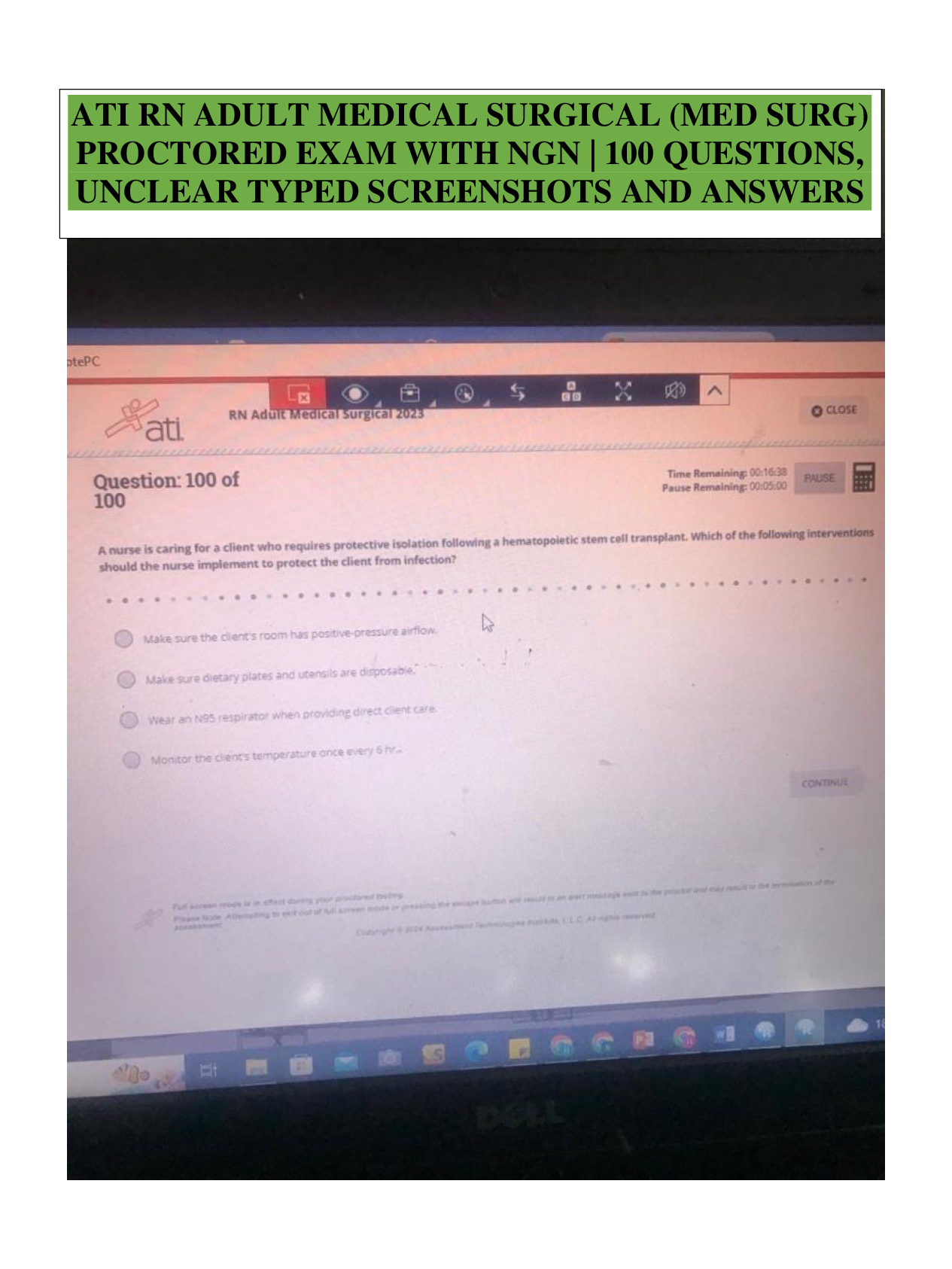
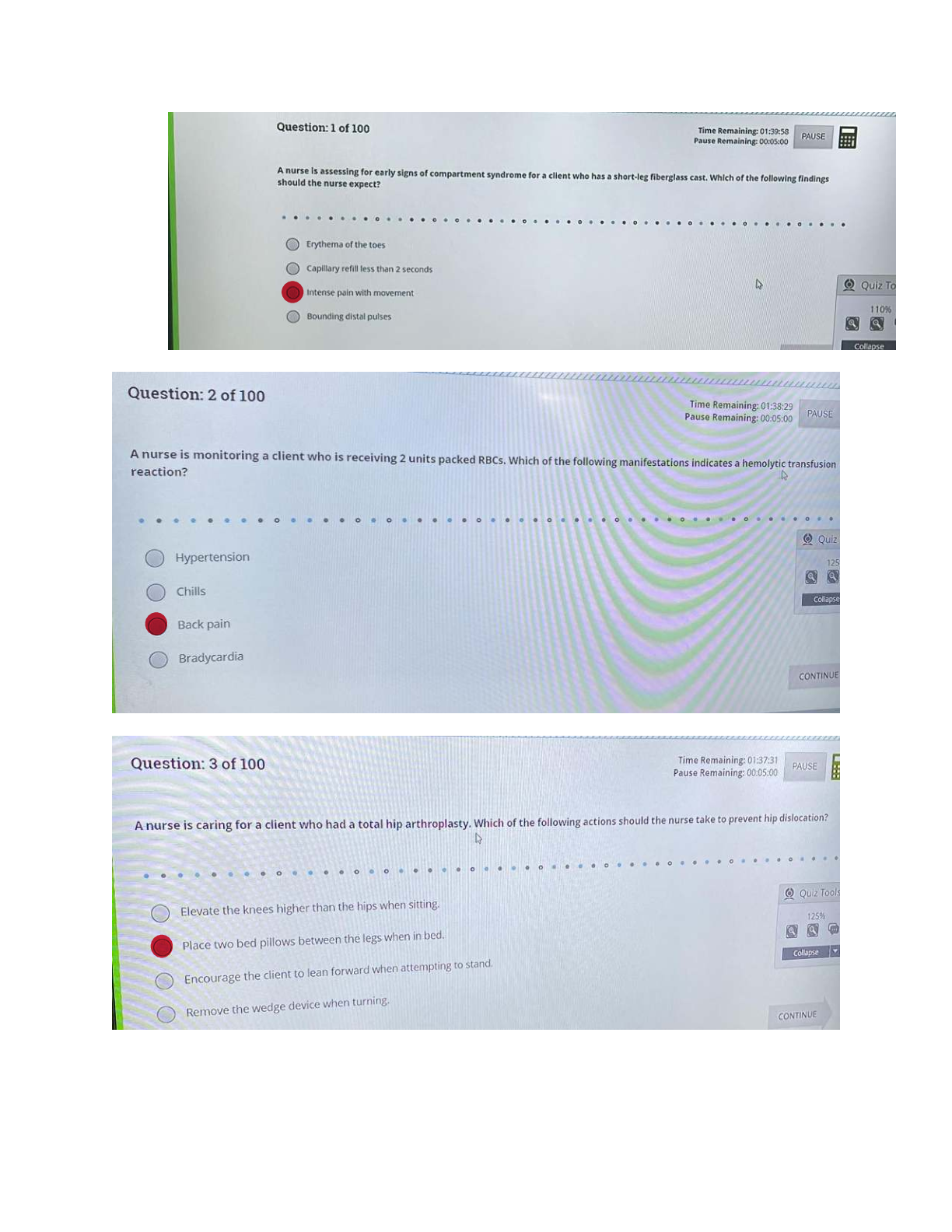
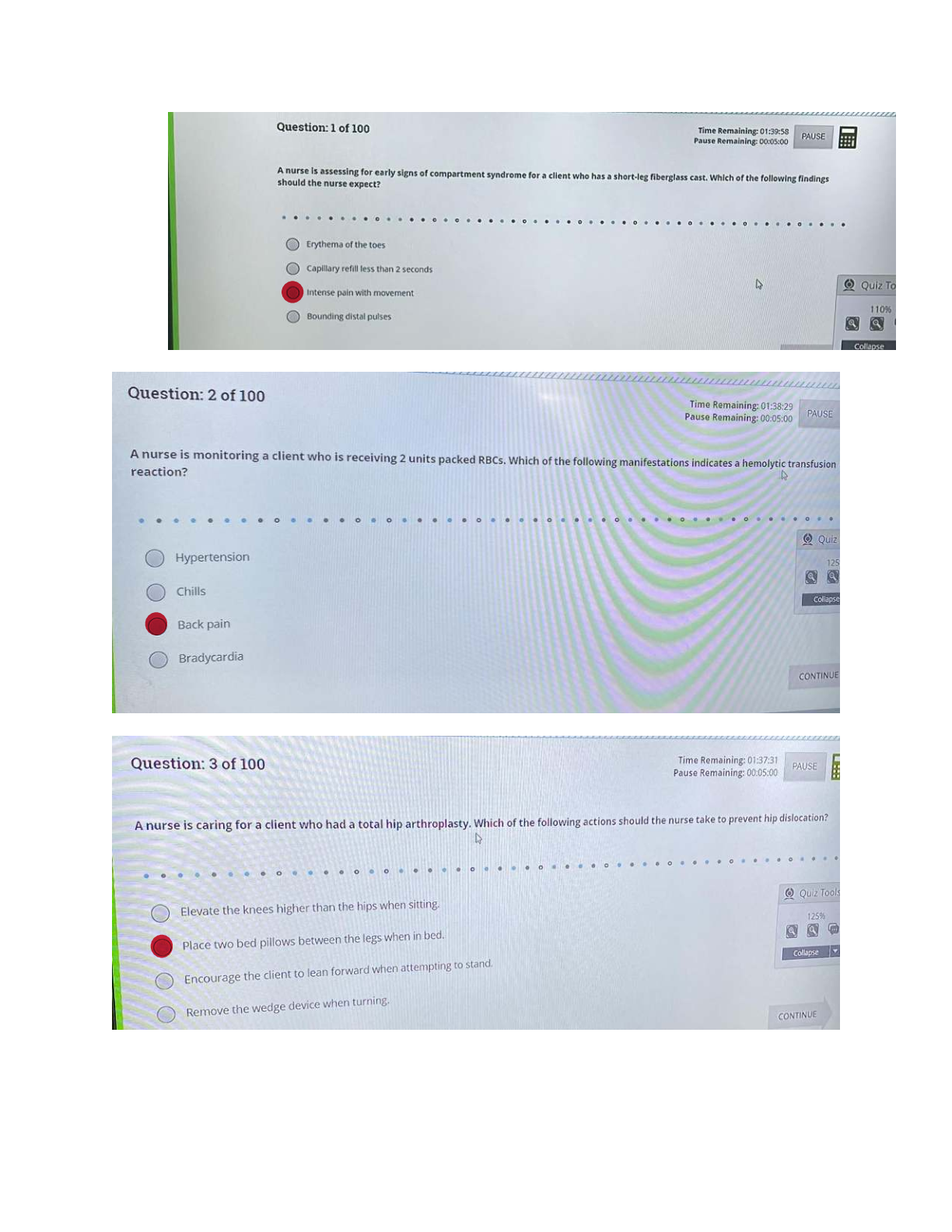
Focus on Mental Health.Q&A
� 1.ID: 9476853992
� A nurse overhears a hospitalized client with mania telling another client, “I’m
actually a journalist writing an article for a magazine — I’m just posing as a
person wi
...
Focus on Mental Health.Q&A
� 1.ID: 9476853992
� A nurse overhears a hospitalized client with mania telling another client, “I’m
actually a journalist writing an article for a magazine — I’m just posing as a
person with mental illness.” How should the nurse respond?
A. Ignoring the delusion
B. Taking the client to a quiet room
C. Supporting the client’s denial of illness
D. Presenting the client with the actual situation Correct
� Rationale: When dealing with a delusional client, it is important for the nurse to
state clearly that the nurse does not share the client’s perceptions. All three of
the other options — ignoring the delusion, taking the client to a quiet room, and
supporting the client’s denial of illness — do not focus on reality, and they
ignore the issue. Presenting the client with the actual situation helps orient the
client to reality.
� Test-Taking Strategy: Use the process of elimination and your knowledge that
reality orientation is the priority. The correct option illustrates a means of helping
orient the client to reality. Review care of the client experiencing delusions if you
had difficulty with this question.
� Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying
� Client Needs: Psychosocial integrity
� Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation
� Content Area: Mental Health
� Giddens Concepts: Communication, Psychosis
� HESI Concepts: Cognition – Psychosis, Stress and Coping – Caregiving
� Reference: Varcarolis, E. (2013). Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health
Nursing: A communication approach to evidence-based care. (revised reprint))
(2nd ed. pp. 305, 318-320). St. Louis: Saunders.
� Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points.
� 2.ID: 9476861052
� A client who is hallucinating fearfully says to the nurse, “Please tell that demon
to get out.” How should the nurse respond to the client?
A. “If you tell the demon to go away, it will.”
B. “I’ll stay here with you until the demon leaves your room.”
C. “If you return to bed, you will find that the demon will leave.”
D. “I know you must be very upset by this, but I don’t see a demon.”
Correct
� Rationale: If the client hallucinates, it is best to provide reality-based
perceptions and not negate the client’s experience, because this may lead to a
regressive struggle with the client. Giving advice or false reassurance is
incorrect because such techniques indicate that demons actually are present,
which feeds into the client’s hallucination and reinforces the client’s behavior.
� Test-Taking Strategy: Use your knowledge of therapeutic communication
techniques, noting that the client is hallucinating. Remember that it is most
important to maintain reality with the client. This will direct you to the correct
option. Review communication techniques for the client who is hallucinating if
you had difficulty with this question.
� Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying
� Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity
� Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation
� Content Area: Mental Health
� Giddens Concepts: Communication, Psychosis
� HESI Concepts: Cognition – Psychosis, Communication
� References: Stuart, G. (2013). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (10th
ed., pp. 25-29). St. Louis: Mosby.
� Varcarolis, E. (2013). Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing: A
communication approach to evidence-based care. (revised reprint)) (2nd ed. p.
320). St. Louis: Saunders.
� Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points.
� 3.ID: 9476835369
� The mother of a 3-year-old says, “My child hit his teddy bear after being scolded
for picking the neighbors’ flowers.” Which defense mechanism was the child
using?
A. Projection
B. Sublimation
C. Displacement Correct
D. Identification
� Rationale: The defense mechanism of displacement involves the discharge of
intense feelings for one person onto a less threatening substitute person or
object to satisfy an impulse. Projection involves attributing an attitude, behavior,
or impulse to someone else, such as that which occurs in blaming or
scapegoating. Sublimation is rechanneling an impulse into a more socially
acceptable object. Identification involves modeling behavior after someone
else's.
� Test-Taking Strategy: Use the process of elimination and your knowledge
regarding defense mechanisms. Focusing on the child’s behavior will direct you
to the correct option. Review these defense mechanisms if you had difficulty
with this question.
� Level of Cognitive Ability: Understanding
� Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity
� Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Analysis
� Content Area: Mental Health
� Giddens Concepts: Development, Coping
� HESI Concepts: Developmental, Stress and Coping
� Reference: Varcarolis, E. (2013). Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health
Nursing: A communication approach to evidence-based care. (revised reprint))
(2nd ed. pp. 171, 173). St. Louis: Saunders.
� Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points.
� 4.ID: 9476840153
� A client says to the nurse, “Even though my husband and I keep telling them we
don’t want to have children, our parents are pressuring us to ‘start a family.’
What should we say to them?” Which of the following responses by the nurse is
therapeutic?
A. “This must be very difficult for both of you.” Correct
B. “Maybe you should say you can’t have children.”
C. “How do you usually cope with that kind of interference?”
D. “Tell them to have more children if they want them so badly.”
� Rationale: Childless families may elect not to have children or to postpone
having them until they have established themselves occupationally or
financially. Telling the client to tell the parents that the couple can’t have children
is incorrect because the client is being encouraged to lie about life decisions
rather than helping the parents understand the couple’s choices. Asking how
they usually cope with such interference is incorrect because it indicates that
the nurse is judgmental and has decided that the parents are interfering with the
client and spouse. Saying, “Tell them to have more children if they want them so
badly,” is incorrect because it is sarcastic and ridicules the situation over which
the client has expressed concerns.
� Test-Taking Strategy: Use your knowledge of therapeutic communication
techniques and remember to focus on the client’s feelings. This will direct you to
the correct option. Review these techniques if you had difficulty with this
question.
� Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying
� Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity
� Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation
� Content Area: Mental Health
� Giddens Concepts: Communication, Family Dynamics
� HESI Concepts: Communication, Family Dynamics
� Reference: Stuart, G. (2013). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (10th
ed., p. 27). St. Louis: Mosby.
� Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points.
� 5.ID: 9476840163
� A young adult client says, “I just can’t seem to stop snapping at my parents. I
know they work hard to support me, but what do I do when they’re so
overbearing?” Which responses by the nurse is therapeutic?
A. “It’s important not to be rude to your parents.”
B. “You need to be more patient with your parents.”
C. “Snapping at your parents is childish. How could you?”
D. “Have you talked to your parents about your frustrations?”
E. Correct
� Rationale: The correct response is focused on the client’s concerns and
encourages the therapeutic technique of formulating a plan of action. “It’s
important not to be rude to your parents” and “You need to be more patient with
your parents” are both nontherapeutic, judgmental responses that do not
encourage the client to further explore her feelings and problem-solve.
“Snapping at your parents is childish. How could you?” is incorrect because it is
sarcastic and condescending, which is nontherapeutic.
� Test-Taking Strategy: Use your knowledge of therapeutic communication
techniques and remember to focus on the client’s feelings. This will direct you to
the correct option. Review these techniques if you had difficulty with this
question.
� Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying
� Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity
� Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation
� Content Area: Mental Health
� Giddens Concepts: Communication, Family Dynamics
� HESI Concepts: Communication, Family Dynamics
� Reference: Stuart, G. (2013). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (10th
ed., pp. 29, 31). St. Louis: Mosby.
� Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points.
� 6.ID: 9476853973
� A client says, “I have so much trouble caring for my husband’s child from his
first marriage. I resent the money we have to pay for child support because we
have to deprive my own child of things. How can I stop feeling this way?” Which
response by the nurse is therapeutic?
A. “Your child benefits from having a sibling.”
B. “Have you shared your feelings with your husband?” Correct
C. “You need to take a second job to give your child what you think
she deserves.”
D. “I wonder why you married him, knowing that he wouldn’t desert his
biological child.”
� Rationale: Remarried individuals often encounter problems as a result of the
stressors they bring into a marriage without prior discussion with the new
partner. Bonding sometimes does always occur when a child is not one’s
biological offspring. The correct answer is focused on the client’s feelings. “Your
child benefits from having a sibling” is not facilitative. “I wonder why you married
him, knowing that he wouldn’t desert his biological child” is incorrect because it
prejudges the client. “You need to take a second job to give your child what you
think she deserves” is not open ended, does not facilitate feelings, and gives
advice.
� Test-Taking Strategy: Use your knowledge of therapeutic communication
techniques and remember to focus on the client’s feelings. This will direct you to
the correct option. Review these techniques if you had difficulty with this
question.
� Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying
� Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity
� Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation
� Content Area: Mental Health
� Giddens Concepts: Communication, Family Dynamics
� HESI Concepts: Communication, Family Dynamics
� Reference: Stuart, G. (2013). Principles & practice of psychiatric nursing (10th
ed., p. 27). St. Louis: Mosby.
� Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points.
...........Continued............
[Show More]