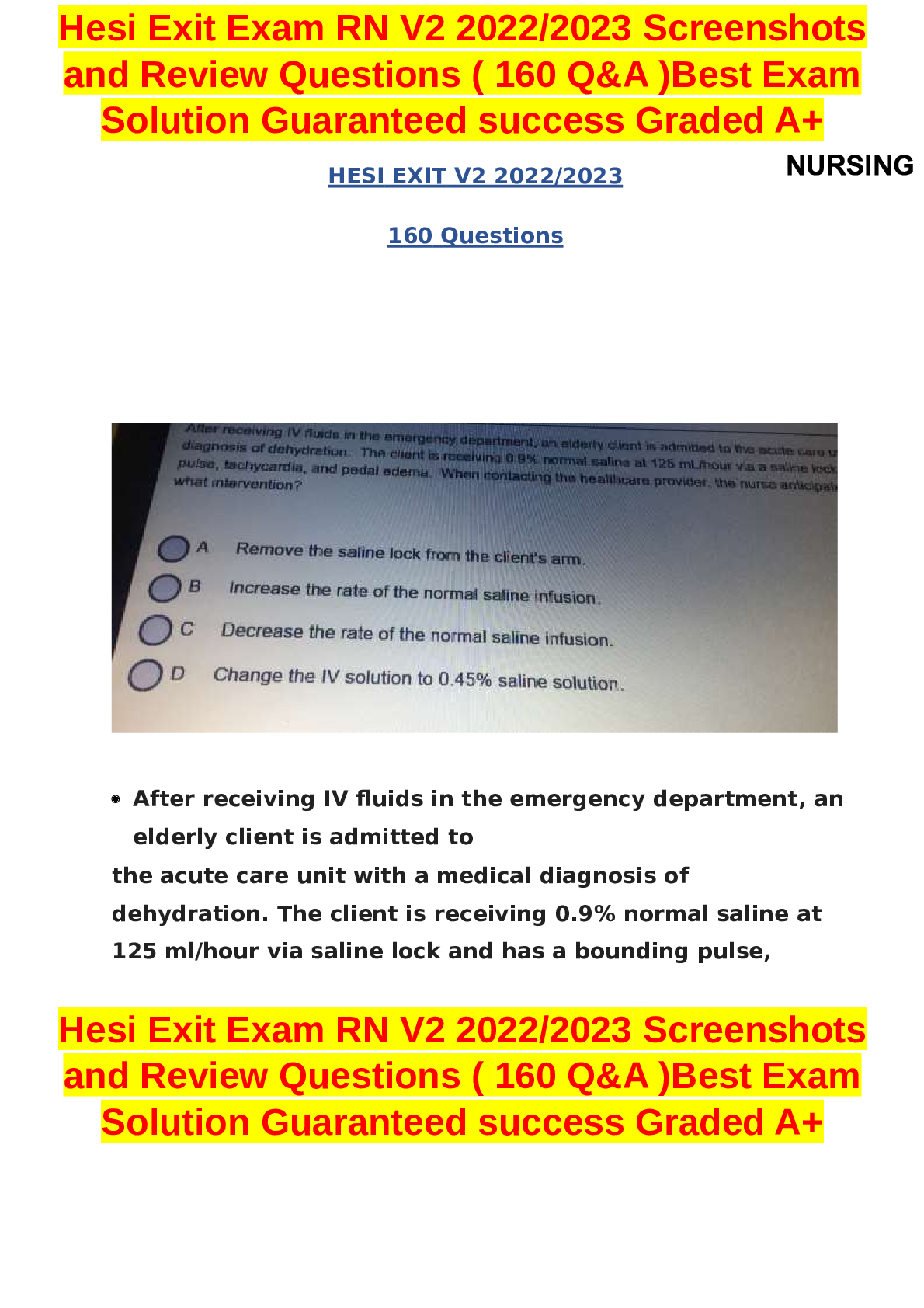
Pharm_Final.pdf (2).pdf. VERIFIED
A patient who has diabetes reports intense discomfort when needing to
void. A urinalysis is normal. To treat this, the primary care NP should
consider prescribing
This patient is des
...
Pharm_Final.pdf (2).pdf. VERIFIED
A patient who has diabetes reports intense discomfort when needing to
void. A urinalysis is normal. To treat this, the primary care NP should
consider prescribing
This patient is describing urge incontinence, or overactive bladder, which occurs when
the detrusor muscle is hyperactive, causing an intense urge to void before the bladder is
full. Urge incontinence is associated with many conditions, including diabetes.
Oxybutynin chloride, which is an anticholinergic, acts to decrease detrusor overactivity
and is indicated for treatment of urge incontinence. Flavoxate is used to treat dysuria
associated with UTI. Bethanechol is indicated for urinary retention. Phenazopyridine is
used to treat dysuria.
- A patient reports difficulty returning to sleep after getting up to go to the
bathroom every night. A physical examination and a sleep hygiene history
are noncontributory. The primary care NP should prescribe:
taking the drug in the morning.
Donepezil is typically taken in the evening just before going to bed; however, in patients
experiencing sleep disturbance, daytime administration is preferred. The dose should
not be increased or decreased.
- A 5-year-old child who has no previous history of otitis media is seen in
clinic with a temperature of 100° F. The primary care NP visualizes bilateral
erythematous, non-bulging, intact tympanic membranes. The child is taking
fluids well and is playing with toys in the examination room. The NP
should:
Initiate antibiotic therapy if the child's condition worsens.
Signs and symptoms of otitis media that indicate a need for antibiotic treatment include
otalgia, fever, otorrhea, or a bulging yellow or red tympanic membrane. This child has a
low-grade fever, no history of otitis media, a non-bulging tympanic membrane, and no
otorrhea, so watchful waiting is appropriate. When an antibiotic is started, amoxicillin is
the drug of choice.
- An 80-year-old patient with congestive heart failure has a viral upper
respiratory infection. The patient asks the primary care NP about treating
the fever, which is 38.5° C. The NP should:
Patients with congestive heart failure may have tachycardia from fever that aggravates
their symptoms, so fever should be treated. High doses should be given with caution in
elderly patients because of possible decreased hepatic function. Antibiotics should not
be given without evidence of bacterial infection
NURSING
- A patient who takes levodopa and carbidopa for Parkinson’s disease
reports experiencing freezing episodes between doses. The primary care
NP should consider using:
Apomorphine injection is used for acute treatment of immobility known as "freezing."
- A patient is being tapered from long-term therapy with prednisolone and
reports weight loss and fatigue. The primary care NP should counsel this
patient to:
Increase the dose of prednisolone to the most recent amount taken. Sudden
discontinuation or rapid tapering of glucocorticoids in patients who have developed
adrenal suppression can precipitate symptoms of adrenal insufficiency, including
nausea, weakness, depression, anorexia, myalgia, hypotension, and hypoglycemia.
When patients experience these symptoms during a drug taper, the dose should be
increased to the last dose. Vitamin D deficiency is common while taking glucocorticoids,
but these are not symptoms of vitamin D deficiency. Changing to another glucocorticoid
is not recommended. Patients should be taught to report the side effects so that action
can be taken and should not be told that they are to be expected.
[Show More]