Instructions for creating the database and more information can be found at the following link: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/11lV5T0ojoq4wKe44ZQnA3vGOpqZXgG1U?usp=sharing **
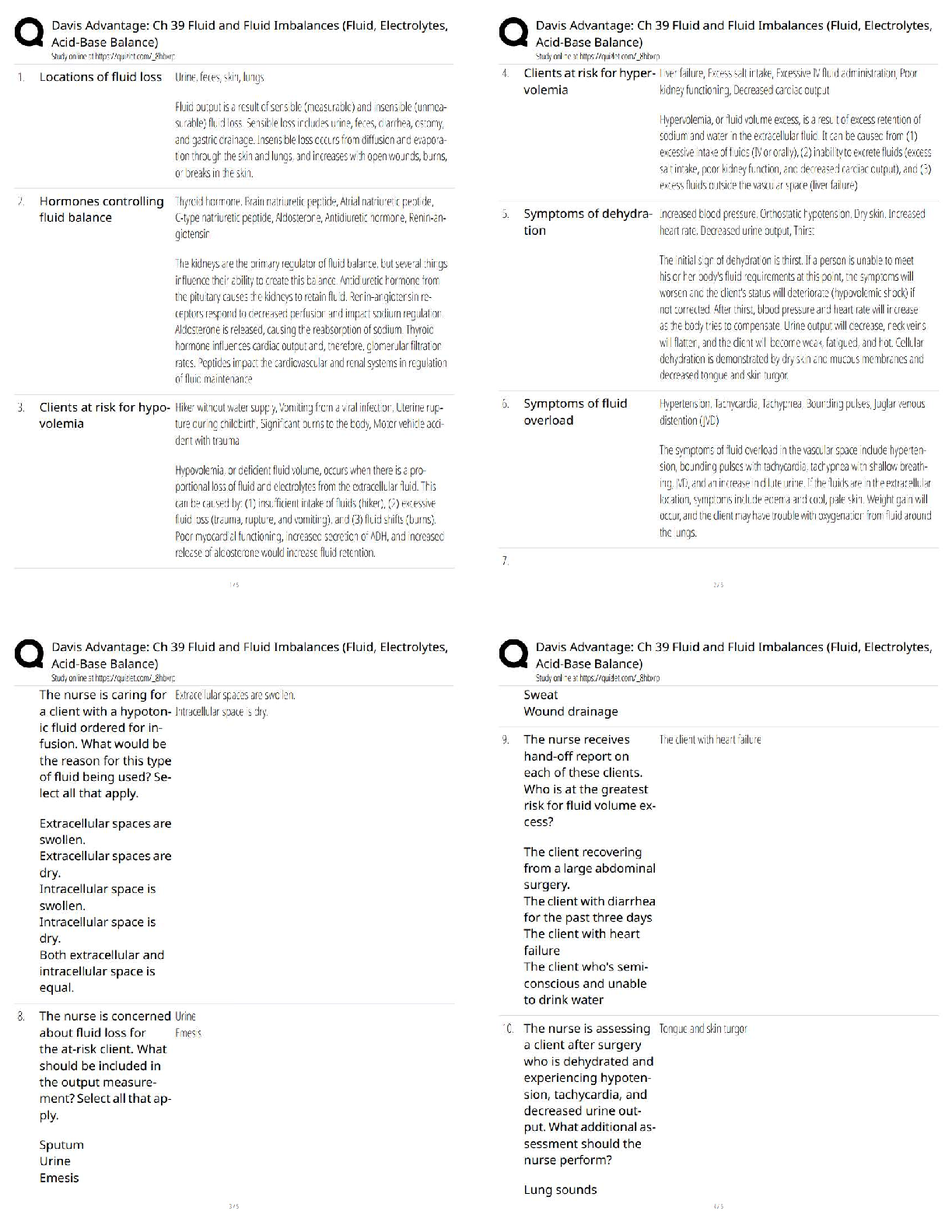
1. Write a SELECT statement that
...
Instructions for creating the database and more information can be found at the following link: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/11lV5T0ojoq4wKe44ZQnA3vGOpqZXgG1U?usp=sharing **
1. Write a SELECT statement that returns one column from the Customers table named
full_name that joins the last_name and first_name columns.
Format this column with the last name, a comma, a space, and the first name like this:
Doe, John
Sort the result set by last name in ascending sequence.
2. Write a SELECT statement that returns these columns from the Products table:
product_name The product_name column
list_price The list_price column
date_added The date_added column
Return only the rows with a list price that's greater than 500 and less than 2000.
Sort the result set in descending sequence by the date_added column.
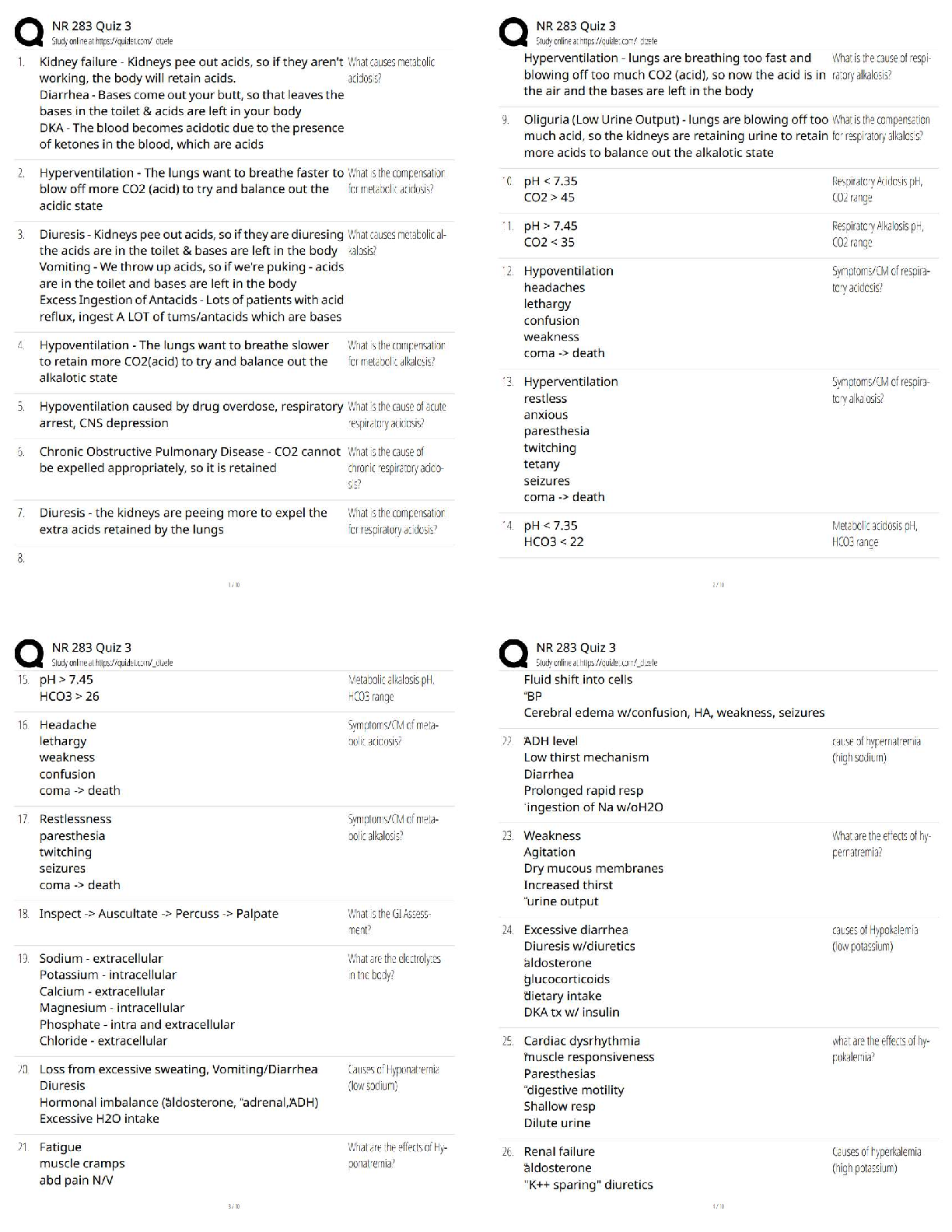
3. Write a SELECT statement that returns these column names and data from the
Products table:
product_name - The product_name column
list_price - The list_price column
discount_percent - The discount_percent column
discount_amount - A column that's calculated from the
previous two columns
discount_price - A column that's calculated from the
previous three columns
Round the discount_amount and discount_price columns to 2 decimal places.
Sort the result set by discount price in descending sequence.
Use the LIMIT clause so the result set contains only the first 5 rows.
4. Write a SELECT statement that returns these column names and data from the
Order_Items table:
item_id The item_id column
item_price The item_price column
discount_amount The discount_amount column
quantity The quantity column
price_total A column that's calculated by multiplying
the item price by the quantity
discount_total A column that's calculated by multiplying
the discount amount by the quantity
item_total A column that's calculated by subtracting
the discount amount from the item price and
then multiplying by the quantity
Only return rows where the item_total is greater than 500.
Sort the result set by item total in descending sequence.
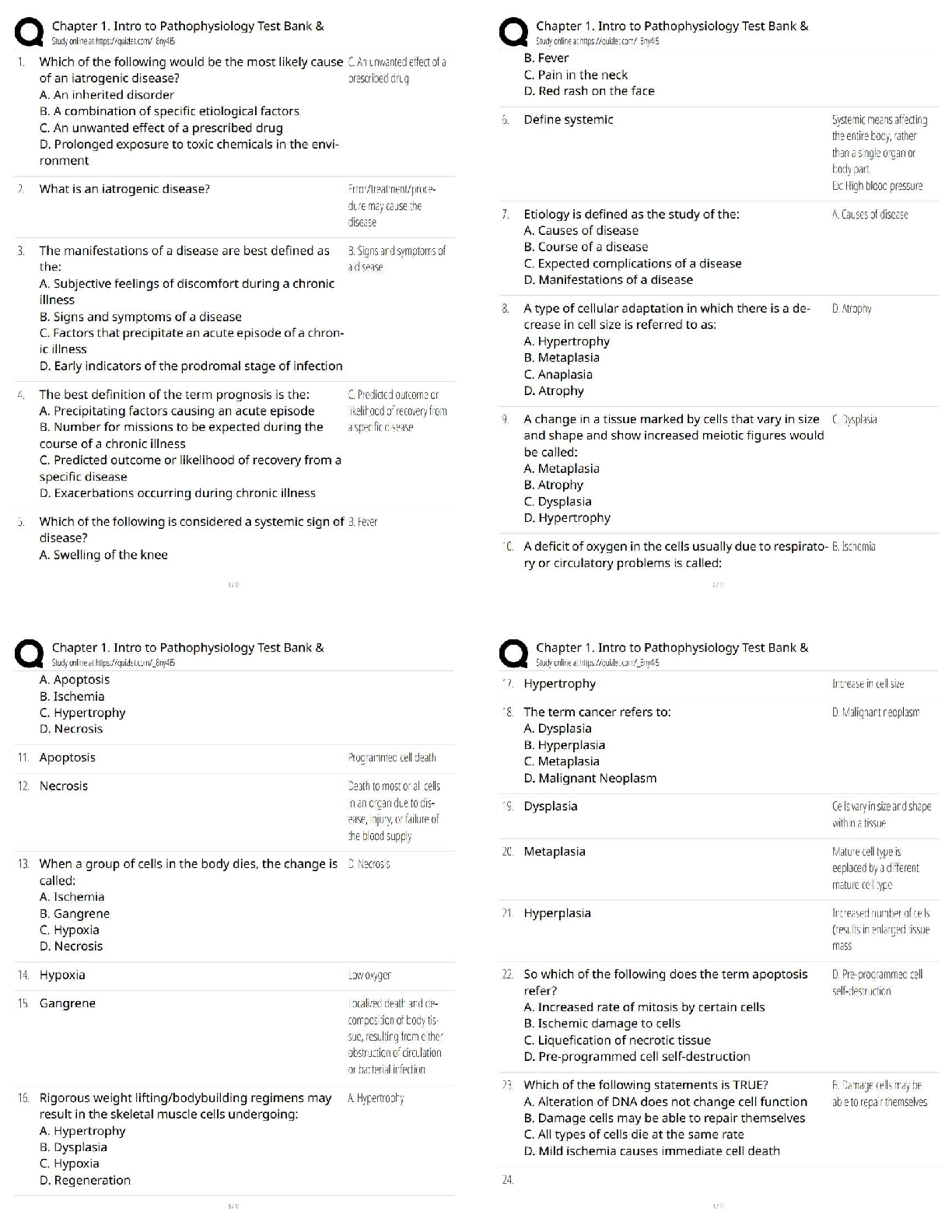
5. Write a SELECT statement that returns these columns from the Orders table:
order_id The order_id column
order_date The order_date column
ship_date The ship_date column
Return only the rows where the ship_date column contains a null value.
6. Write a SELECT statement that joins the Categories table to the Products table and
returns these columns: category_name, product_name, list_price.
7. Write a SELECT statement that joins the Customers table to the Addresses table and
returns these columns: first_name, last_name, line1, city, state, zip_code. NOTE - The WHERE clause is NOT needed for this one.
8. Write a SELECT statement that joins the Customers, Orders, Order_Items, and
Products tables. This statement should return these columns: last_name, first_name,
order_date, product_name, item_price, discount_amount, and quantity.
Sort the final result set by last_name, order_date, and product_name.
9. Write a SELECT statement that returns these two columns:
category_name: The category_name column from the Categories
table
product_id: The product_id column from the Products table
Following each of these, write a SELECT statement that shows the results. Also, please use the MyGuitarShop Database.
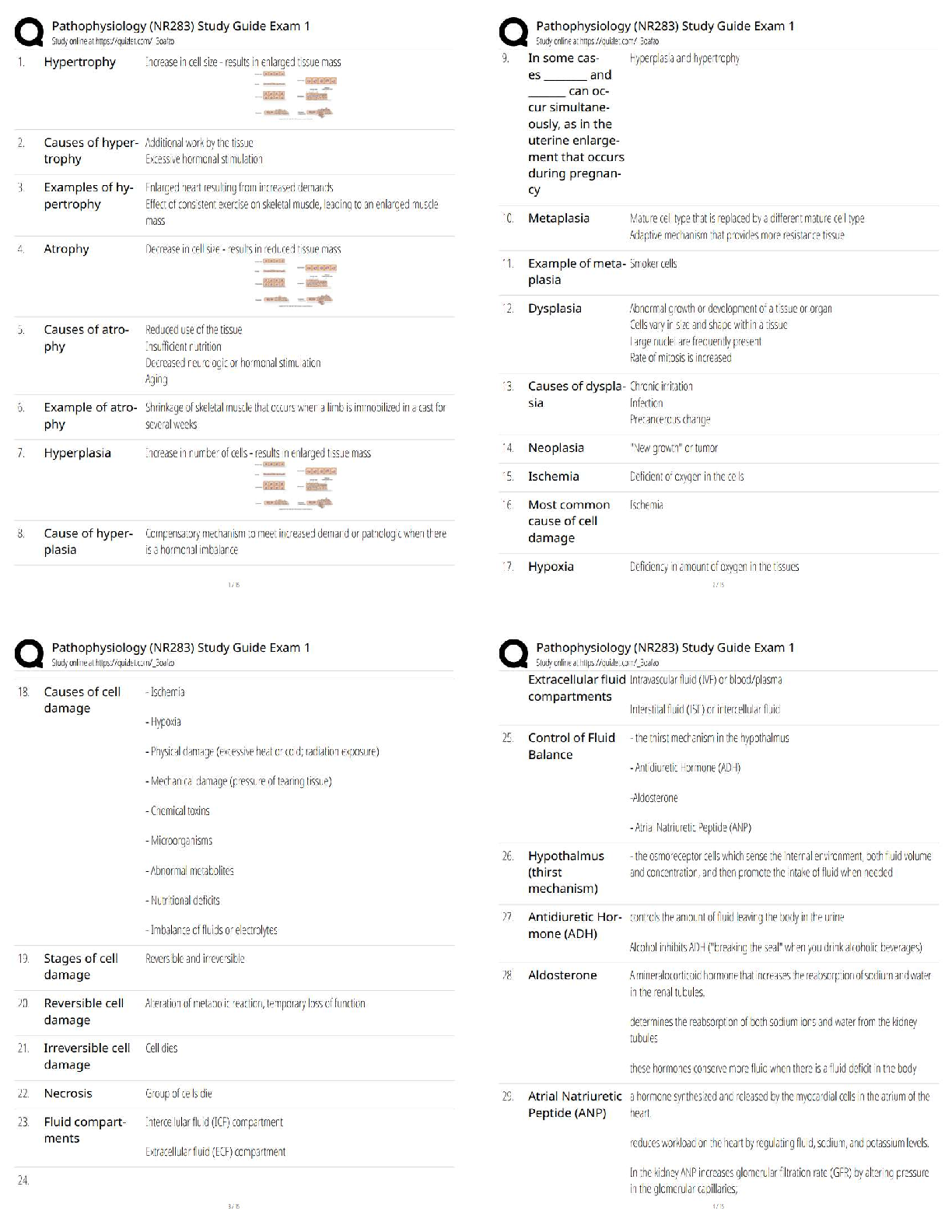
10. Write an INSERT statement that adds this row to the Categories table:
category_name: Brass
Code the INSERT statement so MySQL automatically generates the category_id column.
11. Write an UPDATE statement that modifies the row you just added to the Categories table. This statement should change the category_name column to "Woodwinds", and it should use the category_id column to identify the row. NOTE - Double-check that the correct row is updated.
12. Write a DELETE statement that deletes the row you added to the Categories table in exercise 10. This statement should use the category_id column to identify the row.
13. Write an INSERT statement that adds this row to the Products table:
product_id: The next automatically generated ID
category_id: 4
product_code: dgx_640
product_name: Yamaha DGX 640 88-Key Digital Piano
description: Long description to come.
list_price: 799.99
discount_percent: 0
date_added: Today's date/time.
Use a column list for this statement. NOTE - You could use the NOW() function for the date_added column.
14. Write an UPDATE statement that modifies the product you added in #13. This statement should change the discount_percent column from 0% to 35%. NOTE - Using the discount_percent condition in the WHERE clause may UPDATE more rows than needed.
15. Write a SELECT statement that returns these columns:
The count of the number of orders in the Orders table
The sum of the tax_amount columns in the Orders table
16. Write a SELECT statement that returns three columns: email_address, order_id, and the order total for each customer. To do this, you can group the result set by the email_address and order_id columns. In addition, you must calculate the order total from the columns in the Order_Items table.
17. Write a SELECT statement that returns the name and discount percent of each product that has a unique discount percent. In other words, don't include products that have the same discount percent as another product.
Sort the results by the product_name column.
18. Write a SELECT statement that returns these columns from the Orders table:
The order_id column
The order_date column
A column named approx_ship_date that's calculated by adding 2 days to the order_date column
The ship_date column
A column named days_to_ship that shows the number of days between the order date and the ship date
When you have this working, add a WHERE clause that retrieves just the orders for May 2015.
Computer Science Engineering & Technology MYSQLCS 206
[Show More]