Exam Questions PATHO 3140
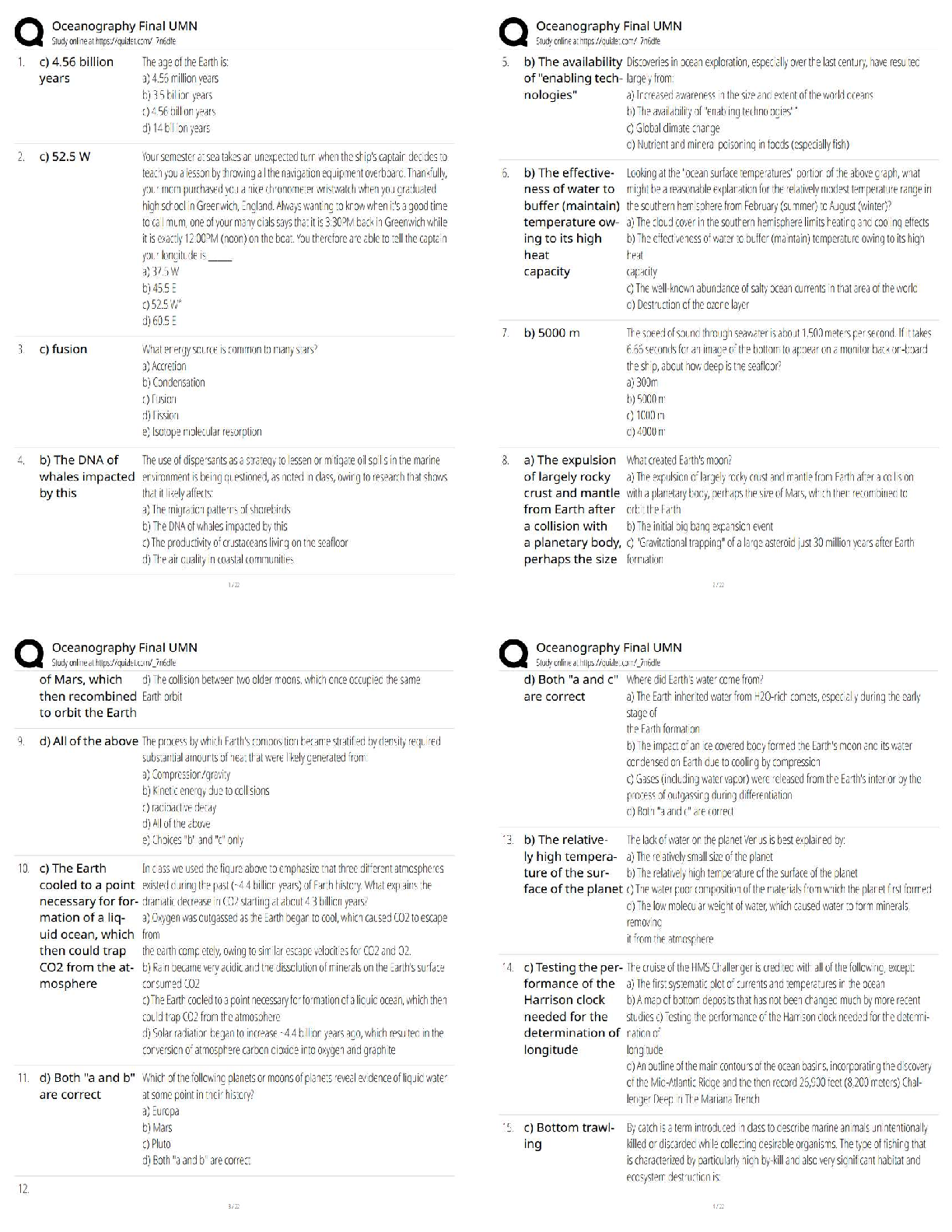
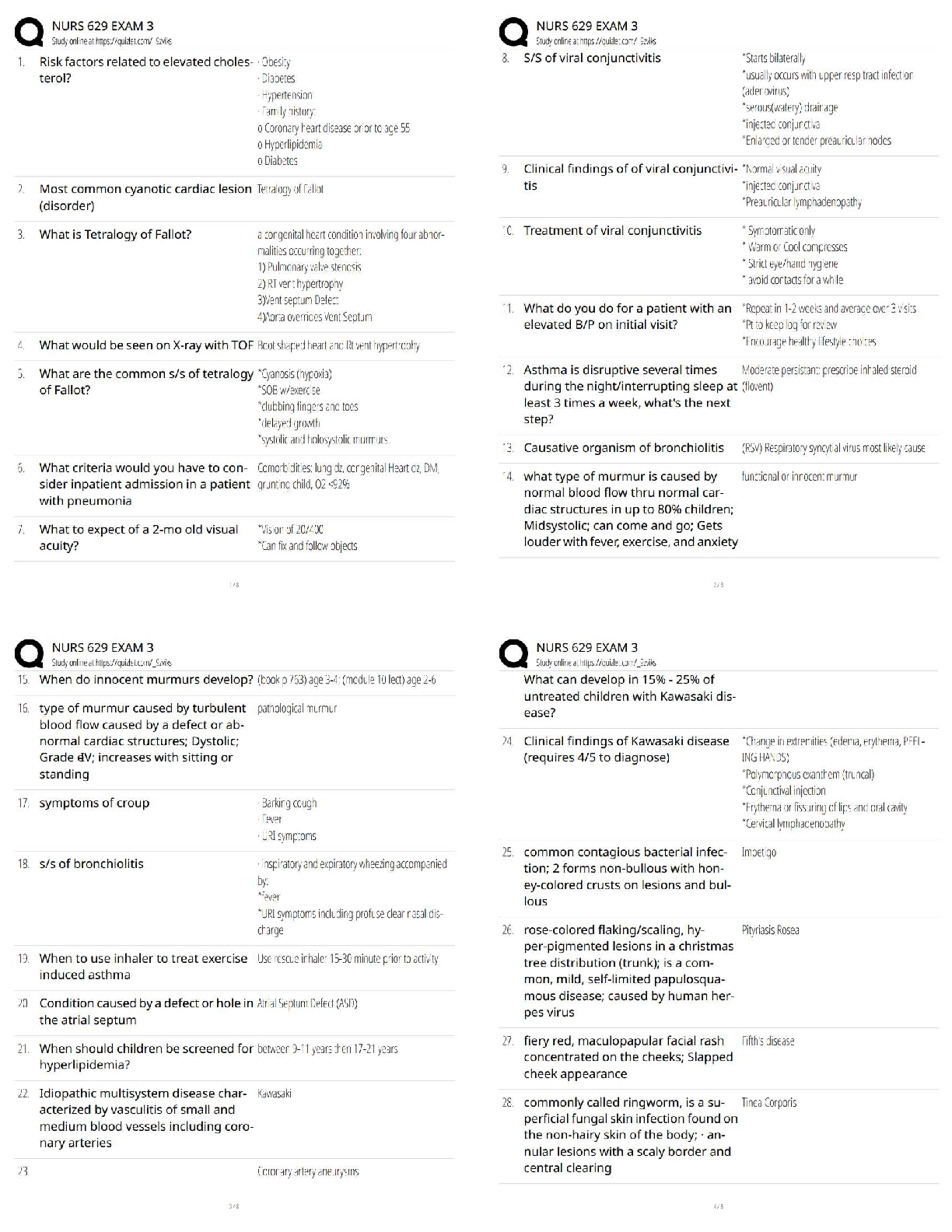
1. People will start to see symptoms of Renal Failure when they have lost what percentage of their nephrons?
a. 50%
b. 75%
c. 25%
2. Glomerular Filtration rate can be effected by:
a. Num
...
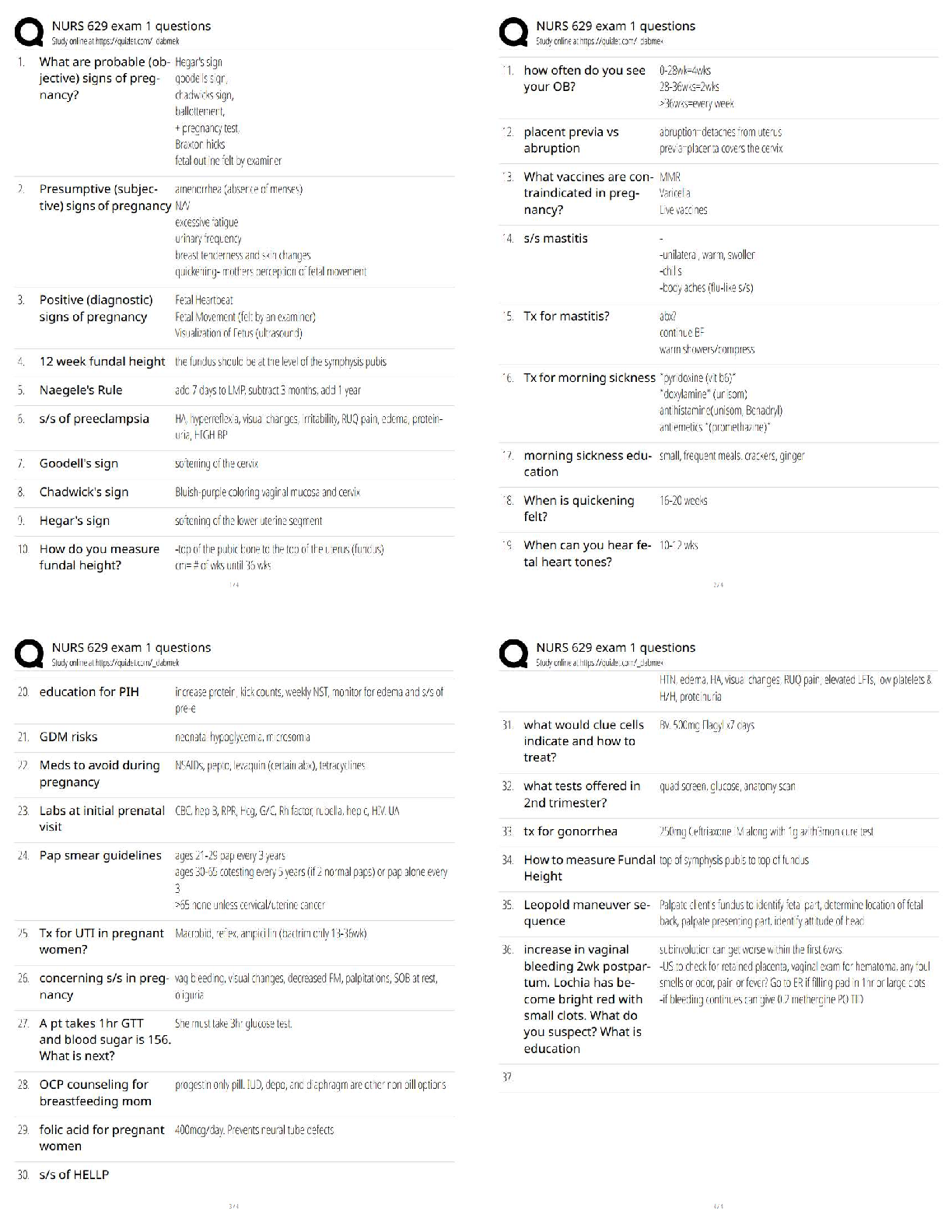
Exam Questions PATHO 3140
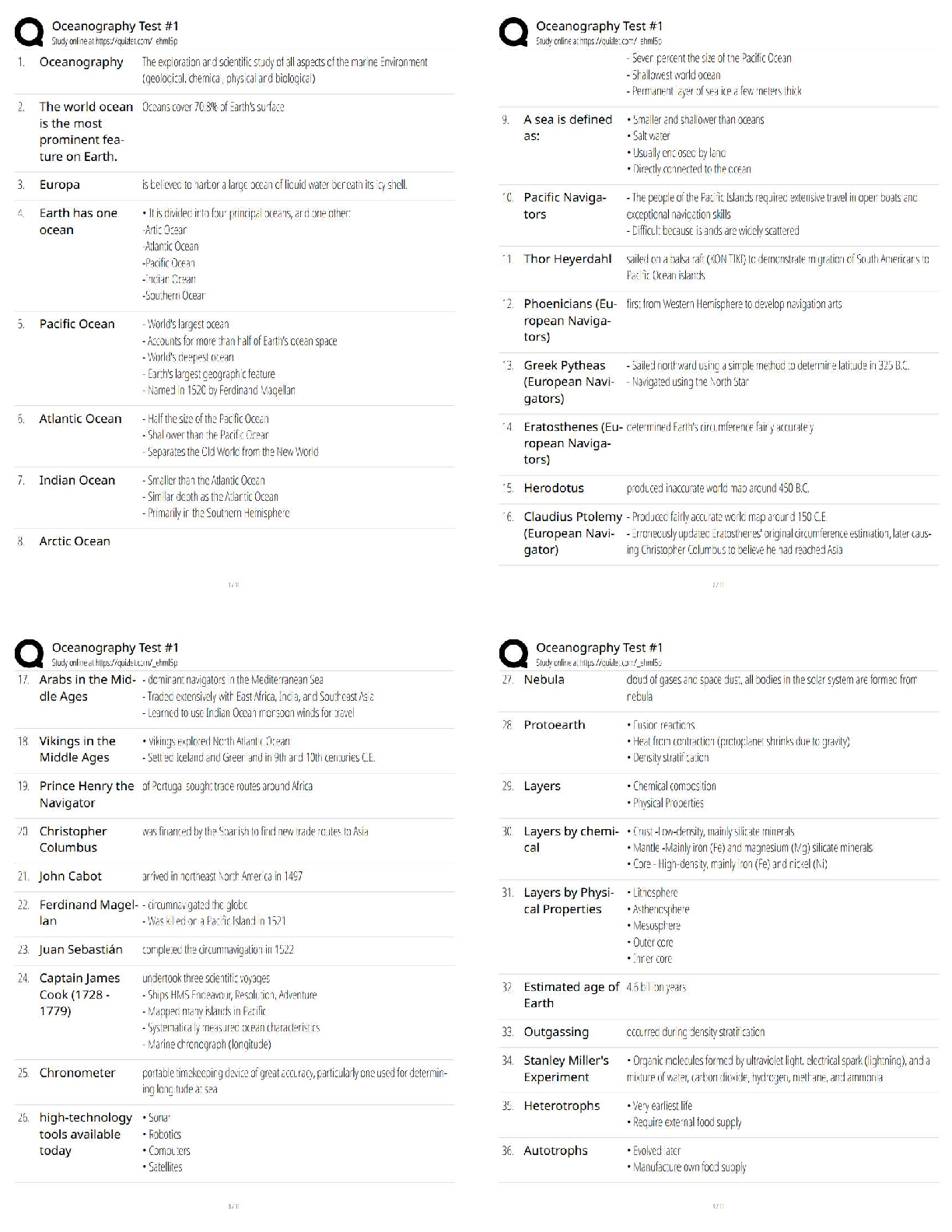
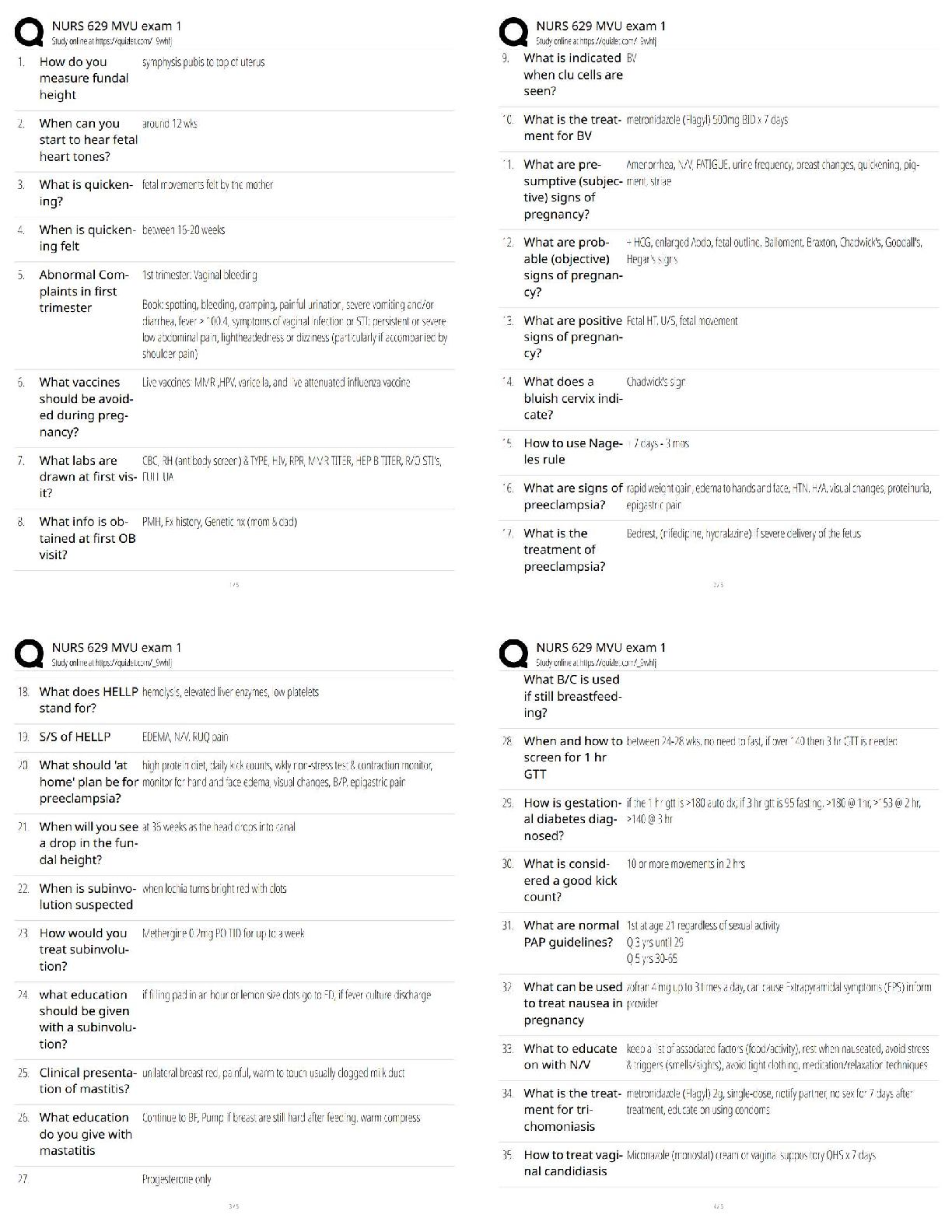
1. People will start to see symptoms of Renal Failure when they have lost what percentage of their nephrons?
a. 50%
b. 75%
c. 25%
2. Glomerular Filtration rate can be effected by:
a. Number of glomeruli
b. Viscosity of blood
3. Which of the following can lead to renal failure? Select all that apply.
a. SLE A. 1 and 2
b. Lead poisoning B. 2 only
c. Herpes C. 1, 2, and 4
d. UTI D. all of the above
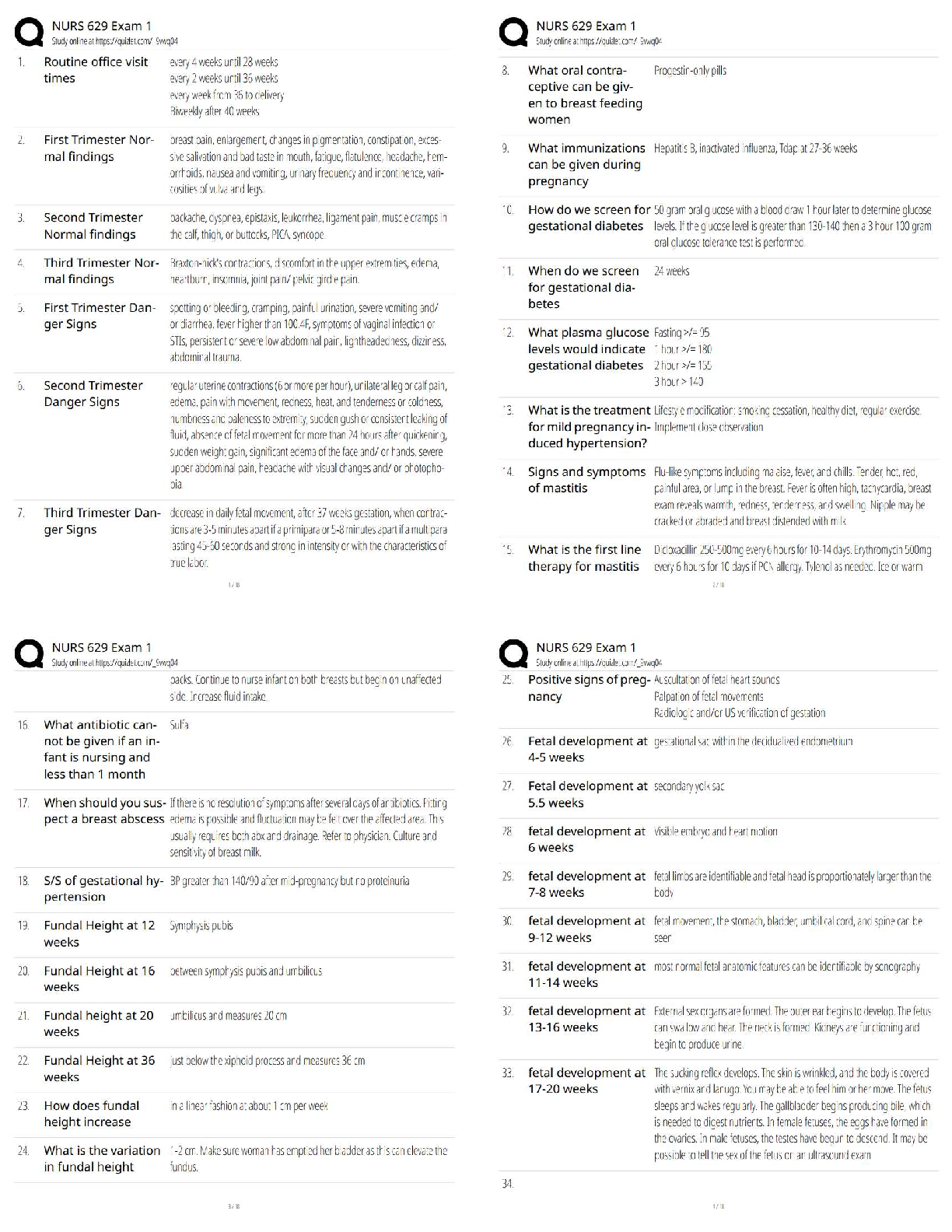
4. UTIs are more common in:
a. Males
b. Females
c. Children
5. Infection of the urinary bladder
a. Pyelonephritis
b. Cystitis
c. Urethritis
6. What hormone increase in pregnancy causes women to become even more susceptible to UTIs?
a. Estrogen
b. Progesterone
c. Oxytocin
d. Prolactin
7. Inflammation of glomeruli is called:
a. Uremic syndrome
b. Glomerulonephritis
c. Pyelonephritis
d. Hyperuricemia
8. Complications seen in glomerulonephritis include:
a. Proteinuria A. 1 and 2
b. Azotemia B. 3 and 4
c. Reduced GFR C. 1, 2, 3, and 4
d. Renal failure D. 1, 2, 4, and 5
e. Hypertension E. All of the above
9. Acute Glomerulonephritis is classically caused by:
a. Antibody mistake
b. Nephrotoxin
c. Diabetes
d. Vascular disease
10. Which of the following will you see with acute GN? Select all that apply.
1. Edema A. 2, 3, and 4
2. Hypotension B. 1, 2, and 5
3. Wasting of nitrogenous substances C. 1, 4, and 5
4. Hyperuricemia D. 1, 3, 4 and 5
5. Mental status changes E. all of the above
11. A person presents to the Emergency Department in diabetic ketoacidosis. Which test would be considered best to assess their kidney function?
a. CK-MD
b. Blood urea nitrogen
c. Creatinine clearance
d. AST/ALT
e. Rationale A person in diabetic ketoacidosis will be suffering severe dehydration (due to large amounts of Na and water excretion). BUN is affected by hydration status and would increase in times of dehydration, making it a less accurate test of kidney function than creatinine.
12. In chronic GN the nephrons atrophy and the kidney decreases to about the size of your fist. How much does the kidney weight at this point?
a. 350g
b. 150 g
c. 50g
d. 75g
13. When a person has a BP of 210/150 the Kidneys compensate by _______ the afferent and _______ the efferent to reduce the pressure in the nephron.
a. Dilating and constricting
b. Constricting and dilating
14. Disease in which multiple cysts develop on the kidneys
a. SLE
b. Polycystic Kidney Disease
c. Rental Tubular Disease
d. Pyelonephritis
15. In what population is Classic Renal tubular acidosis more commonly seen?
a. Men
b. Women
16. What analgesic is known to cause damage to distal tubules of the nephron?
a. Acetaminophen
b. Aspirin
c. Ibuprofen
17. Proximal RTA is associated with the
a. Loss of HCO3 in urine
b. Retention of HCO3 in vascular system
c. Loss of H+ in urine
d. Retention of H+ in vascular system
18. Classic RTA is associated with the
a. Loss of HCO3 in urine
b. Retention of HCO3 in vascular system
c. Loss of H+ in urine
d. Retention of H+ in vascular system
19. A complication of classic RTA is:
a. Excess H+ in blood stream, rise in pH, and metabolic acidosis
b. Excess H+ in blood stream, drop in pH, and metabolic acidosis
c. Drop in H+ in blood stream, rise in pH, and metabolic alkalosis
d. Drop in H+ in blood stream, drop in pH, and metabolic acidosis
20. With Type II RTA, the pH of the urine will be:
a. Acidic
b. alkalotic
21. Primary Gout is more commonly seen in:
a. Females
b. Males
22. A person is considered to have uremic syndrome when they have lost _____ of the GFR?
a. 50%
b. 75%
c. 80%
d. 90%
23. Which of the following would you see in renal failure?
a. Metabolic acidosis
b. Metabolic alkalosis
24. What is the etiology of acute renal failure caused by a severe burn?
a. Postrenal
b. Intrinsically renal
c. Prerenal
25. Fracture that is at an angle across the bone.
a. Transverse
b. Spiral
c. Oblique
d. Impaction
26. Manipulating the bone fragments back to their original location.
a. Recognition
b. Reduction
c. Retention
d. Rehabilitation
27. Risser’s Sign is:
a. Bone growths that stop the spine from curving and rotating
b. Bone growths that stop spine from curving but not rotating
c. Bone growths that stop the spine from rotating but not curving
28. Characteristics of Giant Cell Tumors. Select all that apply
1. Almost always malignant A. 1 and 3
2. Usually seen in young people B. 2 and 3
3. Occurs at ends of long bones C. 1 and 2
D. all of the above
29. Characteristics of osteogenic sarcoma include:
a. 1. Usually seen in young males A. 2, 3, and 4
b. 2. Occurs at ends of long bones B. 3 and 4 only
c. 3. Slow to metastasize C. 1, 2, and 3
d. 4. Benign D. all of the above
30. Which of the following are characteristics of osteoarthritis? Select all that apply
a. More common in females
b. Commonly seen in the Distal phalangeal joints
c. Seen in younger population
d. Runs in the family
e. Heberdens nodes
31. Which of the following are characteristics of SLE? Select all that apply
a. More common in males
b. Symmetrical joint pain
c. Raynaud’s
d. Butterfly Rash
32. Occurs in adults and is caused by excessive excretion of the growth hormone. Facial bones will begin to grow wider.
a. Acromegaly
b. Gigantism
33. What are the hormones released by the anterior pituitary?
a. FSH
b. LH
c. prolactin
d. TSH
34. Characteristics of Hyperthyroidism. Select all that apply
a. Cold intolerance
b. Decreased appetite
c. Increased sweating
d. Increased movement
35. Hypothyroidism in which the TSH is elevated and the T3 and T4 are decreasing.
a. Primary
b. Secondary
36. Characteristics of Hypercalcemia. Select all that apply.
a. Increase in serum calcium above 10.5
b. Hypotension
c. Bone cysts
d. EKG changes
37. The Adrenal Cortex produces:
a. cortisol
b. androgens
c. aldosterone
d. estrogens
38. Syndrome caused by an excess of cortisol
a. Addison’s
b. Cushing’s
39. Characteristics of Addison’s. Select all that apply.
a. Hypoglycemia
b. Increased excretion of Sodium
c. Hypertensive
d. Acidotic
40. Insulin dependent diabetes
a. Type 1
b. Type 2
41. Which cells do not have insulin receptors on them and are thus more susceptible to damage from hyperglycemia?
a. Optic nerve/retina
b. glomeruli
c. peripheral nerves
d. Skin cells
e. Skeletal muscle
[Show More]











.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)