Computer Science > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ISYE 6414 Regression Analysis - Endterm Closed Book Section - Part 1. Score 100%. Georgia Institute (All)
ISYE 6414 Regression Analysis - Endterm Closed Book Section - Part 1. Score 100%. Georgia Institute Of Technology
Document Content and Description Below
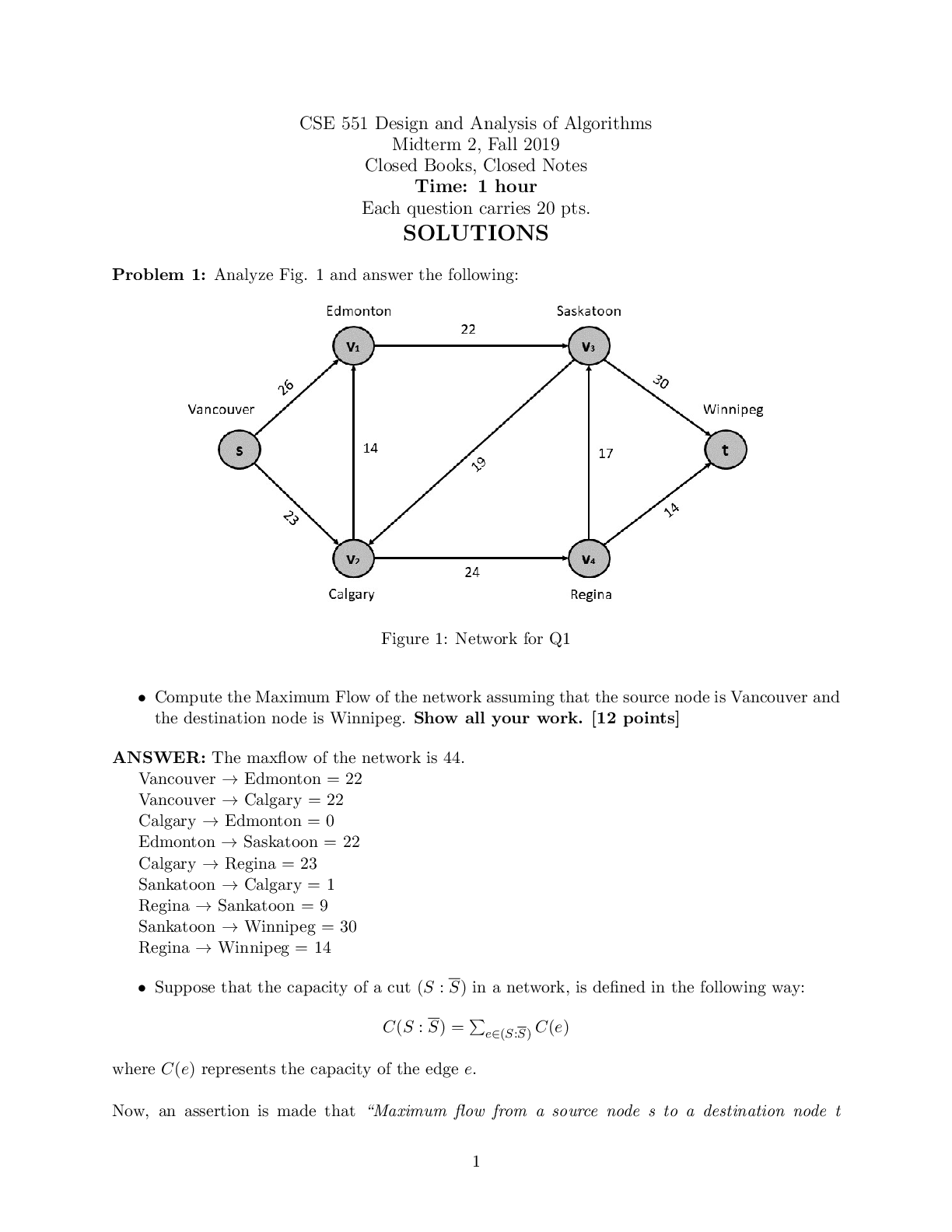
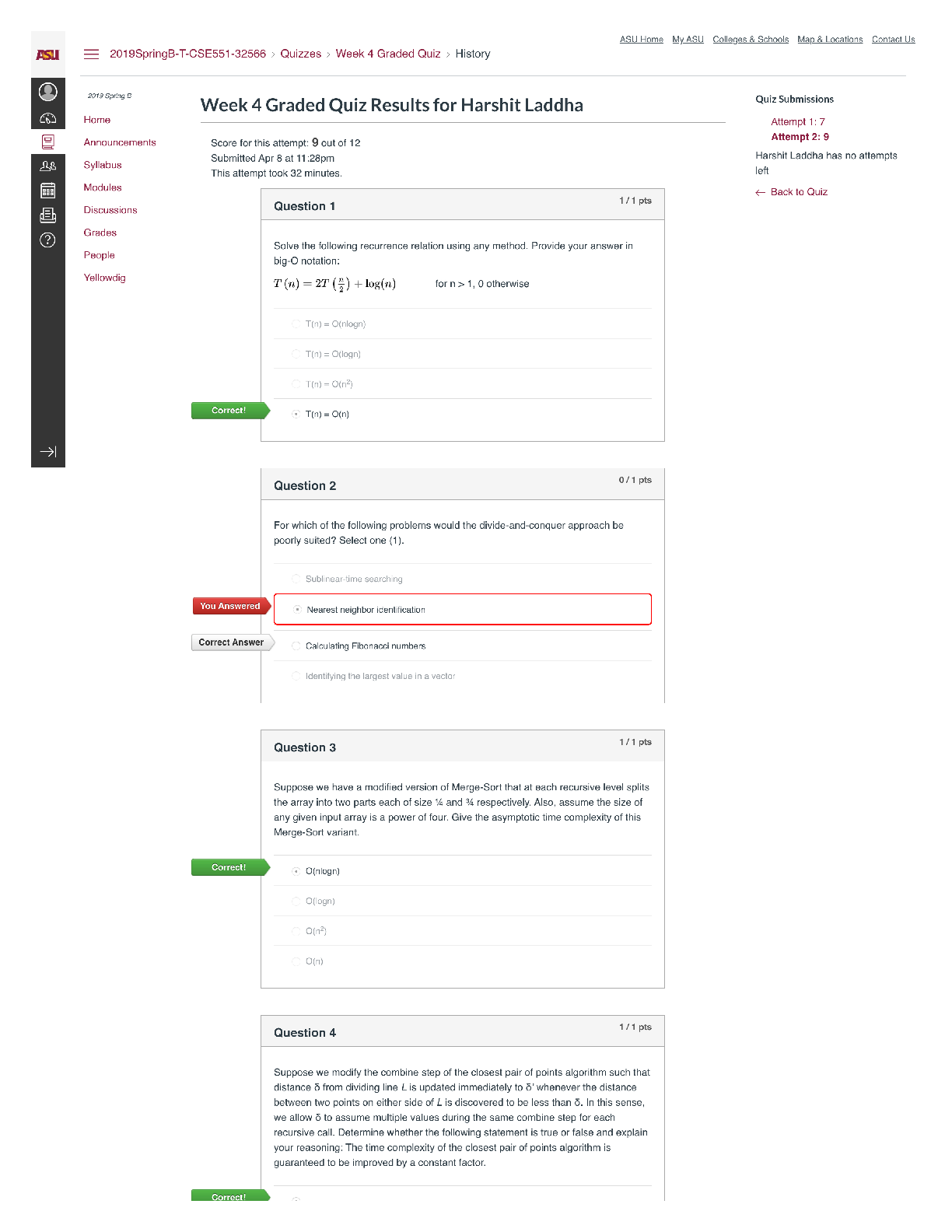
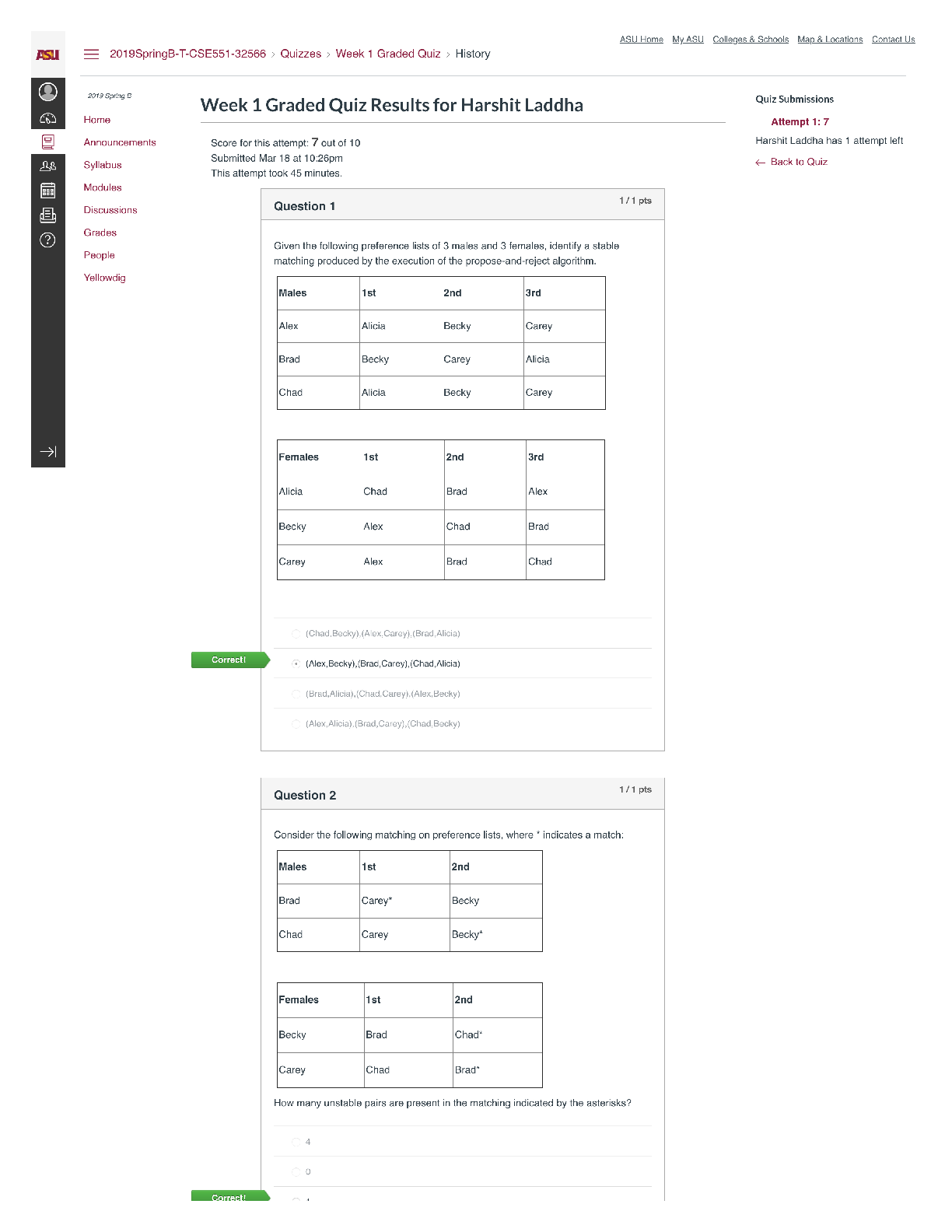
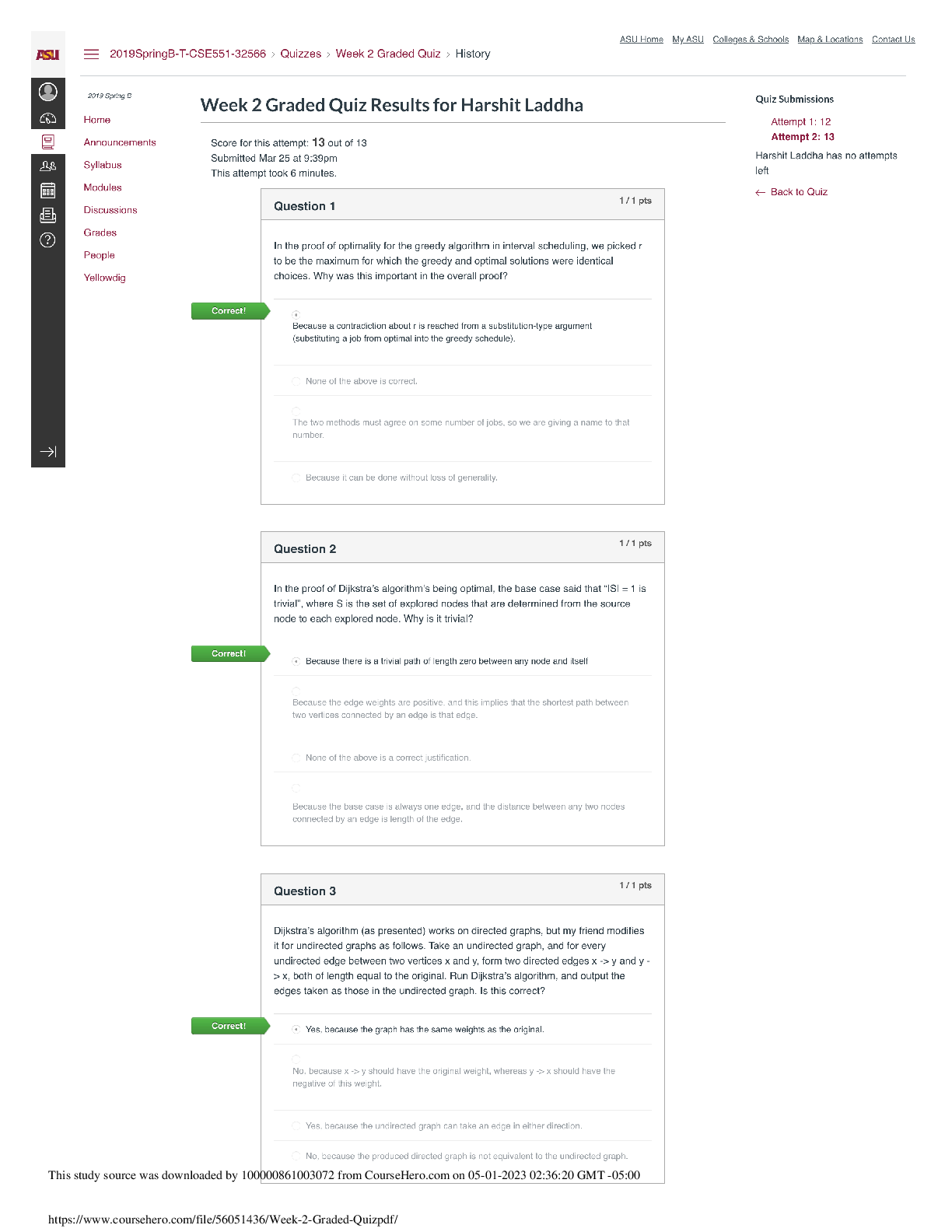
Endterm Closed Book Section - Part 1 Score for this quiz: 40.5 out of 50 Submitted Dec 5 at 5pm This attempt took 52 minutes. Question 1 1.5 / 1.5 pts The adjusted R-squared of a multiple linear ... regression model is not greater than its Rsquared. Correct! True False Question 2 1.5 / 1.5 pts When using the same variable selection criteria, forward stepwise regression and backward stepwise regression always select the same set of predictors. True Correct! False Unit 5.1.4: Forward stepwise regression does not necessarily select the same model as the one selected using backward stepwise regression, especially when p is large. Question 3 1.5 / 1.5 pts Goodness-of-fit assessment for logistic regression with replications involves checking for the independence, constant variance, and normality of the deviance residuals. True Correct! False Unit4.1.1: There is no constant variance assumption in logistic regression. Question 4 1.5 / 1.5 pts When we conduct a goodness-of-fit test for a Poisson regression model, a p-value smaller than a predetermined significance level suggests a good fit. True Correct! False See Unit 4.5.19: The null hypothesis of testing goodness-of-fit for Poisson model is "the model fits data". So we want large p-values to "fail to reject" null hypothesis. Question 5 1.5 / 1.5 pts AIC and BIC are bias-corrected estimators of the prediction risk. Correct! True False Unit 5.1.3: AIC and BIC are bias corrected and commonly used for model selection. Question 6 1.5 / 1.5 pts Forward stepwise selection is more computationally expensive than backward stepwise selection because it takes more iterations to converge. True Correct! False Unit 5.1.3: Backward stepwise is computationally more expensive because it fits larger models. Question 7 1.5 / 1.5 pts You fit a linear regression model using three predictors. You notice the estimated coefficient for predictor X1 is an order of magnitude larger than the estimated coefficient for predictor X2. It is correct to conclude that X1 has a greater effect on the response than X2. True Correct! False We do not know that the variables are on the same scale in order to directly compare them. We can only conclude that a 1-unit change in X1 is associated with a greater change in the response than a 1-unit change in X2 holding other variables constant. Question 8 1.5 / 1.5 pts The optimal value of the penalty constant lambda ( ) in Lasso regression for logistic regression is determined by minimizing the mean squared error (MSE). True Correct! False The criterion used is a choice we make. We minimize the deviance or the classification error in the case of logistic regression. Question 9 1.5 / 1.5 pts In linear regression modeling, Lasso regression requires a numerical algorithm to minimize the penalized sum of least squares. Correct! True False See Unit 5.2.7: The objective function of Lasso Regression is to minimize sum of least squares with penalty. There is no closed form solution for LASSO so LASSO regression does need a numerical algorithm. Question 10 1.5 / 1.5 pts When k is greater than 1 and smaller than n, k-fold cross validation would lead to less variance and more bias in the estimate of the model than leave-one-out cross validation. Correct! True False See Unit 5.2.7: The training fold is more towards the entire training set as K increases. The limit case is Leave-One-Out CV where K = N. Larger K means less bias towards overestimating the true expected error and higher variance in model estimation, so Leave-One-Out CV has more variance and less bias in the estimate of model than Kfold CV when 1<K<N. Question 11 1.5 / 1.5 pts One goal of variable selection is to balance the bias-variance tradeoff when making predictions. Correct! True False True. See Unit 5.1.1 Question 12 1.5 / 1.5 pts A reasonable variable selection method is to fit the full model and then drop all predicting variables with high p-values for the statistical significance hypothesis tests in the full model. True Correct! False Significance should be interpreted conditionally. Correlations between predictors may cause multiple predictors to have high p-values despite at least one being useful to the model. By dropping them all at once, you cannot evaluate how one performs without the others. Question 13 1.5 / 1.5 pts You want to examine the relationship between study time and score on exams. You create five exams and recruit 50 participants. For each participant in your study, you record their study time and grades on each of those five exams. If you were to use all the data you recorded to build a simple linear regression model, you would violate the independence assumption. Correct! True False Because you are collecting 5 observations from each person, the observations coming from the same person would be correlated. Similarly, all observations from the same test may be correlated. Question 14 1.5 / 1.5 pts If we fit a Poisson regression model using a small sample size, the estimators of the regression coefficients may not follow an approximate Normal distribution, affecting the reliability of the statistical inference on the coefficients. Correct! True False True. See Unit 4.2.1. Question 15 1.5 / 1.5 pts If considering BIC as the model selection criterion, a model with lower BIC is preferred over a model with higher BIC. Correct! True False See Unit 5.1.3: A lower BIC corresponds to a lower penalized prediction risk, and the statement specified that is the only thing we are considering. Question 16 1.5 / 1.5 pts Adding more predictors to a multiple linear regression model will always lead to a higher adjusted R-squared. True Correct! False See Unit 3.3.13: Adding more predictors will always lead to higher R-squared, but such increase might not bring increase in prediction power. So we introduce adjusted Rsquared, which penalizes more predictors. If you add some useless predictors in the model, the R-squared will increase but the adjusted R-squared will decrease. Question 17 0 / 1.5 pts In multiple linear regression, logistic regression and poisson regression, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) could be used to estimate model parameters. True You Answered False Multiple linear regression, logistic regression and poisson regression can use maximum likelihood estimation to estimate coefficients. Multiple Choice Questions 18-20 A dataset of the global sales (in million dollars) for 300 different video games has been collected. Features include game type, platform, average user score and average critic score. Using the following R output from a fitted poisson regression model, answer the following multiple-choice questions. Call: glm(formula = sales ~., family = poisson, data = data) Coefficients: Estimate Std.Error z-value Pr(>|z|) (Intercept) 2.59835 0.01324 196.25 <2e-16 *** TypeB -0.18073 0.00373 -13.64 <2e-16 *** TypeC 0.530134 0.00353 39.98 <2e-16 *** user_score 0.156187 0.01564 11.77 <2e-16 *** critic_score 0.281801 0.01425 21.22 <2e-16 *** platform2 0.196426 0.00374 14.78 <2e-16 *** platform3 -0.36389 0.00358 -27.36 <2e-16 *** --- Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1 (Dispersion parameter for poisson family taken to be 1) Null deviance : 170283 on 299 degrees of freedom Residual deviance: 3830 on 293 degrees of freedom AIC: 6535 Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 4 Question 18 0 / 2 pts What is the correct interpretation for the coefficient for the user_score predicting variable? For every 1 point increase in user score, the expected number of global sales (in Million) increases by 0.156187 holding the other variables constant. For every 1 point increase in user score, the log expected number of global sales (in Million) increases by 0.156187 holding the other variables constant. You Answered For every 1 point increase in user score, the expected number of global sales (in Million) increases by a factor of exp(0.156187) holding the other variables constant. A and B B and C See Unit 4.5.17 Question 19 2 / 2 pts What is the correct interpretation for the coefficient for the platform2 predicting variable? If the game change from platform 1 to platform2, the log expected number of global sales (in Million) decreases by 0.196426 holding the other variables constant. Correct! The ratio of expected number of global sales for changing platform from 1 to 2 is exp(0.196426) holding all other variables constant. A and B None of them See Unit 4.5.17 Question 20 2 / 2 pts Which of the following values could possibly be the BIC for this model? 600 6000 6513 Correct! 6557 None of them Question 21 0 / 2 pts Mary has a dataset with height (in inches), weight (in lbs), and math_score (final exam score out of 100) of 300 students in an undergraduate math course. She creates another field called BMI (Body Mass Index) calculated as . She wants to examine if math_score is related to height, weight and BMI. She plans to use a linear regression model to study this relationship. Leonard hears about Mary’s plan and tells Mary that BMI should not be used in her experiment because it is created from the height and weight variables which are already included in the model. He says this leads to an issue called multicollinearity in linear regression. Which of the below options is TRUE? Leonard is right; retaining height, weight, BMI in the model will certainly lead to multicollinearity. Leonard is wrong because BMI is not a linear combination of weight and height. You Answered Leonard is wrong; it is impossible to say whether multicollinearity is a problem in a proposed model without first fitting the model. Leonard is right, but the correct name for this issue is homoscedasticity. See Unit 5.1.1: For multicollinearity to exist, there needs to be linear dependence among the predictors, meaning predictors are linear combinations of the others. There is no linear dependence created by the BMI variable. Question 22 0 / 2 pts Suppose you fit Lasso Regression to a data set with 100 features (X1, X2, … , X100). Now, we rescale X1 by multiplying with 10 while keeping all others variables the same, and then refit Lasso regression with the same regularization parameter Which of the following is correct? . You Answered X1 is more likely to be excluded from the model. X1 is more likely to be included in the model. X1 is equally likely to be included or excluded from the model. I cannot say without more information. See Unit 5.2.7: With larger feature value of X1, the coefficient of X1 will be smaller, thus the penalty will decrease. Hence, X1 is more likely to be kept in the model. Question 23 2 / 2 pts When working to create a logistic regression model, an analyst is considering two models: • Model one includes only one predicting variable A. • Model two includes variable A in addition to predicting variable B. The analyst notices that the sign of the estimated coefficient for A is negative in model one and positive in model two. This is most likely because: A is significant in Model two. B is significant in Model two. A is a controlling variable. Correct! B is correlated with A. Unit 3.3.13: Correlated data B being significant is not enough to explain the change in direction of the relationship between A and the response. Calling A a controlling variable implies that A is not the variable whose effect we are interested in but rather one we may need to control for, which is not implied by the problem description. Question 24 0 / 1.5 pts Which of the following problems can be addressed by Ridge Regression? Select ALL s. High Dimensionality Correct! Multicollinearity Overfitting (Low bias and high variance) You Answered Underfitting (High bias and low variance) See Unit5.2.7 Ridge Regression does not force any to zero, so it does not do model selection. By shrinkage, Ridge Regression can address multicollinearity. Low bias and high variance suggests that a small change of one predicting variable would result in great change of response variable, so shrinking coefficients can make sure that response variable is not overly sensitive to some predictors, thus address problem of low bias and high variance. Question 25 1 / 1.5 pts Which of the following problems can be addressed by Elastic Net Regression? Select ALL s. Correct! High Dimensionality Correct! Multicollinearity Correct! Overfitting (Low bias and high variance) You Answered Underfitting (High bias and low variance) See Unit5.2.7 Lasso Regression does force some ββs to zero, so it can be used for model selection. If there is a group of variables with high correlation, the Lasso tends to select only one variable from the group. So Lasso can also be used for multicollinearity. Lasso Regression penalize complex models and reduce number of variables thus can reduce overfitting. Question 26 1.5 / 1.5 pts Which of the following is correct? Overdispersion is a concern for Poisson regression but not for logistic regression. For both logistic and Poisson regression, the variance of the response equals the expectation of the response given the predicting variables. Correct! Overdispersion affects the reliability of our statistical inferences if not modeled correctly. With overdispersion, the observed variance is smaller than the variance implied by our model. See Unit 4.5.3. Overdispersion means the observed variance is larger than implied by the model. For logistic regression, variance is while the mean would be . Question 27 2 / 2 pts Suppose you are given the following training inputs X =[-3, 5, 4] and Y = [-10, 20, 20] and you fit a simple linear regression model to this data. Which of the following is closest to the Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) estimated coefficient of the slope ? -1.32 Correct! 3.95 0.55 -14.24 See Unit 1.2.4. Question 28 2 / 2 pts Which of the following is true regarding logistic regression? Logistic regression can also be replaced by standard linear regression if there are repetitions. Logistic regression can only be used with continuous predicting variables. Logistic regression can only be used when the response variable is binary. Correct! Logistic regression requires replications for residual analysis See Unit 4.2.3. Logistic regression can be used with binomial data so (c) is false. Logistic regression and standard linear regression do not have the same model form, so they are not interchangeable, even with many successes per observation. Question 29 2 / 2 pts If there are more predictors than the sample size, which of the following options can not be applied? Correct! Backward stepwise regression Forward stepwise regression Ridge regression Lasso regression Unit 5.1.4: Backward stepwise selection cannot be performed when p>n. When p>n, we can still use Lasso regression, but the number of variables selected is limited up to n. Question 30 2 / 2 pts In simple linear regression, what is the relation between the correlation coefficient ρ and R-squared? R-squared = ρ Correct! R-squared = ρ^2 R-squared= ρ + Adjusted R-squared There is no relation between the two See Unit 1.2.4. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 26, 2023
Number of pages
18
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 26, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
97