Test Bank For Technical Communication, 16th Edition by John M. Lannon Chapter 1-24
$ 15.5

NR 293 ATI Pharmacology Final Review latest - Chamberlain College of Nursing.pdf
$ 9.5

CLT Practice Final Exam Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A
$ 9

ATI-RN Assessment Level 1: Test A 2022
$ 11

NURS-6521-MIDTERM-EXAM-Set-1 (GRADED A+)
$ 11

AQA GCSE MATHEMATICS 8300/3H Higher Tier Paper 3 Calculator Mark scheme June 2020
$ 12

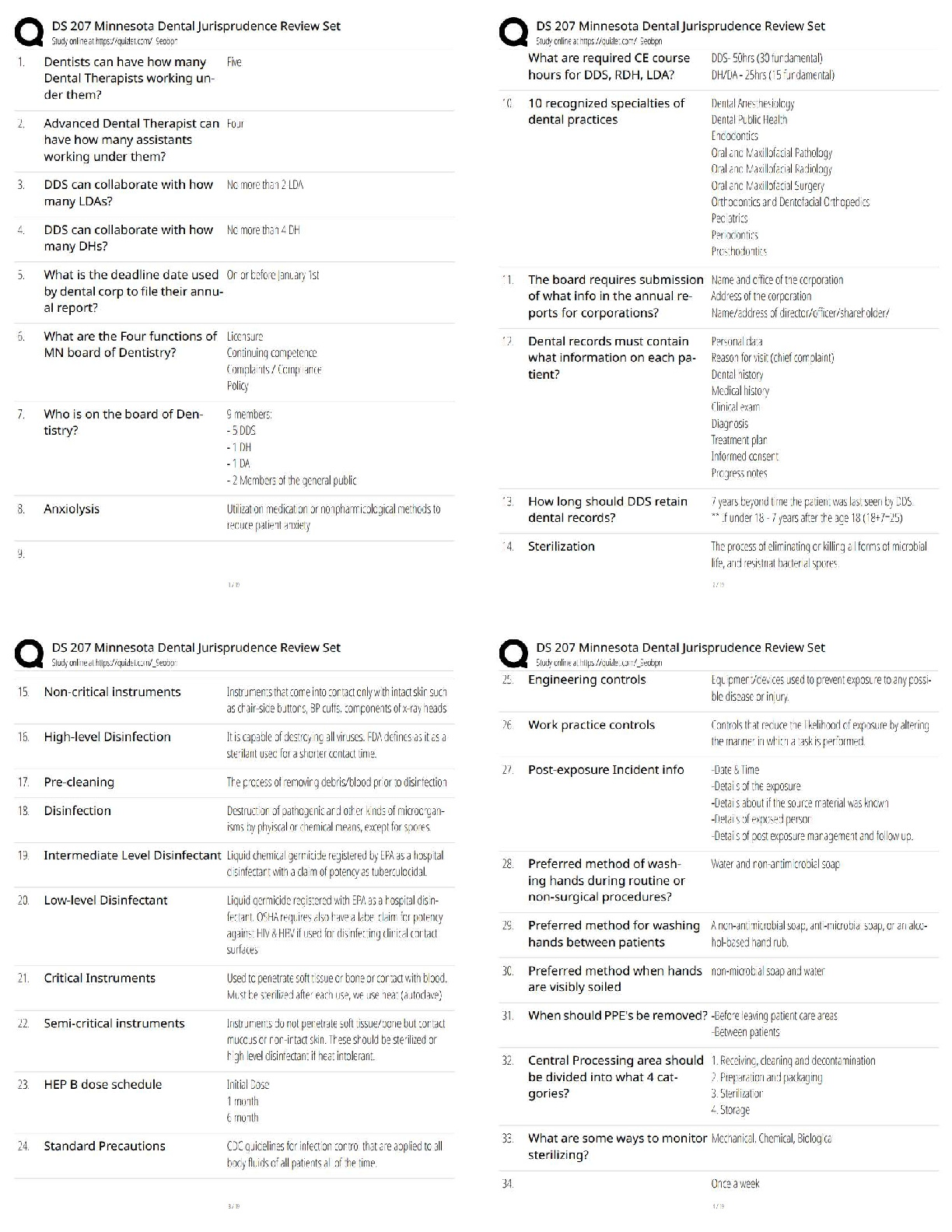
DANB Radiation Health and Safety Practice Exam 1
$ 20

McKinney: Evolve Resources for Maternal-Child Nursing, 5th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE CHAPTER 1-30
$ 20

Test Bank for Business Communication: Process & Product, 10th Edition by Mary Ellen Guffey & Dana Loewy - All Chapters (1-16) Included and Updated
$ 29

Midterm+Exam+Winter+2021+with+solutions+for+web LATEST FOR 2021/2022
$ 14
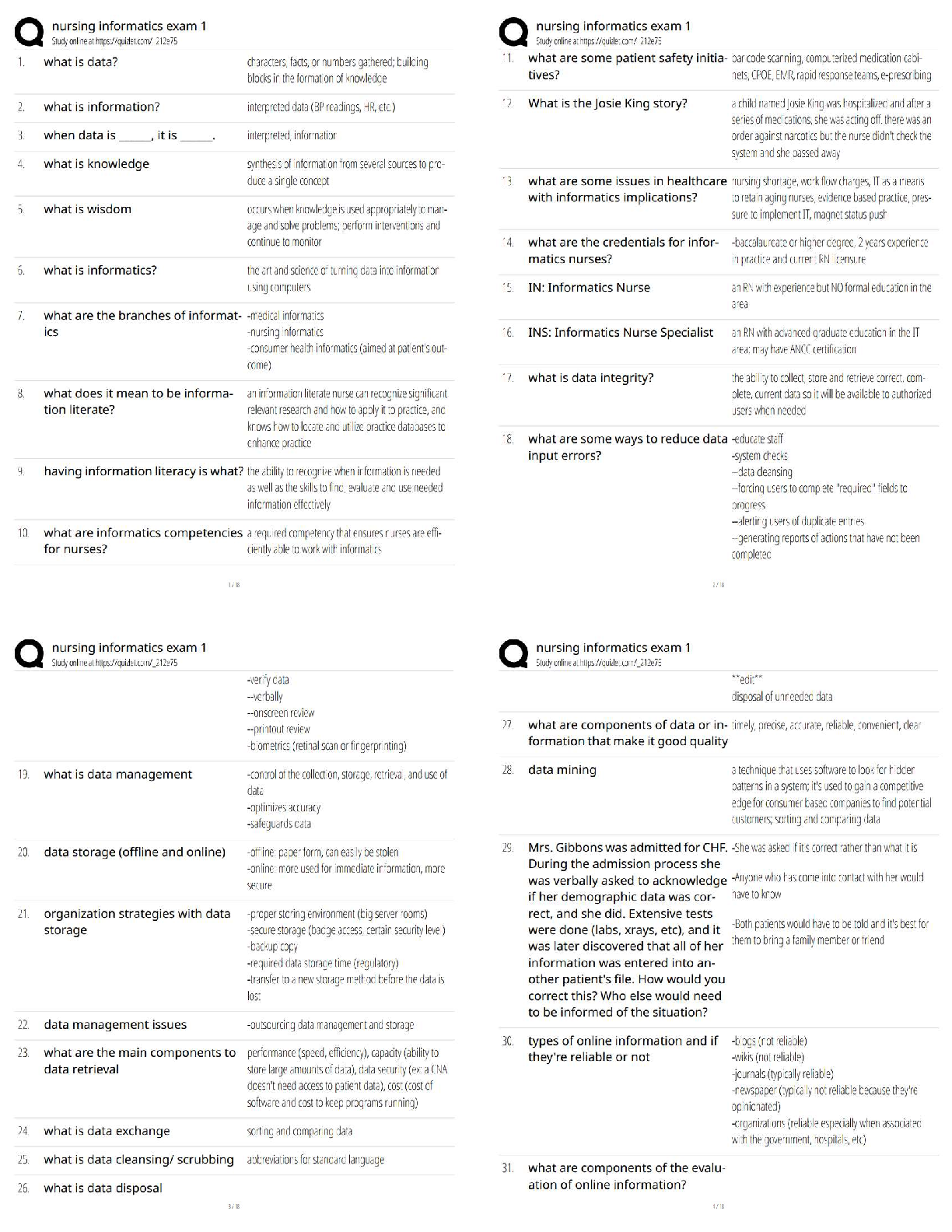
Nursing Informatics Exam 1 Study Guide / Score 100% / New Version / 2025 Update
$ 10
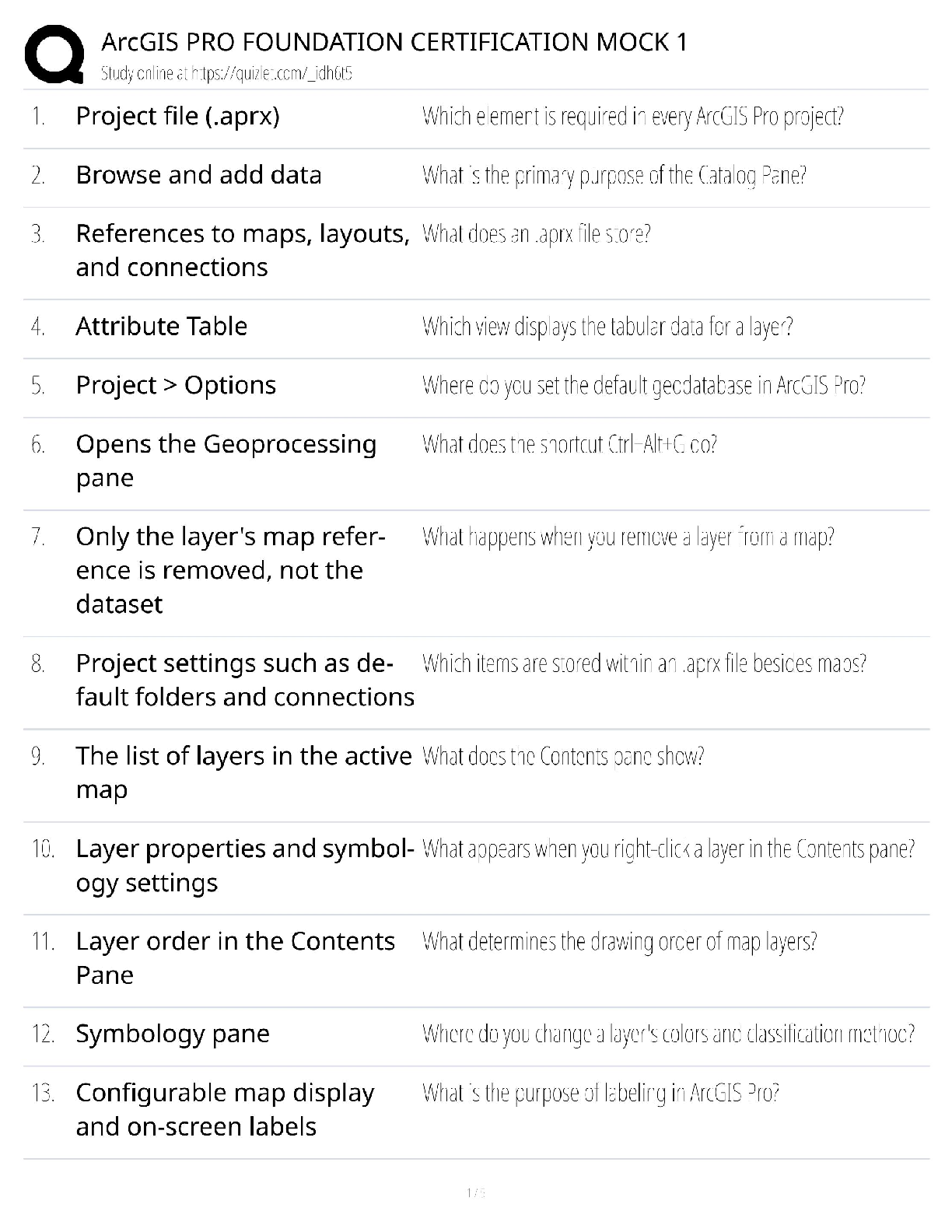
ArcGIS Pro Foundation Certification Mock Exam 1 / Score 100% / New 2025 Update / Complete Study Guide & Practice Test
$ 22

Math 302 Knowledge Test 1 Questions And Answers( Complete Solution)
$ 15

NURSING 812 SOAP Note Migraine
$ 10

TESTBANK FOR STATISTICS THE ART AND SCIENCE OF LEARNING FROM DATA FOURTH EDITION (Global Edition) Answers At The End Of Each Chapter
$ 16.5

CASE STUDY; An Elderly Hispanic Man With Major Depressive Disorder.
$ 6

SCI 200--Final Milestone Unit 4 Exams 2022/2023
$ 11.5
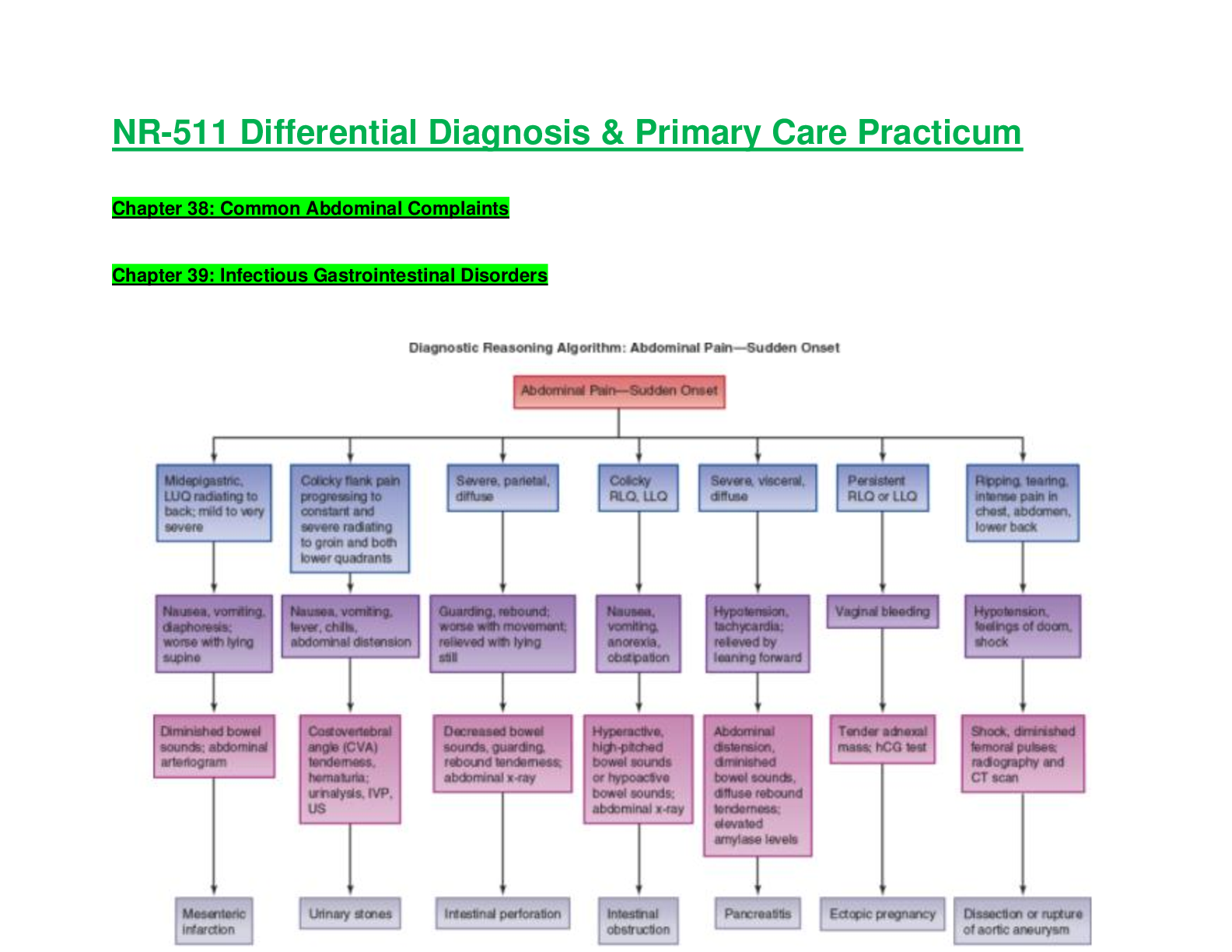
NR511 / NR 511: Differential Diagnosis & Primary Care Practicum Week 2 Chapter 38 Notes - Common Abdominal Complaints & Chapter 39 Notes - Infectious Gastrointestinal Disorders (2021 / 2022) Chamberlain College Of Nursing
$ 7

NR 328 RUA Ethical Dilemma: Treating a Septic Newborn with Herbal Therapy
$ 13

NURSING 442Initial+OB+SOAP+Note+Sample.pdf
$ 9.5

NR 328 ETHICAL DILEMMA ASSIGNMENT
$ 15

NR-708 Week 5 Discussion 1: Changes in Healthcare Policy | GRADED A
$ 8

eBook The Photographic Invention of Whiteness The Visual Cultures of White Atlantic Worlds 1st Edition By Stephanie Polsky
$ 30

HESI Exit Exam RN 2019
$ 11

NURS 6512N Week 10 Quiz,100% correct
$ 15
[Ebook][Pdf] Proofs: A Long-Form Mathematics Textbook by Jay Cummings
$ 14.5

NR-535 Week 7 Case Study: Academic Integrity – Part I
$ 8.5

eBook Tuning the World The Rise of 440 Hertz in Music, Science, and Politics 1st Edition By Fanny Gribenski
$ 30

NR 501 Week 7 Theoretical Framework PowerPoint (A+ Rated, Complete solution guide)
$ 10

Week 6 Math 225n Statistics Quiz
$ 6

NUR 550 Topic 4 DQ 1&2