VATI PREDICTOR EXAM 2022 UPDATED
$ 15
Grade 10 Biology Notes 123069402 / Complete Study Guide / 2025 Exam Update
$ 7
.png)
ALS/ACLS - Team Response Scenario - Katherine Archer [2022] COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 4

Boating License FL Questions and Answers 100% Pass
$ 10
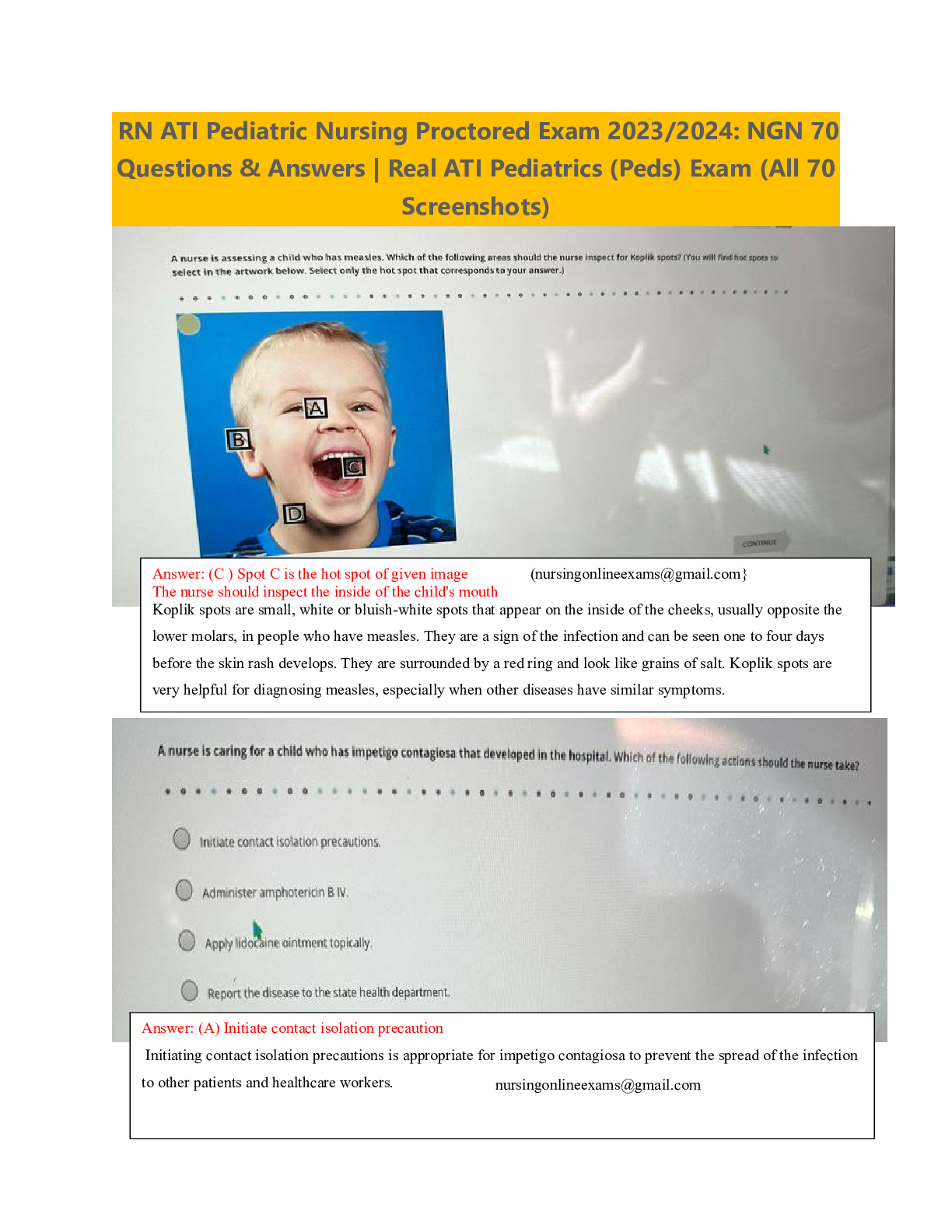
ATI RN Pediatric Nursing Proctored Exam 2023/2024: NGN 70 Questions & Answers | Comprehensive Study Guide & Practice Test For Pediatric Nursing (PED)
$ 41
 (2).png)
American Military University> EDMG 220 Mid term Exam- Answered 2021
$ 15

TNCC Written Exam 2022 (92 Questions with 100% Correct Answers)
$ 7

Principles of Design-Build and Post Award & Contracts,
$ 19.5

Data and Computer Communications, 10e William Stallings (Solution Manual)
$ 25

WGU C172 NETWORK AND SECURITY FOUNDATION EXAM GUIDE
$ 15

NR 602 Week 3 iHuman SOAP SOAP Note Template Completed
$ 8

PAD 599 Competency Exam 2 with Answers [Graded A]
$ 13

STAT 200 Week 6 Homework Problems, full solution guide, 100% correct
$ 10

Ethics NCLEX Review Questions / Score 100% / New Version / 2025 Update – Study Guide & Practice





.png)