Bridgett Allen Scenario 3
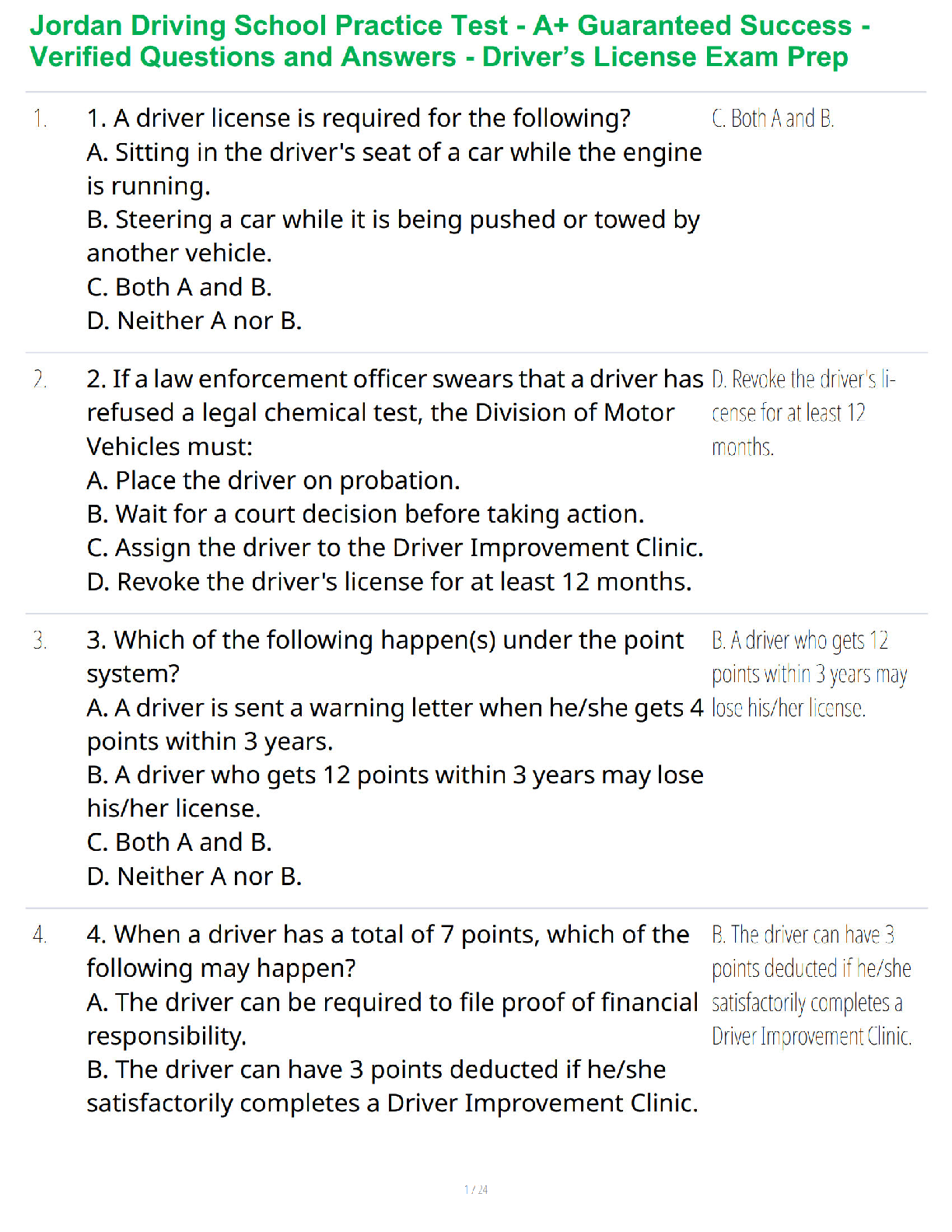
Bridgett responds well to the digoxin, furosemide, and potassium chloride and her ultrasound indicates a
slight reduction in ventricular size. She is able to tolerate increased activity and he
...
Bridgett Allen Scenario 3
Bridgett responds well to the digoxin, furosemide, and potassium chloride and her ultrasound indicates a
slight reduction in ventricular size. She is able to tolerate increased activity and her resting oxygen
saturation is improved. The surgeon elects to surgically patch the ventricular septal defect and Bridgett is
placed on cardiopulmonary bypass. Following the surgery, Bridgett is extubated and able to ventilate and
oxygenate while receiving 4 liters O 2 via simple mask. During the surgical closure Bridgett is noted to
have a pneumothorax and a chest tube is inserted. The chest tube is put to water seal with a portable
chambered drainage device. Following an uneventful stay in the post-anesthesia care unit, Bridgett is
transferred to the cardiac intensive care unit for an overnight observation. Bridgett’s mother is very
distressed about the chest tube and her daughter’s appearance post-operatively. The nurse provides
teaching about the chest tube and how Bridgett will progress with the chest tube in the next few days.
Which order should the nurse use to teach the mother what to expect in the next few days?
1. The drainage may be bright red
2. Chest tube drainage will become serous
3. The suture and chest tube are removed
4. Petrolatum-covered gauze
5. Breath sounds are auscultated
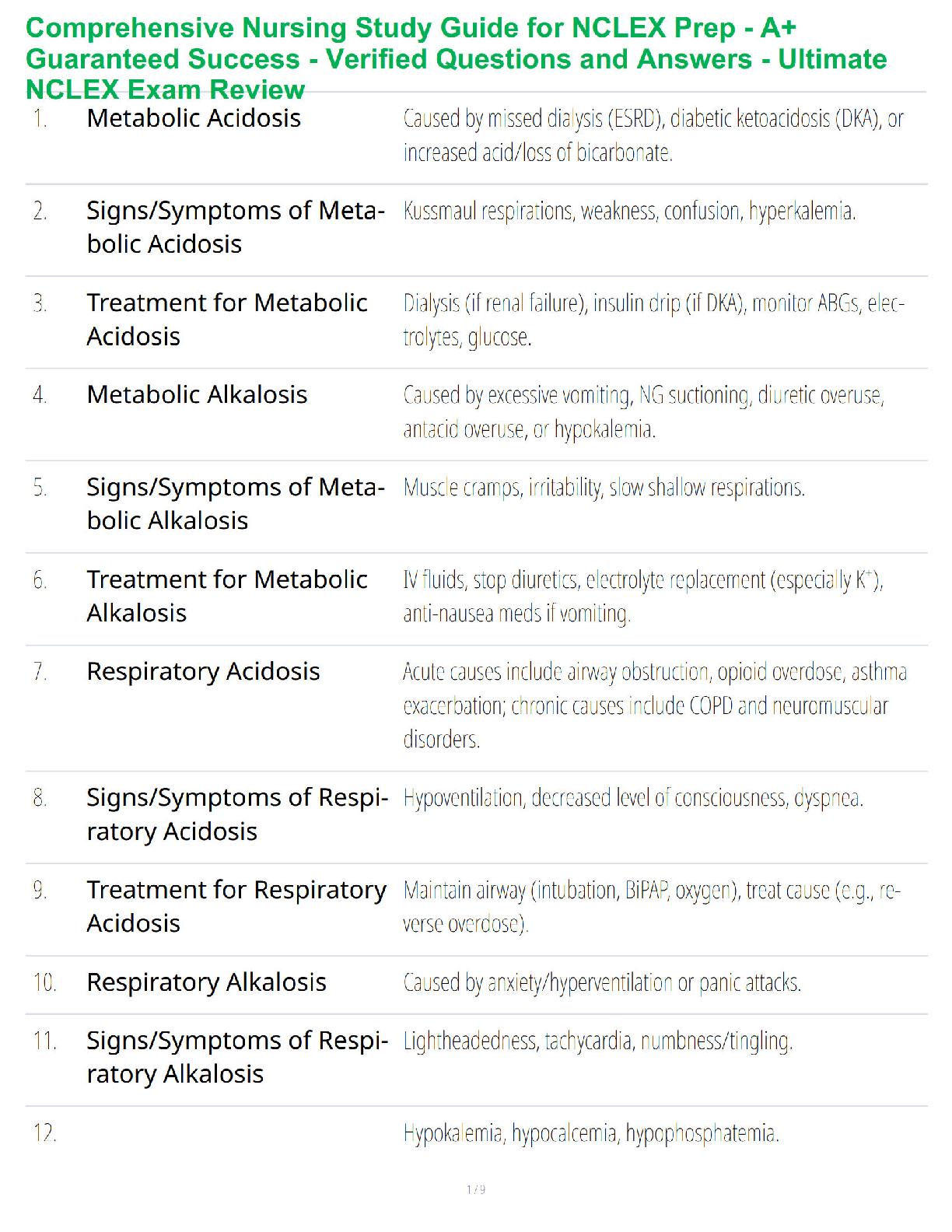
Scenario 4
Bridgett experiences significant incisional pain following her surgery. She is prescribed to receive
intravenous ketorolac around the clock, intravenous morphine sulfate every 2-4 hours as needed, and oral
acetaminophen as needed for temperature or mild pain. At the time of the nurse’s assessment of
Bridgett’s pain, Bridgett is noted to be crying and screaming, is difficult to console, is laying in a rigid
position in the bed with legs tense, and her chin is quivering as she is crying. Using the FLACC scale, the
nurse assesses Bridgett’s pain to be a 9/10. Which actions should follow the nurse’s assessments?
1. Determine ketorolac was administered
2. Check EHR
3. Prepare Morphine
4. Admin morphine
5. Assess
Scenario 5
Bridgett is taking oral fluids well, eating small amounts, and her incision is dry and intact. Her incisional pain is being
managed with oral acetaminophen, she is stooling and voiding urine in her normal pattern, and she is tolerating her
medications, including digoxin, furosemide, and potassium chloride. Her weight is close to her baseline at 23.6 kg. The
nurse provides discharge instructions to the mother. The nurse reinforces the need to assess the pulse with digoxin
and to hold the medication and contact the cardiologist with a low heart rate. The nurse begins to teach about the
other medications when the mother begins to cry. The mother states, “I am a single parent. This is so overwhelming. I
have two sons that are older teens and Bridgett. Why did she have to have Down syndrome AND a heart problem?”
The nurse explains to the mother about the increased incidence of septal defects in children with Down syndrome. The
mother than asks about Bridgett’s growth and development. She states “Bridgett is a lot slower than her brothers. She
can’t take care of herself.” The nurse provides the mother with some information about local support groups for
parents of children with Down syndrome. The nurse shares a list of developmental tasks and the ages at which
children with Down syndrome achieve these developmental milestones. Place the milestones in the order in which a
child with Down syndrome is expected to achieve these skills.
1. Finger Foods
2. Spoon and fork
3. Bowel training
4. Bladder training
5. Dress self
Med admin
Dig = 1 K = 35
[Show More]






.png)