Computer Science > EXAM > DBI 202 Exam (Full) | Questions and Answers (Complete Solutions) (All)
DBI 202 Exam (Full) | Questions and Answers (Complete Solutions)
Document Content and Description Below
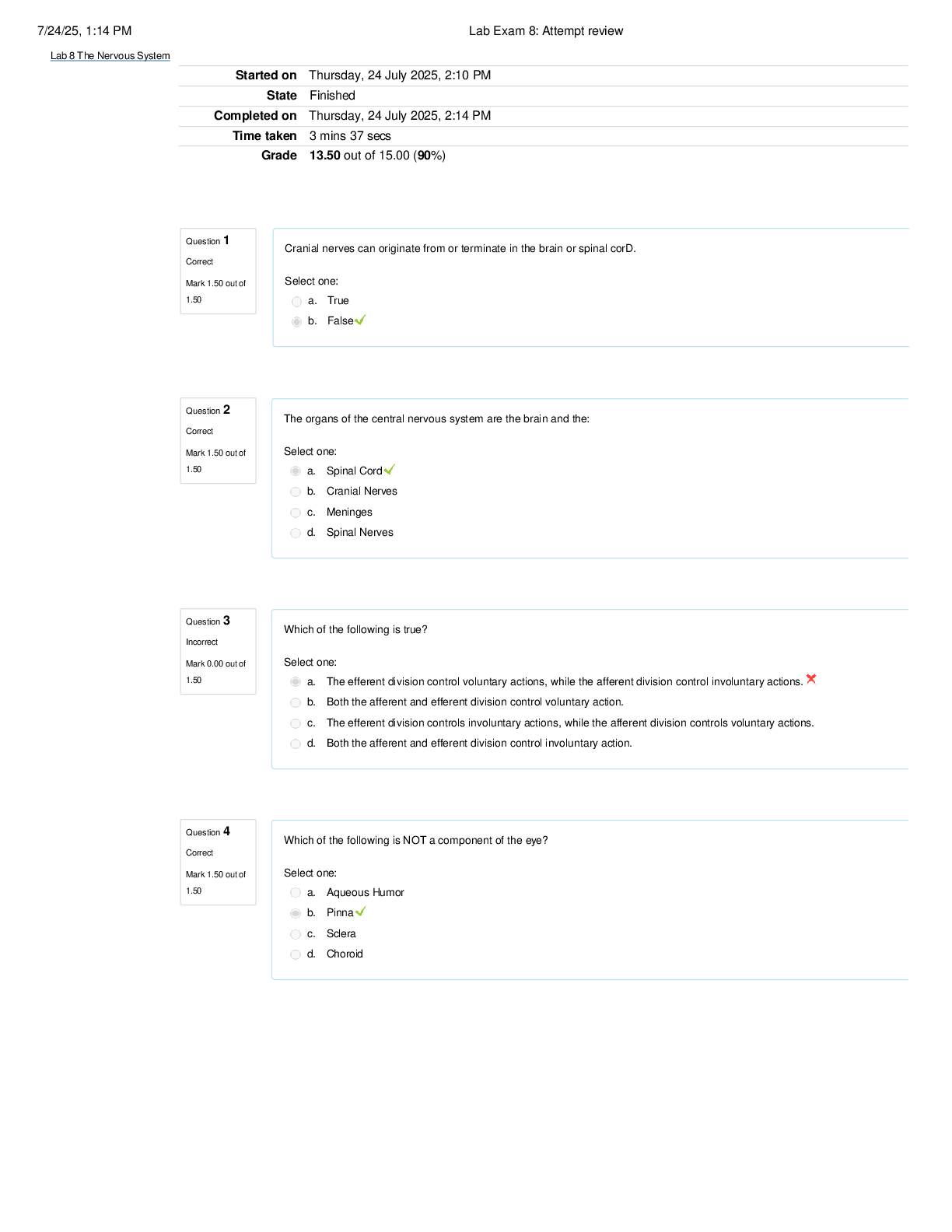
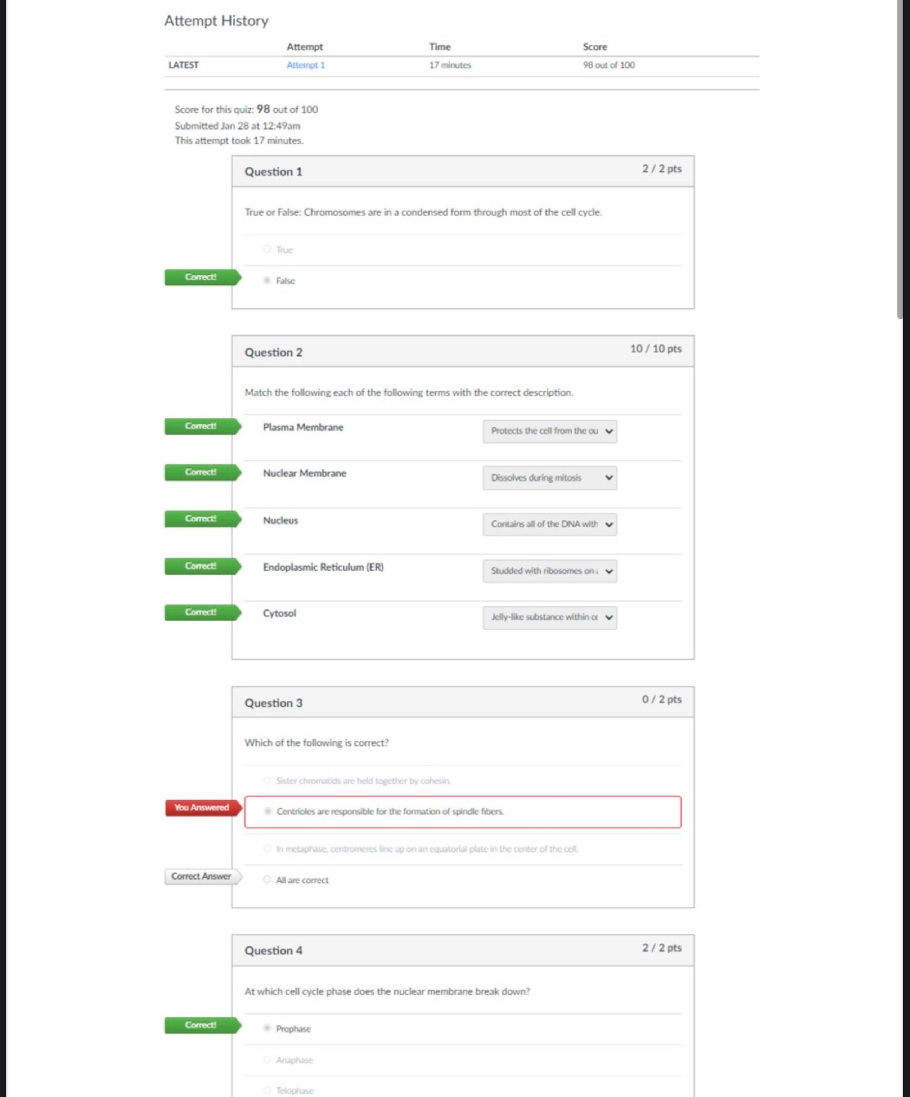
DBI 202 Exam (Full) | Questions and Answers (Complete Solutions) QN=1 (6803) A ____ is a logically coherent collection of data with some inherent meaning, representing some aspect of real world and ... being designed, built and populated with data for a specific purpose a. Database b. Database Instance c. Schema d. Schema Instance QN=2 (6801) Choose the most correct statement. a. Database is created and maintained by a DMBS b. All of the others c. Database is a collection of data that is managed by a DBMS d. Database is a collection of information that exists over a long period of time QN=3 (6802) Which of following is never used as a data model? a. Hierarchical data model b. None of the others c. Graph-based data model d. Tree-based data model e. Relational data model QN=4 (6817) A ____ is a relation name, together with the attributes of that relation. a. schema b. database c. database instance d. schema instance QN=5 (6824) A ___ is a notation for describing the structure of the data in a database, along with the constraints on that data a. data model b. database management system c. data operation d. data manipulation QN=6 (6827) A _____ is a language for defining data structures a. DDL b. DML c. DCL d. None of the others QN=7 (6834) Which statement is used to remove a relation named R? a. DROP TABLE R; b. REMOVE TABLE R; c. DELETE TABLE R; d. TRUNCATE TABLE R; QN=8 (6829) What is another term for a row in a relational table? a. Attribute b. Tuple c. Field d. Relation QN=9 (7961) Given a relation R(A,B,C,D). Which of the followings is trivial? a. A->AB b. A->->AB c. A->BCD d. A->->BCD QN=10 (7972) Let R(ABCD) be a relation with functional dependencies {A -> B, C -> B, B -> D} What is the key for R (choose one) a. AB b. AC c. AD d. BD QN=11 (7966) Suppose R is a relation with attributes A1, A2, A3, A4. The only key of R is {A1, A2}. So, how many super-keys do R have? a. 4 b. 8 c. 12 d. 16 QN=12 (7990) Consider the following functional dependencies a,b -> c,d e,g,h -> f,j a,c -> b,d p,q -> r,s e,f,g -> h,i s -> t f,g -> j q -> u g,h -> i Which of the following best describes the relation R(e,f,g,h,i,j)? a. R is in First Normal Form b. R is in Second Normal Form c. R is in Third Normal Form d. R is in Boyce Codd Normal Form QN=13 (7978) The relation R(ABCD) has following FDs: { A -> B ; B -> A ; A -> D ; D -> B } a. R is in 3NF b. R is not in 3NF c. R is not in 2NF d. None of the others QN=14 (7976) Given a R(A,B,C,D) with the following FDs: AB->D BC->A AD->B CD->B AD->C Choose a correct statement about R: a. The FD set of R is not canonical and R is in BCNF b. The FD set of R is canonical and R is not in BCNF c. The FD set of R is not canonical and R is not in BCNF QN=15 (7999) What is the difference between the 2NF and the 3NF? a. 2NF deals with partial functional dependency, while 3NF deals with transitive functional dependency b. 2NF deals with transitive functional dependency, while 3NF deals with partial functional dependency QN=16 (7993) What is "de-normalization"? a. De-normalization means allowing redundancy in a table b. De-normalization means allowing duplicate columns appeared in a table c. De-normalization means allowing a table to have more than 3 columns d. De-normalization means allowing a table to have more than 1024 columns QN=17 (8004) What is the benefit of "de-normalization"? a. "de-normalization" has no benefit b. The main benefit of de-normalization is improved performance with simplified data retrieval (this is done by reduction in the number of joins needed for data processing) c. The main benefit of de-normalization is eliminating redundant information from a table and organizing the data so that future changes to the table are easier QN=18 (8022) The key for a weak entity set E is ......... a. Zero or more attributes of E b. The set of attributes of supporting relationships for E c. The set of attributes of supporting entity sets d. Zero or more attributes of E and key attributes from supporting entity sets QN=19 (8019) A class in UML is similar to........... a. An entity set in E/R model b. An attribute in E/R model c. A Relationship in E/R model d. None of the others QN=20 (8013) A(n) _____ provides a means to analyze business requirements so as to standardize organizational vocabulary, enforce business rules, and ensure adequate data quality a. Entity Relationship Diagram b. Relation Schema Design c. All of the others d. None of the others QN=21 (8032) An association class in UML is similar to ______ in the ER model a. attributes on a relationship b. Attributes c. Entities d. entity sets QN=22 (8009) In UML, what is the difference between an aggregation and a composition? a. In composition, when the owning object is destroyed, so are the contained objects. In aggregation, this is not necessarily true. b. In aggregation, when the owning object is destroyed, so are the contained objects. In composition, this is not necessarily true. c. All of the others d. There is no difference between an aggregation and a composition QN=23 (8222) Which of the following is NOT a standard aggregation operator? a. GROUP b. SUM c. COUNT d. AVG QN=24 (8238) Consider the law, that holds for set relations: T intersect(R union S) = (T intersect R) union (T intersect S) The above law still hold for bag relations? a. True b. False QN=25 (8236) Choose the correct statement: a. Aggregate functions perform a calculation on a set of values and return a single value b. Aggregate functions perform a calculation on a single value and return a single value c. Aggregate functions perform a calculation on a set of values and return a relation d. Aggregate functions perform a calculation on a set of values and return a row QN=26 (8507) Suppose the relation S(B,C,D) has tuples: B C D ------------------------------------ a 4 6 c 6 8 c 5 5 e 9 9 F 10 10 c 7 9 Compute the result of the following query: SELECT SUM(D) FROM S WHERE D < 8 AND D > 5 Choose the row that appears in the computed result. a. 6 b. 7 c. 8 d. 9 QN=27 (8500) Suppose the relation S(B,C,D) has tuples: B C D ----------------------------------- a 4 6 c 6 8 c 5 5 e 9 9 f 10 10 c 7 9 Compute the result of the following query: SELECT D, SUM(C) FROM S GROUP BY D Choose rows that are appear in the computed result a. (9,12) b. (9,14) c. (9,16) d. (9,18) QN=28 (8509) Column A of a relation has the following list of values in the six rows of the table: NULL, NULL, 10, 10, 20, 30 In SQL Server, which of the following is the correct value of AVG(DISTINCT A)? a. 15 b. NULL c. 20 d. 10 QN=29 (8513) The table Arc(x,y) currently has the following tuples (note that there are duplicates): (1,2), (1,2), (2,3), (3,4), (3,4), (4,1), (4,1), (4,1), (4,2). Compute the result of the query: SELECT a1.x, a2.y, COUNT(*) FROM Arc a1, Arc a2 WHERE a1.y = a2.x GROUP BY a1.x, a2.y; Which of the following tuples is in the result? a. (3,1,2) b. (1,3,4) c. (2,4,6) d. (3,2,6) QN=30 (8517) How we can understand about this statement: "All aggregate functions are deterministic"? a. This means aggregate functions return the same value any time they are called by using a specific set of input values b. This means aggregate functions return the different values each time they are called by using a specific set of input values c. This means aggregate functions return the same value any time they are called by using any set of input values d. None of the others QN=31 (8523) When we apply set operators (UNION, INTERSECT, EXCEPT) to two relations R and S, which conditions on R and S must be satisfied? a. R and S must have schemas with identical sets of attributes and the types (domains) for each attributes must be the same in R and S b. Before we compute the set-theoretic union, intersection, or difference of sets of tuples, the columns of R and S must be ordered so that the order of attributes is the same for both relations c. All of the others QN=32 (8526) How many JOIN conditions are necessary to combine five tables based on common attributes? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 QN=33 (8528) Suppose relation R(A,B) has the tuples: A B ------------------- 10 x 30 y 50 z 70 t and the relation S(B,C,D) has tuples: B C D ------------------------------------ x 40 60 z 60 80 z 50 50 z 70 90 Compute the right outer join of R and S, where the condition is: R.B = S.B. Then identify 2 tuples of R that do not appear in the computed result. a. (10,x) b. (30,y) c. (50,z) d. (70,t) QN=34 (8539) For what values of x, y, and z, including NULL, does the Boolean expression x <= 4 OR NOT(y >= 2 AND z = 10) have the truth value FALSE? Identify one of those values from the list below a. x = 5, y = 3, z = 10 b. x = 3, y = 1, z = 10. c. x = NULL, y = 2, z = 10. d. x = NULL, y = 3, z = 10. QN=35 (8547) What operator tests column for the absence of data? a. IS BLANK operator b. IS ZERO operator c. IS NULL operator d. ISNULL operator QN=36 (8542) What does NULL mean? a. The value NULL means UNKNOWN b. The value NULL means '' (empty string) c. The value NULL means ' ' (space character) d. The value NULL means ZERO QN=37 (8550) What is the value of the query: SELECT 'Nancy' + NULL + 'Smith' when evaluated on Microsoft SQL Server? a. 'Nancy Smith' b. 'Nancy' c. 'NancySmith' d. NULL QN=38 (8557) Which SQL keyword is used to sort the result-set? a. ORDER BY b. SORT BY c. ORDER d. SORT QN=39 (8558) Three properties of a lock in DBMS are: a)Granularity: the size of the lock b) Granularity: the type of the lock c) Mode: the type of the lock d) Duration: the time in seconds that the DBMS waits for a lock to be released a. (a) and (c) and (d) are true b. (a) and (b) and (d) are true c. (b) and (c) and (d) are true d. (a) and (b) and (c) are true QN=40 (8560) A database transaction, by definition, must be ACID (atomic, consistent, isolated and durable). What does "Durable" mean? a. "Durable" means that: Transactions provide an "all-or-nothing" proposition, stating that each work-unit performed in a database must either complete in its entirety or have no effect whatsoever b. "Durable" means that: Transactions must not violate any integrity constraints during its execution c. "Durable" means that: Transactions that have committed will survive permanently d. All of the others QN=41 (8569) Suppose relation R(A,B). Choose the SQL statement that is equivalent to the following RA expression: [file:8569.jpg] a. SELECT * FROM R b. SELECT (A+B) AS C FROM R WHERE (A+B) > 10 c. SELECT (A+B) AS C FROM R d. There is not any choice QN=42 (8575) What is the difference between the WHERE and HAVING SQL clauses? a. The WHERE and the HAVING clauses are identical b. The HAVING SQL clause condition(s) is applied to all rows in the result set before the WHERE clause is applied (if present). The WHERE clause is used only with SELECT SQL statements and specifies a search condition for an aggregate or a group c. The WHERE SQL clause condition(s) is applied to all rows in the result set before the HAVING clause is applied (if present). The HAVING clause is used only with SELECT SQL statements and specifies a search condition for an aggregate or a group d. None of the others QN=43 (8599) Choose the correct statement. a. You can remove a trigger by dropping it or by dropping the trigger table. b. The syntax to remove a trigger is: DROP TRIGGER <trigger_name> c. Use ALTER TRIGGER to change the definition of a trigger d. All of the others. QN=44 (8585) Suppose R and S are 2 relations. R is the parent of S. And the relationship between R and S is set to "ON DELETE CASCADE". This means that: a. We can delete a row from R if that row has children in S (and in this case, the database server will raise up an error) b. We can delete a row from R although that row has children in S (and in this case, all the children will be deleted too) QN=45 (8592) To create a DEFAULT constraint on the "City" column of the table PERSON which is already created, use the following SQL: a. ALTER TABLE Person ALTER COLUMN City SET DEFAULT 'SANDNES' b. ALTER TABLE Person EDIT COLUMN City SET DEFAULT 'SANDNES' c. ALTER TABLE Person UPDATE COLUMN City SET DEFAULT 'SANDNES' d. ALTER TABLE Person MODIFY COLUMN City SET DEFAULT 'SANDNES' QN=46 (8582) Three basic types of database integrity constraints are: (a)Entity integrity (b) Domain integrity (c) Referential integrity (d) Primary key integrity a. (a) and (b) and (c) are true b. (a) and (b) and (d) are true c. (a) and (c) and (d) are true d. (b) and (c) and (d) are true QN=47 (8609) A(an) _____ asserts that a value appearing in one relation must also appear in the primary-key component(s) of another relation a. Unique key constraint b. Primary key constraint c. Foreign key constraint d. Candidate key constraint QN=48 (8600) What is difference between PRIMARY KEY and UNIQUE KEY ? a. A table can have more than one UNIQUE KEY constraint but only one PRIMARY KEY b. A table can have more than one PRIMARY KEY constraint but only one UNIQUE KEY c. UNIQUE KEY and PRIMARY KEY are the same d. None of the others QN=49 (8637) A/An _____ is a data structure that makes it efficient to find those tuples that have a fixed value for an attribute a. Index b. Trigger c. stored-procedure d. View QN=50 (8620) Select the most correct answer a. An index is a data structure used to speed access to tuples of a relation, given values of one or more attributes b. The key for index can be any attribute or set of attributes, and need not be the key of the relation c. We can think of the index as a binary search tree of (key, locations) pairs in which a key a is associated with a set of locations of the tuples d. All of the others. QN=51 (8633) ___ allow the database application to find data fast, without reading the whole table a. Indexes b. Views c. Triggers d. Store-procedures QN=52 (8630) What are the drawbacks of indexes? (a)Indexes require more disk space (b) Indexes make UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE statement slower (c)Indexes have no any drawback (d) Indexes make SELECT statement slower a. (a) and (b) are true b. (a) and (c) are true c. (b) and (c) are true d. (b) and (d) are true QN=53 (8624) Well-designed ____ can reduce disk I/O operations and consume fewer system resources therefore improving query performance a. Triggers b. Indexes c. Views d. Stored Procedures QN=54 (9178) Which of the following statements is the most correct? a. Using Stored procedures reduces network traffic b. Using Stored procedures improves security c. Using Stored procedures improves performance d. All of the others QN=55 (9168) The benefits of stored procedures are: (a)They improve the security by letting the admin to LIMIT the access rights of users (b) They can save a lot of storage space (c) They can be reused many times [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 5 out of 55 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$21.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 05, 2024
Number of pages
55
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 05, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
29