3. A 6yearold boy walking across the street is struck by the front bumper of a sports utility
vehicle traveling at 32 kph (20 mph). Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
a. A flail chest is probable.
b. A symptomatic cardiac contusion is expected.
c. A pulmonary contusion may be present in the absence of rib fractures.
d. Transection of the thoracic aorta is more likely than in an adult patient.
e. Rib fractures are commonly found in children with this mechanism of injury.
4. A 39yearold man is admitted to the emergency department after an automobile
collision. He is cyanotic, has insufficient respiratory effort, and has a GCS Score of 6.
His full beard makes it difficult to fit the oxygen facemask to his face. The most
appropriate next step is to:
a. perform a surgical cricothyroidotomy.
b. attempt nasotracheal intubation.
c. ventilate him with a bagmask device until cspine injury can be excluded.
d. attempt orotracheal intubation using 2 people and inline stabilization of the
cervical spine.
e. ventilate the patient with a bagmask device until his beard can be shaved for
better mask fit.
[Show More]


 (1).png)