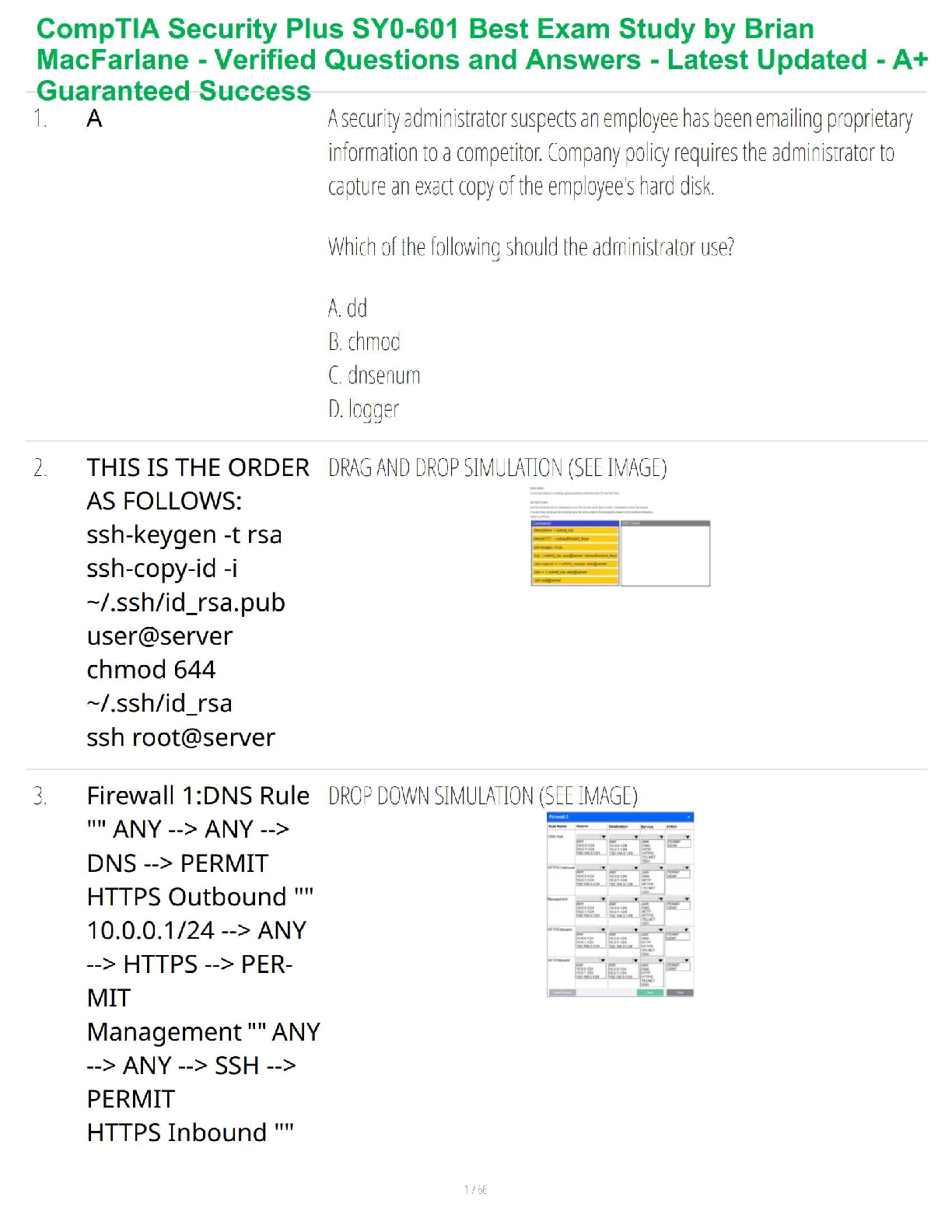
• Health People 2010 – to improve access to comprehensive, quality, primary care services.
Goals PROFESSIONAL
PRACTICE – 17%
(30 QUESTIONS)
Terms & Definitions
• Health People 2010 – to improve access to comprehens
...
• Health People 2010 – to improve access to comprehensive, quality, primary care services.
Goals PROFESSIONAL
PRACTICE – 17%
(30 QUESTIONS)
Terms & Definitions
• Health People 2010 – to improve access to comprehensive, quality, primary care services.
Goals:
o Increase the quality and years of healthy life
o Eliminate health disparities among Americans
• Health People 2020 - The program is an initiative that develops evidence-based practice objectives
designed to improve the health of all Americans. These objectives are targeted to be followed over
a 10-year period
4 foundational healthcare measures
1. General health status
2. Health-related quality of life & well-being
3. Determinants of Health – aim to create social & physical environments that promote good
health for all
4. Reduce Health Disparities
• Electronic Medical Record (EMR) – Pros: allows for sharing of health information between
healthcare entities & with patients, thereby reducing the cost of care, improving care efficiency,
avoiding readmission and decreasing duplicate testing. Cons: the potential for data loss in the
event of computer or system failure
• Medicaid - a government health insurance program for low-income individuals funded by federal &
state entities and administered by the state. * Varies from state-to-state.
• Medicare – federally funded health insurance program for those >65yrs, those with severe disability
no matter income level, or those with ESRD. Qualifying conditions: US citizen, non US citizens
after 5 years of permeant residence in the US, veterans are eligible after 65yrs.
A. Medicare Part A covers medically necessary inpatient care and supplies; skilled nursing
facility
B. Medicare Part B covers nursing home/custodial care (ADL’s), home health services, durable
medical equipment, out patient care & preventative services (i.e. 1 mammogram every 12
months) in women 40 and older. Part B DOES NOT cover eyeglasses or routine dental
care.
• The Barthel Index is a measurement of ability to perform ADL’s
C. Medicare Part C – HMO
D. Medicare Part D covers prescriptions
• A single payer healthcare system refers to a system where in essence the government runs a
nationwide insurance plan that pays for all healthcare costs of its members.
• Peer Review / 360 degree Evaluation – employees rate other employees in the same job
classification, through the use of established criteria. The system has the potential to offer honest &
specific feedback that allows the individual to make improvements or adjustments to meet
objectives and performance standards
• Fidelity – Loyalty & dedication; keeping a promise
• Beneficence – promote good & prevent harm
• Non-Maleficence – To do no harm
• Justice - right to fair and equitable treatment
• Autonomy – The right of patients to make clinical decisions about their medical care, assuming the
patient is rational & can make informed decisions about care
• Veracity – The duty to be truthful
• Utilitarianism – produces the greatest good for the greatest number of people
PROFESSIONAL
PRACTICE – 17%
(30 QUESTIONS)
Policies & Practice
Standards
• State Nurse Practice Act (NPA) – approved by vote through the processes of each individual states
legislature. The Act delineates the legal scope of practice within the geographical boundaries of the
jurisdiction. The purpose of the Nurse Practice Act is to protect the public.
• State Board of Nursing (BON) – determines laws governing nurse practitioner authority; has the
authority to develop administrative rules or regulations that clarify the NPA & make scope of
practice interpretations more specific. The state BON rules and regulations must be consistent with
the legislature.
• Indian Health Care Improvement Act of 2010 – part of patient protection & affordable Care Act.Only Native American enrolled as members of a federally recognized tribe can be eligible for
health care services. Services obtained under the IHS must be prioritized with life threatening
illness or injuries being given the highest priority. IHS formulary drug list may not include all
drugs & medicines.
• Emergency Medical Treatment & Labor Act (EMTALA) – designated to prevent inappropriate
transfers and “patient dumping” for indigent patients. Requires hospitals to assess & treat patients
regardless of ability to pay and provides specific provision for when transfers are allowed.
• The Genetic Information Nondiscriminatory ACT (GINA) – prohibits the use of genetic
information in employment & health care insurance decisions.
• Health Information Technology for Economic & Clinical Health Act of 2009 (HITECH) –
healthcare providers would be offered financial incentives for demonstrating meaningful use of
EHR until 2015 after which penalties may be levied for failing to demonstrate such use. *** CMS
announced in mid 2015 that it will delay final penalties until 2017**
➢ Meaningful Use – to implement clinical decision support (CDS) rule relevant to specialty or
high clinical priority (i.e. abnormal vitals signs appear in red)
➢ Clinical Decision Support (CDS) – provides clinicians, staff, patients & other individuals
with knowledge and person-specific information, intelligently filtered & presented at
appropriate times to enhance health & healthcare. CDS encompass a variety of tools to
enhance decision-making in the clinical workflow. These tools include computerized alerts
& reminders to care providers and patients; clinical guidelines; conditions specific order
sets; focused patient data report summaries; documentation templates; diagnostic support;
contextually relevant reference information.
• Affordable Care Act of 2010 – expands healthcare coverage using a variety of mechanisms on the
state & federal level.
✓ Only US citizens can purchase health insurance through the online market place
✓ Expands Medicaid as well as subsidies available for low income individuals who cannot
afford individual plans. Subsidies are based on the state you live in, # of adults, children &
ages, and annual incomes.
✓ Tax penalties for individuals who do not get health coverage
• The Patient Protection & Affordable Care Act (PPACA)- federal legislation that principally
reforms health reimbursement systems and establishes an individual mandate requiring people to
have health insurance.
• Consensus Model for Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) – a multifaceted proposal
established by the National Counsel of the state BON in conjunction with numerous professional
organizations. Advocates for the APRN title, independent prescriptive authority & establishes
certain minimum standards for NP’s. ***NP’s are not required to have collaborating physician
supervision under the consensus model.
• Medical Home Model – Medical home is the phrase assigned to a model aimed at reorganizing the
delivery of primary healthcare. The purpose of the model is to improve healthcare in America by
transforming how primary care is organized & delivered. In addition, to providing comprehensive
care, patients & their families are encouraged to be active participants in care. The patient-centered
medical home concept is designed to meet the increase demands of both access to and management
of healthcare thereby improving patient outcomes.
• IOM (5) Core Competencies of effective healthcare providers & leaders
1. patient-centered care
2. Work in interprofessional teams
3. Employ evidence-based practices
4. Apply quality improvement
5. Utilize informatics (integrate information technology into care)
• National Institute of Medicine (6) Quality Aims (PPEEET)
1. Patient Safety – care should be as safe for patients in healthcare facilities as in their homes
2. Patient Centeredness- the system of care should revolve around the patient, respect patient
preferences & put the patient in control
3. Effectiveness – the science & evidence behind healthcare should be applied and serves a
standard of care in healthcare delivery
4. Efficiency – service & care should be cost effective and waste should be removed from the
system
5. Timeliness – There should be no waits or delays in the delivery of healthcare or health
services to patients
6. Equity – Unequal treatment should be a fact of the past• National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB) – a national databank of medical malpractice claims &
specifically defined adverse actions associated with healthcare care providers. Any state licensure
or certification action is also a reportable item.
• Prescriptions for Controlled Substances – must include the following:
1. date of issue
2. patient’s name & address
3. practitioner’s name, address & DEA
4. drug name, dosage form, quantity, direction for use
5. # or refills
6. manual signature
**prescriptions for scheduled II controlled substances may be telephoned to pharmacy but must be
followed up with a written prescription within 7 days** Prescriptions for schedule III-V may be written,
oral or transmitted by fax.
• American Telemedicine Association Practice Guidelines – providers shall follow federal, state &
local regulatory & licensure requirements related to their scope of practice and shall abide by state
board & specialty training requirements. Providers shall ensure that the patient is physically
located in a jurisdiction in which the provider is duly licensed and credentialed. Providers shall
practice within the scope of their licensure and shall observe all applicable state and federal legal &
regulatory requirements.
• Criteria to Hospice Admission
❖ The patient must give consent
❖ Have a life expectancy < 6mos
❖ Agree to not use life-sustaining equipment in the event of a life-threatening situation
• State Reportable to Department of Health
• 5 diagnoses: Gonorrhea, Chlamydia, Syphilis, HIV, TB
• Criminal acts & injury from dangerous weapons
• Animal bites
• Suspected and/or actual child or elder abuse
➢ Elder abuse, also know as elder mistreatment, involves the physical abuse, emotional abuse,
financial abuse, sexual abuse, neglect, and self-neglect inflicted upon an elderly individual.
Abandonment or neglect is the most common elder abuse
***Domestic violence is NOT state reportable***
PROFESSIONAL
PRACTICE – 17%
(30 QUESTIONS)
FRAMEWORKS/MODELS
• The Swiss Cheese Model (James Reason) – systems approach to understanding errors. Declares
humans are fallible & errors ae to be expected even in the best organizations. The holes represent
opportunities for the process to fail.
• Kotters 8-Step Change Model
1. Create a sense of urgency
2. Build a guiding coalition - assembling a group with the power & energy to lead and support
a collaborative change effort (i.e. NP’s creating a task force to address scope of practice
concerns)
3. Form a strategic mission & initiative
4. Enlist a volunteer army
5. Enable action by removing barriers
6. Generate short-term wins
7. Sustain acceleration
8. Institute change
• Lewin’s Change Model
1. 1st Stage (Unfreezing) “reason for the change” – where barriers to change should be
assessed. Dissatisfaction with the status quo is identified, bench mark operations are
identified and internal barriers, driving forces & resistant forces to performance are
understood. Unfreezing involves formulating a plan to modify or eliminate an existing
practice that is the target of change.
2. 2nd Stage (Driving forces) – redesigning organizational roles, responsibilities/relationships,
training for newly required skills, promoting supporters, removing resisters. The change
phase is the actual modification of practices, beliefs, or thoughts surrounding the targeted
change.
3. 3rd Stage (refreezing) – involves aligning pay/reward systems, re-engineering
measurement/control systems & creating new organizational structure to support the
change. Refreezing is the establishment of the new practice as a habit or standard
procedure.
• Family Developmental Theory Framework (Duvall & Miller)
❖ Examines and analyzes the basic changes & developmental tasks common to most families
during their life cycle❖ The stages and developmental tasks illustrate common family behaviors that may be
expected at specific times in the family life cycle (Stages: beginning families, families w/
children, aging families)
❖ Families change over time because of the influence of environmental factors
• The Health Belief Model (HBM) – conceptual framework for understanding health behavior. The
premise of this model is that individuals are motivated to take positive health actions because they
want to avoid negative health consequences.
➢ Self efficacy – confidence in one’s ability to take action
➢ Perceived Susceptibility – one’s opinion of chances of getting a condition
➢ Perceived Severity – one’s opinion of how serious a condition is & how serious its
consequences are
➢ Perceived health benefits - one’s belief in efficacy of the advised action to reduce risk or
seriousness of impact.
➢ Perceived Barrier’s – one’s opinion of tangible & psychological costs of the advised action.
INDEPENDENT
PRACTICE – 46%
(81 QUESTIONS)
CULTURAL
COMPETENCY
➢ Cultural differences in the perception of illness
➢ Chinese – perceive illness as the result of a disruption between yin & yang
➢ Hispanics – perceive illness as an imbalance between the individual & the environment
➢ Africans – view illness as the “Will of God”
➢ Haitians - incorporate older traditional beliefs, feel that illness is a punishment
➢ Native Americans – believe that illness is punishment; Shamans “cure” the illness by
performing rituals & using herbal medicines
➢ Collectivistic Cultures (China, Korea, Japan, & middle eastern cultures) – emphasize
family & work goals above individual needs or desires. Characterized by lifelong ties to
family & older adults and hierarchical figures being highly respected. Loyalty - values the
needs of a group or a community over individual needs.
➢ Elders are highly respected in the Asian population and family members are expected to care
for their elders.
➢ Chinese
➢ Women partake in a “sitting month” for a period of time after childbirth. During this time,
they avoid cold foods, cold water and cold conditions in order to restore the energy in their
bodies that were lost during the blood loss associated with childbirth.
➢ Amish Culture & Community
➢ welfare and government assistance are not acceptable. Medical bills and expenses are paid
by the
community. (An individual is not solely responsible for his own medical bills)
➢ Cancer & related illnesses are real and should be treated appropriately
➢ Individualistic Cultures (North American cultures) – focus on the individual. Personal
accomplishments, values or productivity & self-expression are characteristic.
➢ Native Americans
➢ respect is communicated through avoidance of eye contact (can be interpreted as an
intrusion into the spirit).
➢ Avoiding loud volume when speaking (stern or loud speaking is considered to be
aggressive)
➢ Allowing for silence during conversation (felt to be disrespectful to interrupt someone’s
conversation).
➢ Greet with light handshake.
➢ Mexicans
➢ Emphasizes the mother as the health care decision maker. Fathers are usually in charge of
everything else besides health care decision making
➢ Families are very close and patients often bring many family members to their appointments
➢ Hispanics (Latino’s)
➢ Yerba burna (mint tea) is commonly used for headaches in Hispanic cultures & is safe in
usual quantities
➢ Stress levels can be very high when Latino patients come to the US. (Emotional distress may
present with headaches or other somatic complaints).
➢ Respect is a normative Latino cultural value along with kindness, friendliness & modesty
➢ It is considered respectful to address elders as Senor/Senora
INDEPENDENT
PRACTICE – 46%
(81 QUESTIONS)
• Confidence interval – specified probability of the parameter being estimated. A small confidence
interval implies a very precise range of values.RESEARCH TERMS
• Standard Deviation – the average amount of deviation of values from the mean
• Reliability – the degree to which an assessment tool produces stable & consistent results
• Validity – the degree in which a variable measure what it is intended to measure
• Level of Significance – (P-value) the probability level of which the results of statistical analysis are
judged to indicate a statistically significant difference between 2 groups
➢ P – Value – the alpha used in statistical analysis establishes level of significance for
outcomes being evaluated. 0.05 is the benchmark used to interpret p –values. P-values >
0.05 indicates there is a greater than 5% chance that the study outcome is due to random
chance & thus non-significant. <0.05 is statistically significant meaning – 95% chance that
the results did not occur by chance.
• Perfect Correlation – a measure of interdependence of 2 random variables that range in value
from -1 to +1
➢ -1 indicates perfect negative correlation
➢ 0 absence of correlation
➢ +1 perfect positive correlation
• Evidence Base Practice (EBP) – integration of best research evidence with clinical expertise
& patient values to guide medical decision making. The 4 A’s
1. Asking a focus question is the 1st step in seeking an evidence-based answer
PICO
a) Patient/Population/Problem
b) Intervention/Exposure
c) Comparison/Control
d) Outcome
2. Acquiring the best evidence you can find
3. Appraising the evidence
4. Applying to patient care
• Experimental – includes experimental manipulation of variables utilizing randomization & a
control group to test the effects of the intervention or experiment
1. Quasi-experimental – manipulation of variable but lacks comparison group or
randomization
• Non Experimental – includes (2) broad categories of research.
1. Descriptive – aims to describe situation, experience & phenomena as they exist
2. Expost-facto/ correlational Research – aims to examine relationships among variables
• Qualitative – includes case studies, open-ended questions, field observations, participant
observations & ethnographic studies where observation & interview techniques are used to
explore phenomena through detailed descriptions of people, events, situations or observed
behavior. Research bias is a potential problem. Calls into question the generalizability of the
findings. Produces very rich data through no other means
• Systemic Reviews & Meta Analysis – A systematic review or meta analysis offer the highest
level of strength of evidence in research. Systemic reviews & meta analysis are often found
together within the same publication, but they are distinct entities.
➢ Systematic review – refers to a literature search & summarization process. Provides a
comprehensive review of all relevant studies on a particular clinical or health related
question/topic. Created after reviewing and combining all the information from both
published and unpublished studies and then summarizing the findings.
➢ Meta-analysis - refers to the application of statistical techniques to analyze this process. A
subset of systematic reviews; a method for systematically combining pertinent qualitative
and quantitative study data from several selected studies to develop a single conclusion that
has the greatest statistical power.
• Order of Evidence Strength
1. Systematic Review / Meta- Analysis – reviews of multiple studies and articles, which
summarize the findings of the group
2. Randomized Controlled double-blinds – the best design to determine the benefit/risk of an
intervention. Consists of subjects who are randomly assigned to treatment or non-treatment
groups. They represent a high level of relevance
3. Cohort Studies (longitudinal study, quasi-experiment)) – follows individuals with a
particular condition over a period of time. It is the best design to obtain valid information
about the prognosis of a condition.
4. Case-Control Studies (observational study) – compares patients who have a disease or
outcome of interest (cases) with patients who do not have the disease or outcome (control),
looks back retrospectively5. Cross sectional study (observational study) –analyzes data from a population, or a
representative subset, at a specific point in time. (causal effects of independent and
dependent variables; the best design to evaluate a diagnostic test)
6. Case Reports – a review of one patient’s case, treatments and outcomes
7. Editorials/Opinions
8. Animal Research
9. Vitro Research
• SMART CRITERIA - Developing specific, measureable objectives requires time, orderly
thinking, and a clear picture of results expected from program activities. The more
specific your objectives, the easier it will be to demonstrate success.
[Show More]











.png)