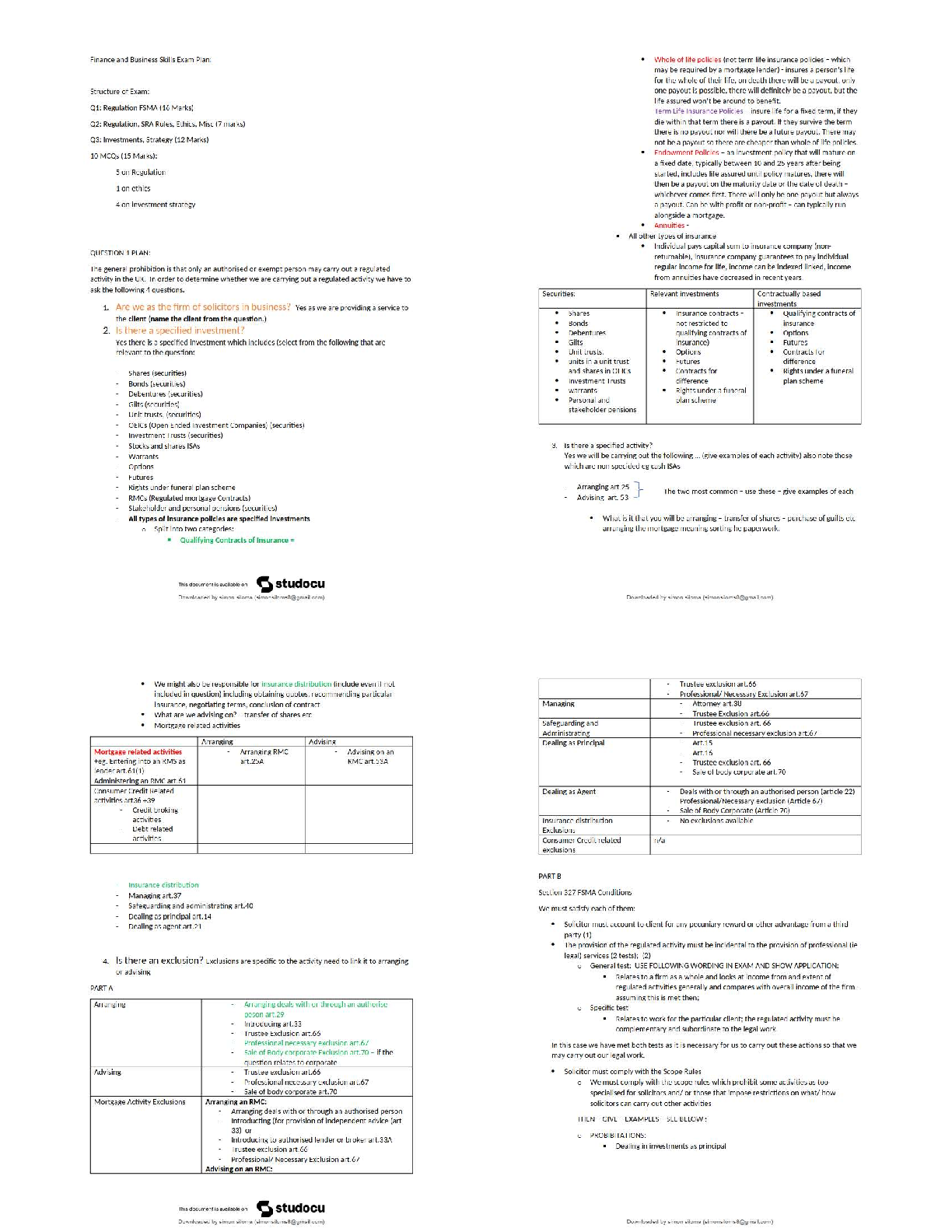
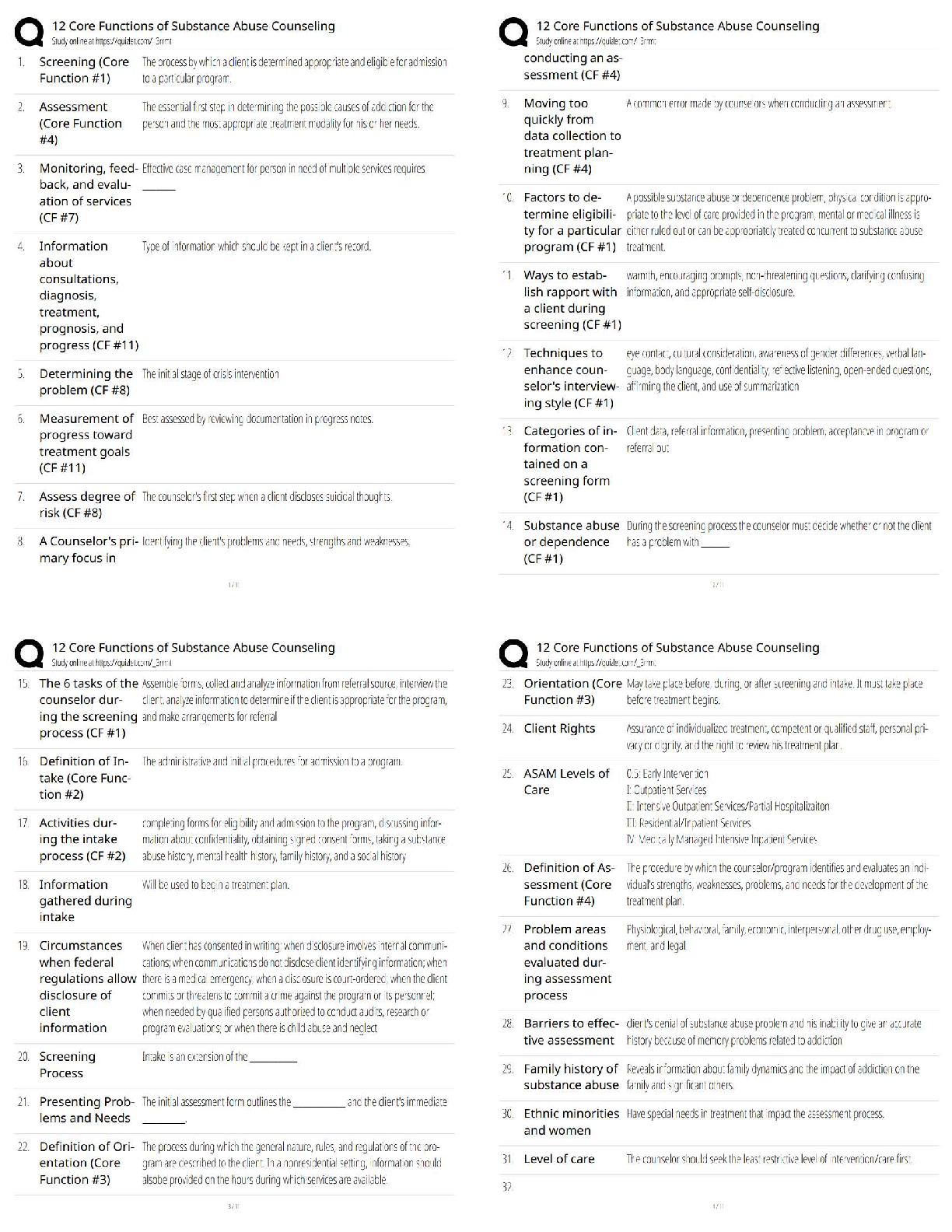
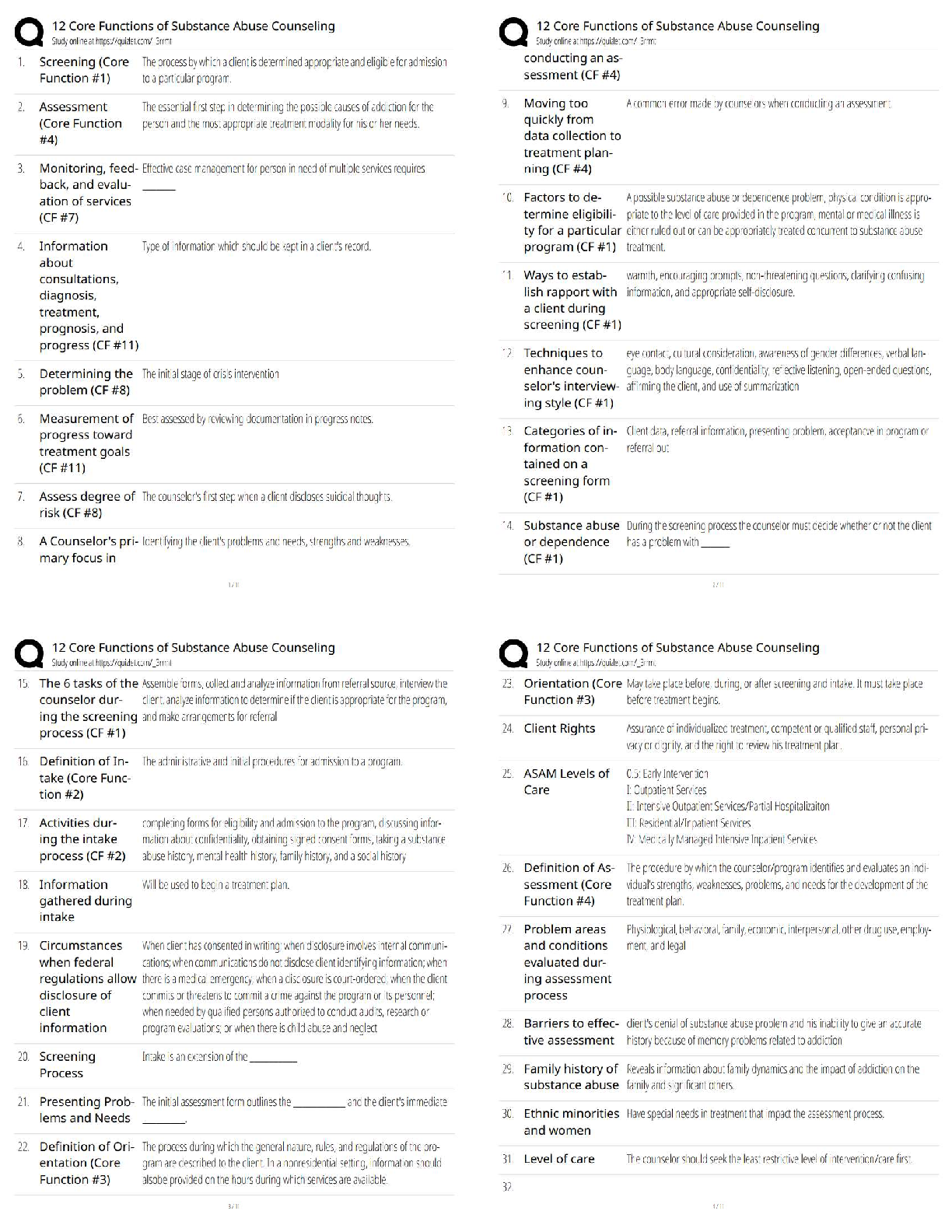
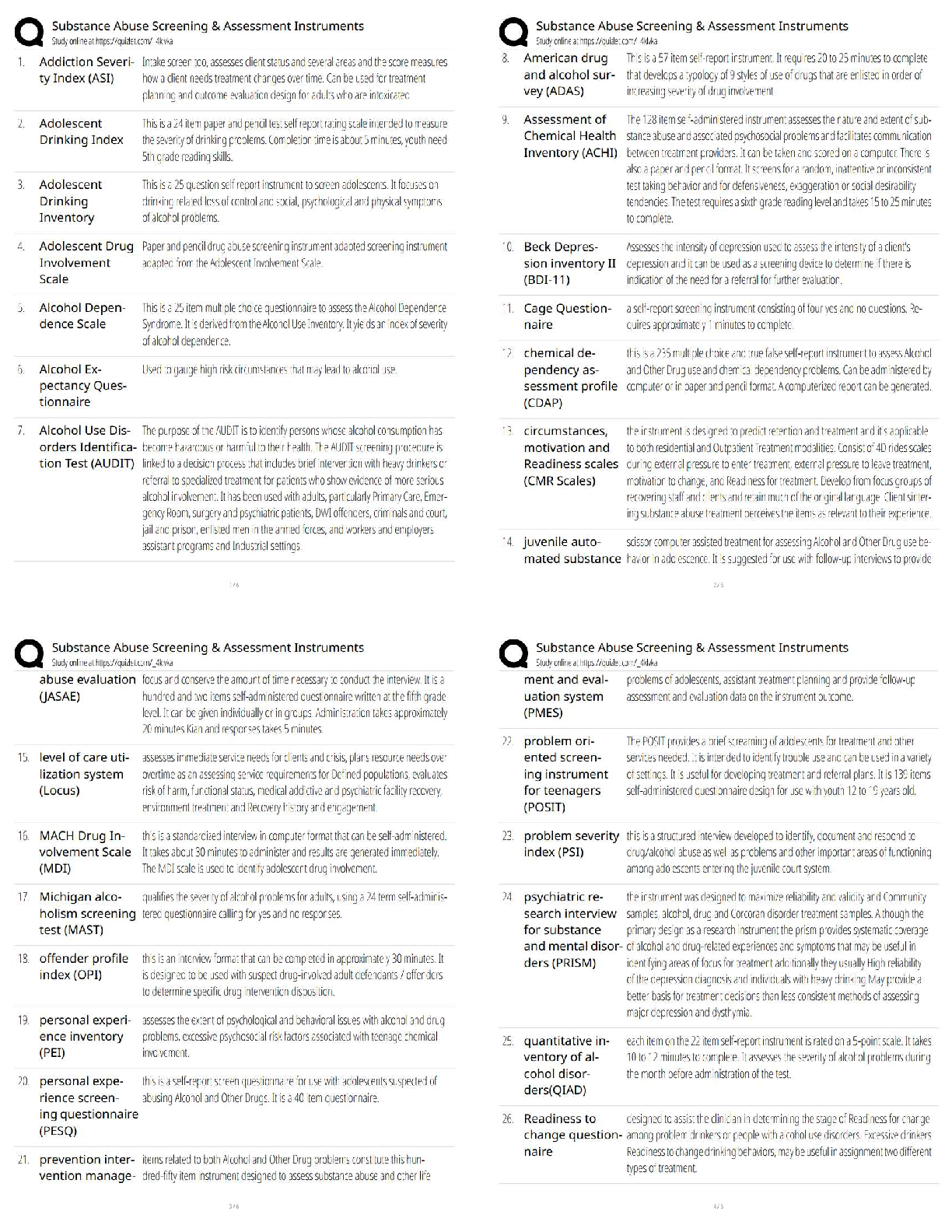
Glasgow
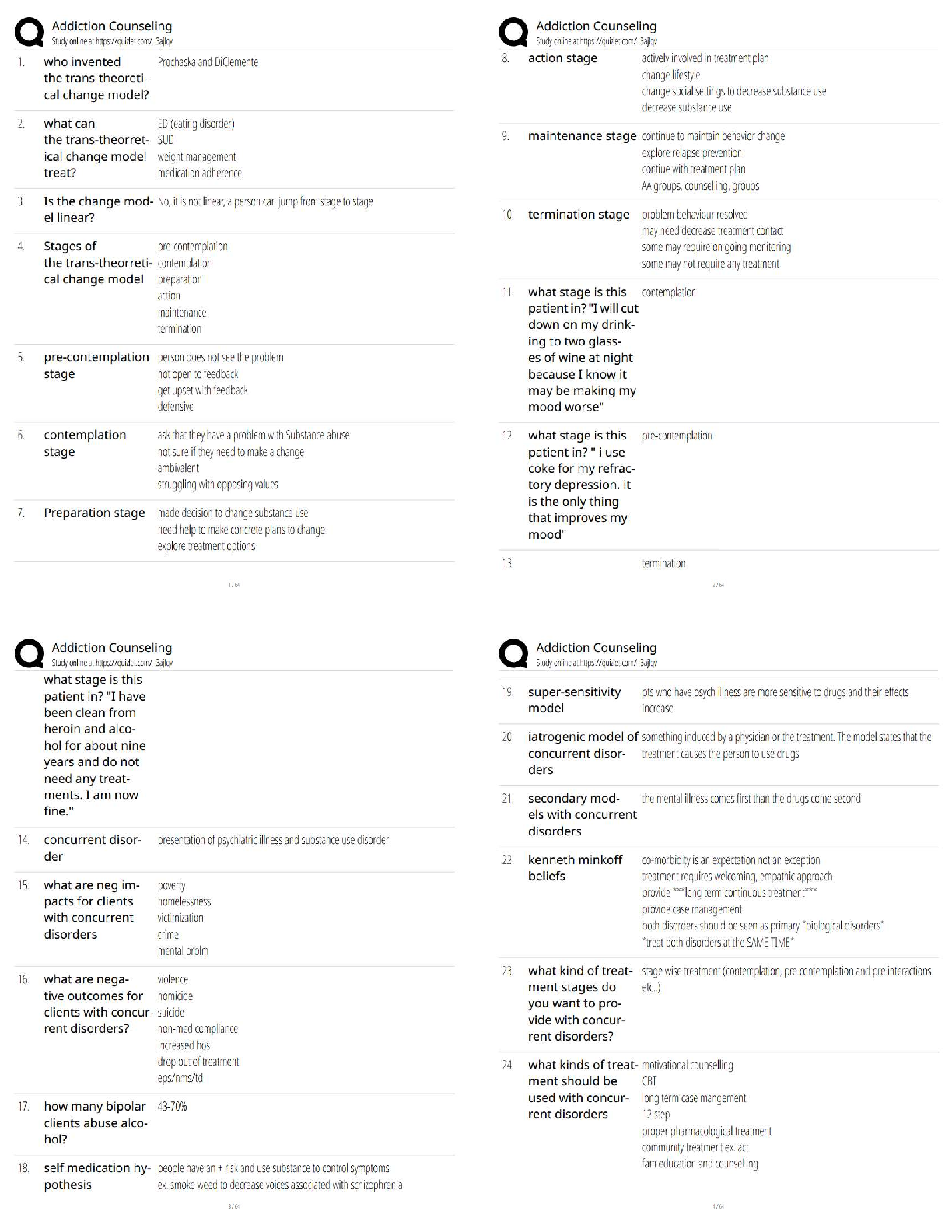
Coma
Scale Correct ans -
Chance fracture Correct ans - Transverse fracture through vertebra.
In children usually associated with enterc disruption. Seen in motor vehicle
accidents involving only lap belt.
M
...
Glasgow
Coma
Scale Correct ans -
Chance fracture Correct ans - Transverse fracture through vertebra.
In children usually associated with enterc disruption. Seen in motor vehicle
accidents involving only lap belt.
May be associated with retroperitoneal and Abdominal visceral injuries.
Anterior hip dislocation Correct ans - Flexed, abducted, externally
rotated.
Burst fracture Correct ans - Associated with vertebral-axial
compression injuries
Posterior hip dislocation Correct ans - Flexed, aDDucted, internally
rotated
Anterior shoulder dislocation Correct ans - Squared off appearance
Posterior shoulder dislocation Correct ans - Lock in internal rotation.
Ankle dislocation Correct ans - Most are Externally rotated, with a
prominent medial malleolus.
FULL thickness (3rd degree) burn Correct ans - Dark or white and
leathery. Translucent white as well. Painless and generally "dry" Does not
blanch with pressure. Very little swelling of burned tissue.
Principle Life saving measures for patients with burn injuries include
Correct ans - -Establishing airway control
-Stopping the burning. process
-Intravenous access
Factors that increase the risk for upper AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION in burns
include: Correct ans - -Burns to the head and face
-Burn size and depth
-Burns inside the mouth
Partial thickness burn Correct ans - Red remodeled appearance with
associated swelling and blister formation. May have weeping or wet
appearance and is painfully hypersensitive even to air current.
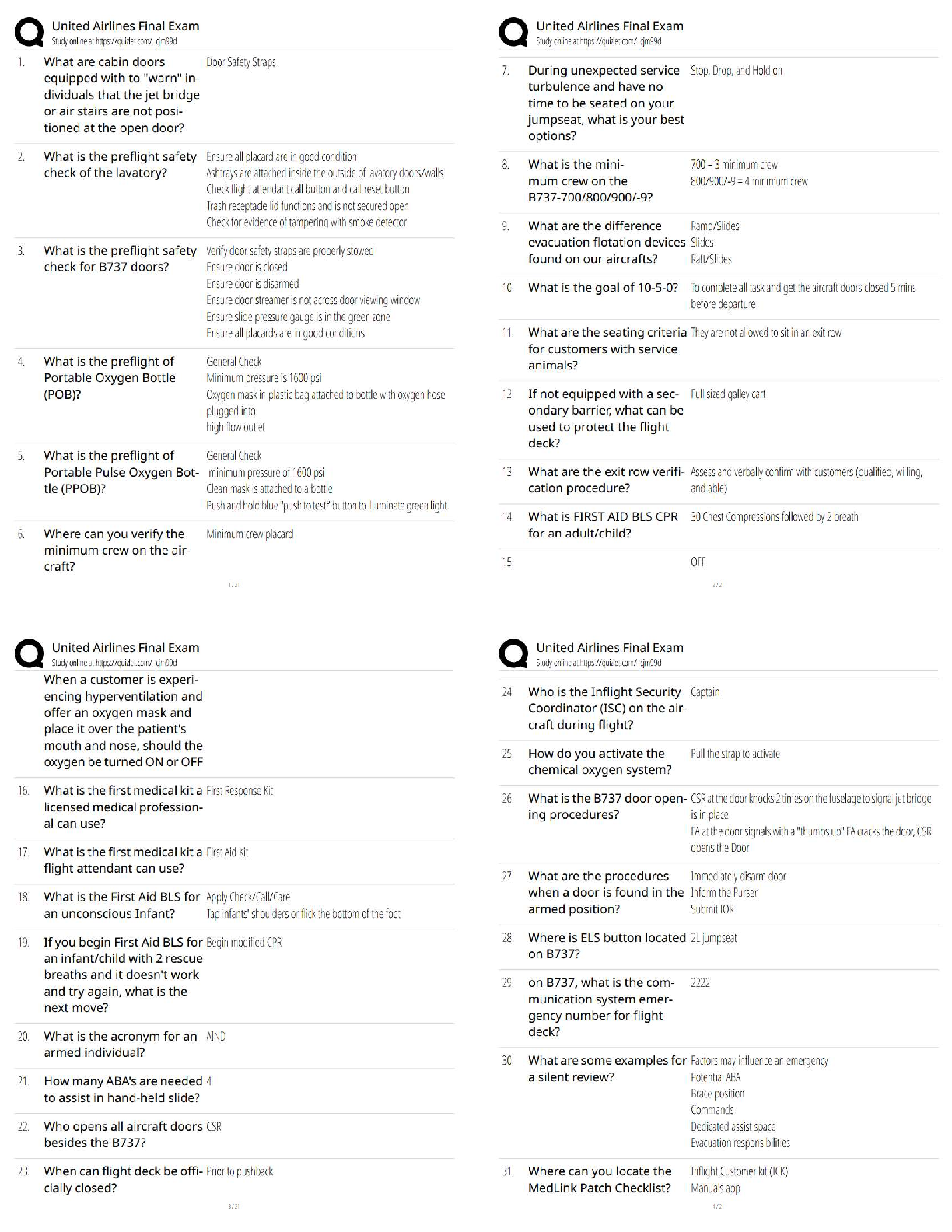
ATLS 216 QUESTIONS
Signs and symptoms and history that suggest INHALATION INJURY include:
Correct ans - These patients should be intubated. Inhalation injury is an
indication for transfer to a burn center.
Rule of nines - adult Correct ans - The palm represents 1% of the body
total surface area.
Symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning and respective levels Correct
ans - PaO2 does not reliably predict carbon monoxide poisoning because a
CO partial pressure of only 1 mmm Hg results in a hemoglobin CO level of
40% or greater.
Carbon monoxide has how many times greater affinity for hemoglobin than
oxygen Correct ans - 240 times.
It displaces the oxyhemoglobin desaturated curve to the LEFT.
Two criteria required for the diagnosis of smoke inhalation injury Correct
ans - -Exposure to a combustible agent
-Signs of exposure to smoke in the lower airway, below the vocal cords, by
bronchoscopy.
Performing this action will help reduce neck and chest wall edema in patients
with burn and inhalation injury. Correct ans - Elevation of the head and
chest by 30 degrees.
IV fluid administration formula for burn victims Correct ans - Indicated
in burns involving over 20% of the body surface area.
*(2-4 mL/kg of LR/NS) (weight in kg) (% area of burn); give 1/2 of this volume
in first 8 hours. Remainder in over 16 hours.
Large caliber, at least 15 gauge intravenous line should be introduced.
Pitfalls for IV fluid requirements for burn victims. Correct ans - These
patients require greater fluid requirements: ~immolation injury
~pediatric burn victims
~concomitant blunt or crush
injuries.
Basic rules regarding IV fluids administration in burn victims Correct ans
- IV fluid Rate should not be based on the time of actual injury.
In very small children, less than 10 kilograms, it may be necessary to add
glucose to the IV fluids to avoid hypoglycemia.
Any adjustment in IV fluid rate should be based on urine output. In an adult,
urine output above 0.5 ml/ kilogram should result in reduction of IV fluid rate.
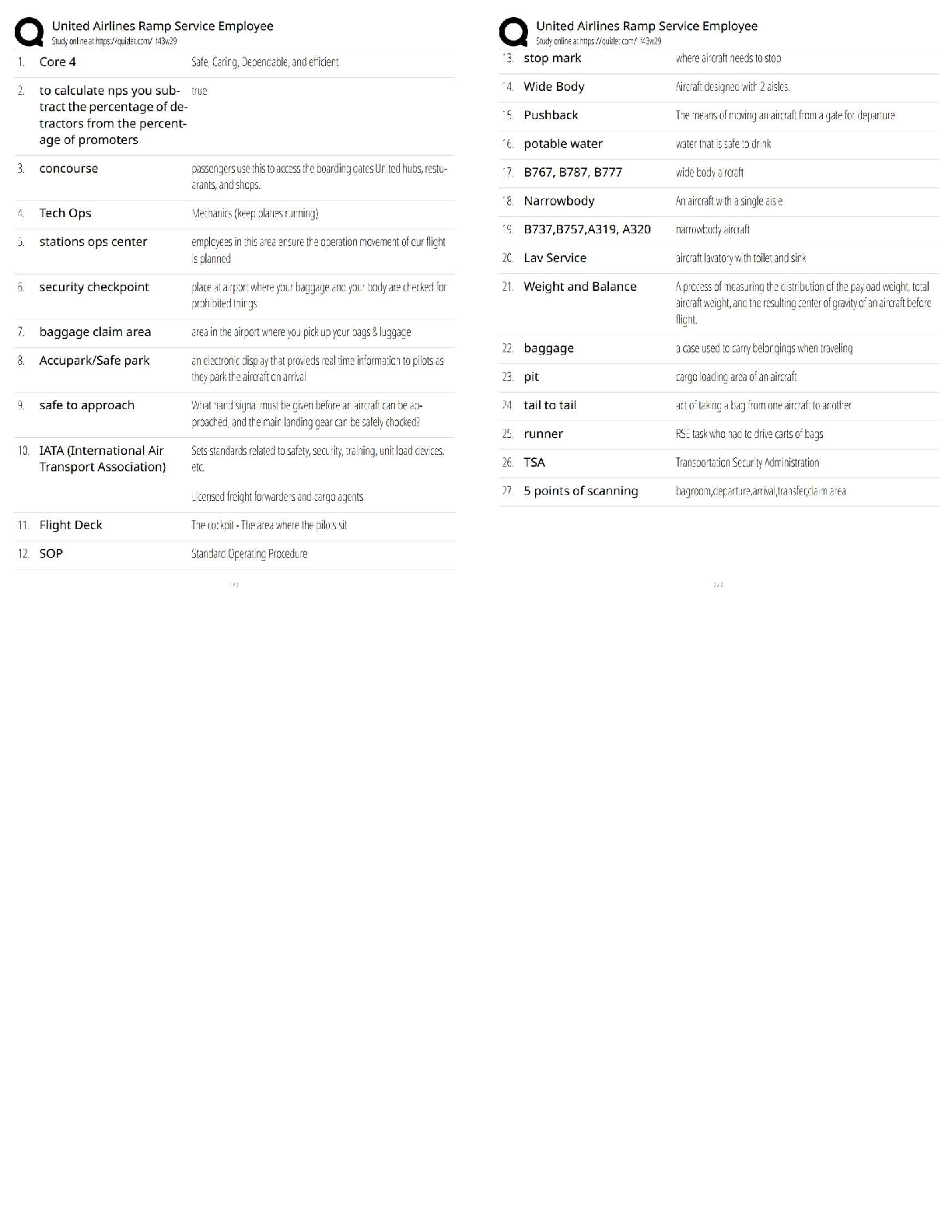
Initial treatment of frostbite/ cold injuries Correct ans - Place injured
part in circulating water and a constant 40 degrees centigrade until pink
color and perfusion return, usually within 20 to 30 minutes.
Antibiotics are not indicated empirically unless infection develops later.
Persisted ACIDEMIA in burn victims may reflect... Correct ans -
Cyanide poisoning. (Cyanide is a naturally occurring toxin that may be
inhaled in a confined space fire).
Hypothermia
Severe hypothermia Correct ans - Core temperature of 36 degrees
centigrade
Temperature below 32 degrees centigrade
Definition of frostbite. Correct ans - Freezing of tissue with intracellular
ice crystal formation, microvascular occlusion, subsequent tissue anoxia.
First degree frostbite Correct ans - Hyperemia and edema without skin
necrosis
Second-degree frostbite Correct ans - Large clear vesicle formation
accompanies hyperemia and edema with partial thickness skin necrosis
3rd degree frostbite Correct ans - Full thickness and subcutaneous
necrosis occurs, commonly with hemorrhage and vesicle formation.
Although a compartment pressure > systolic blood pressure is required to
lose a pulse distal to in extremity burn, a pressure of what was in the
compartment may lead to muscle necrosis Correct ans - 30 mm Hg. If
a pressure of greater than 30 mm Hg in a burned extremity is present,
eschatotomy is indicated.
Difference between fasciotomy and eschatotomy Correct ans -
Compartment syndrome is also present with circumferential chest and
abdominal burns, which lead to increased peak inspiratory pressures.
Eschatotomy in circumferential chest and abdominal burns. Correct ans
- We are generally not needed before the first 6 hours after a burn.
[Show More]