Information Technology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > OSI vs TCPIP, Troubleshooting Methodology CAT Ratings IEEE standards, connector types, commands, (All)
OSI vs TCPIP, Troubleshooting Methodology CAT Ratings IEEE standards, connector types, commands, ports, Top Exam questions and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+
Document Content and Description Below
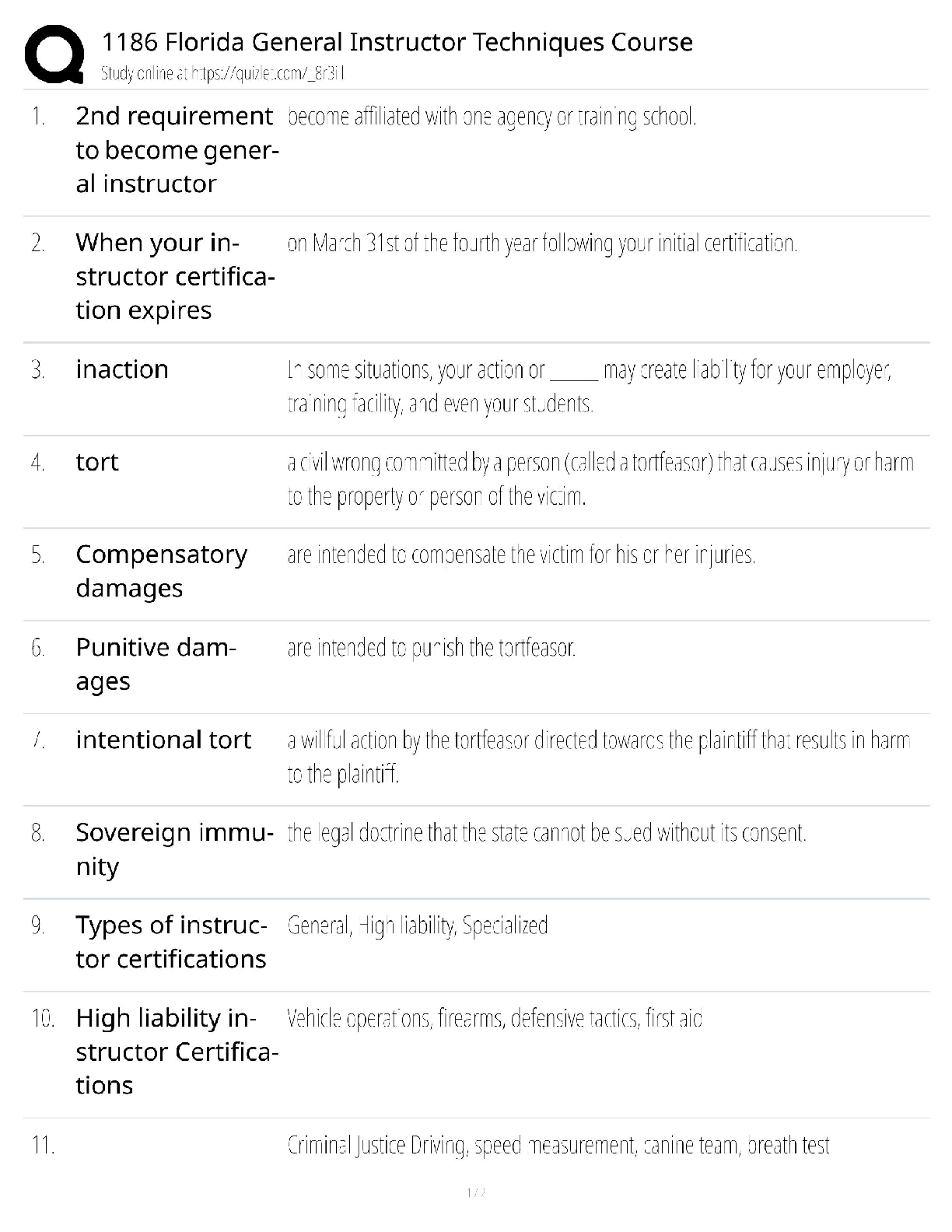
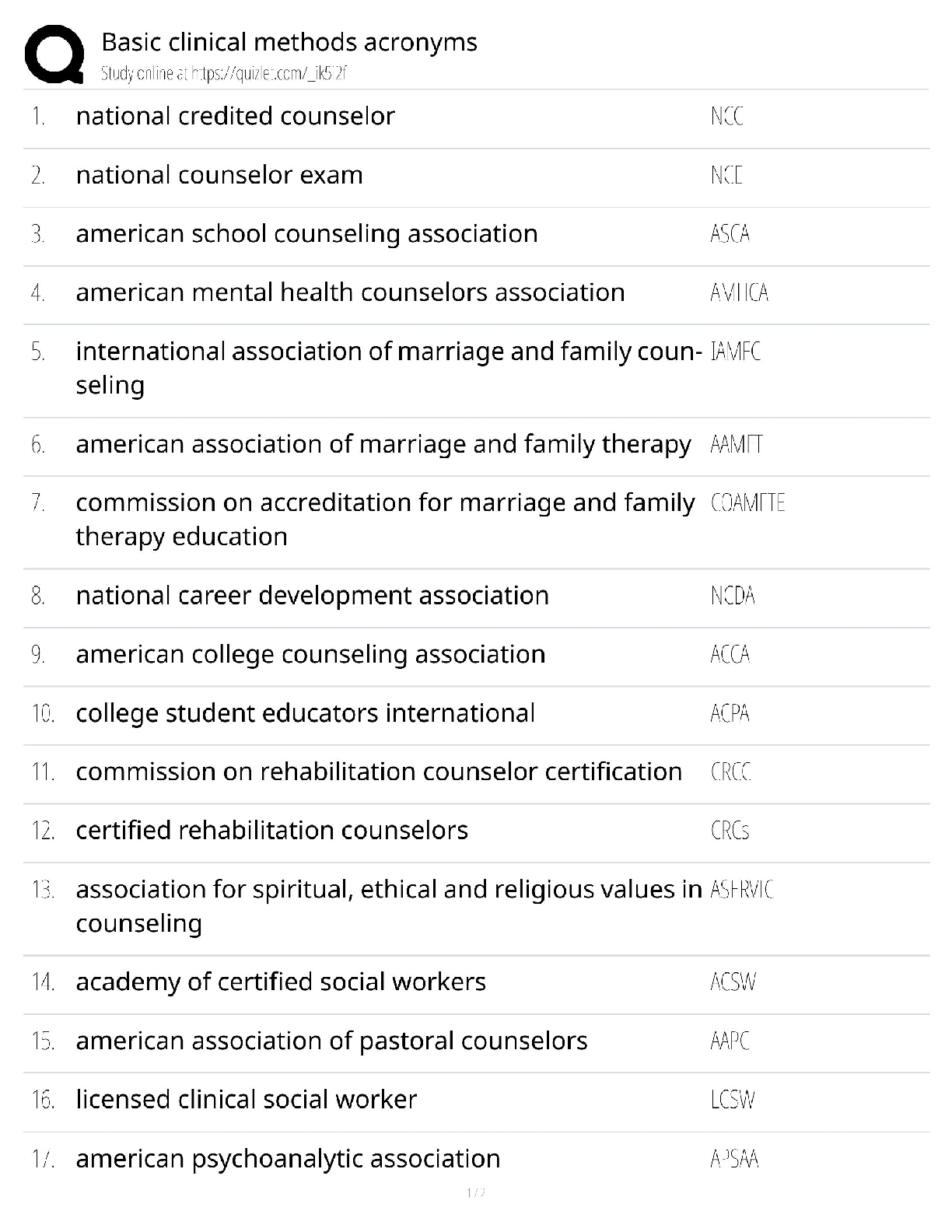
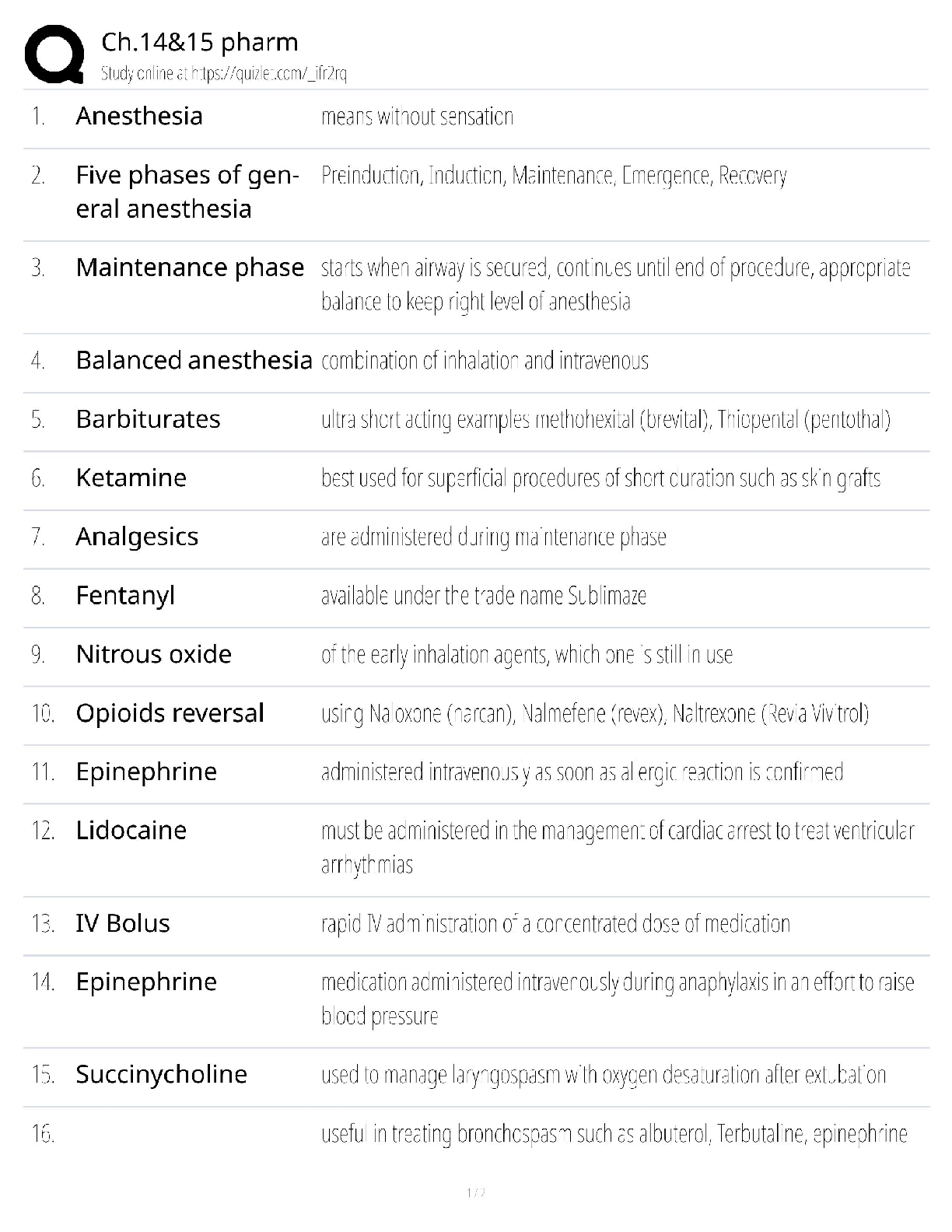
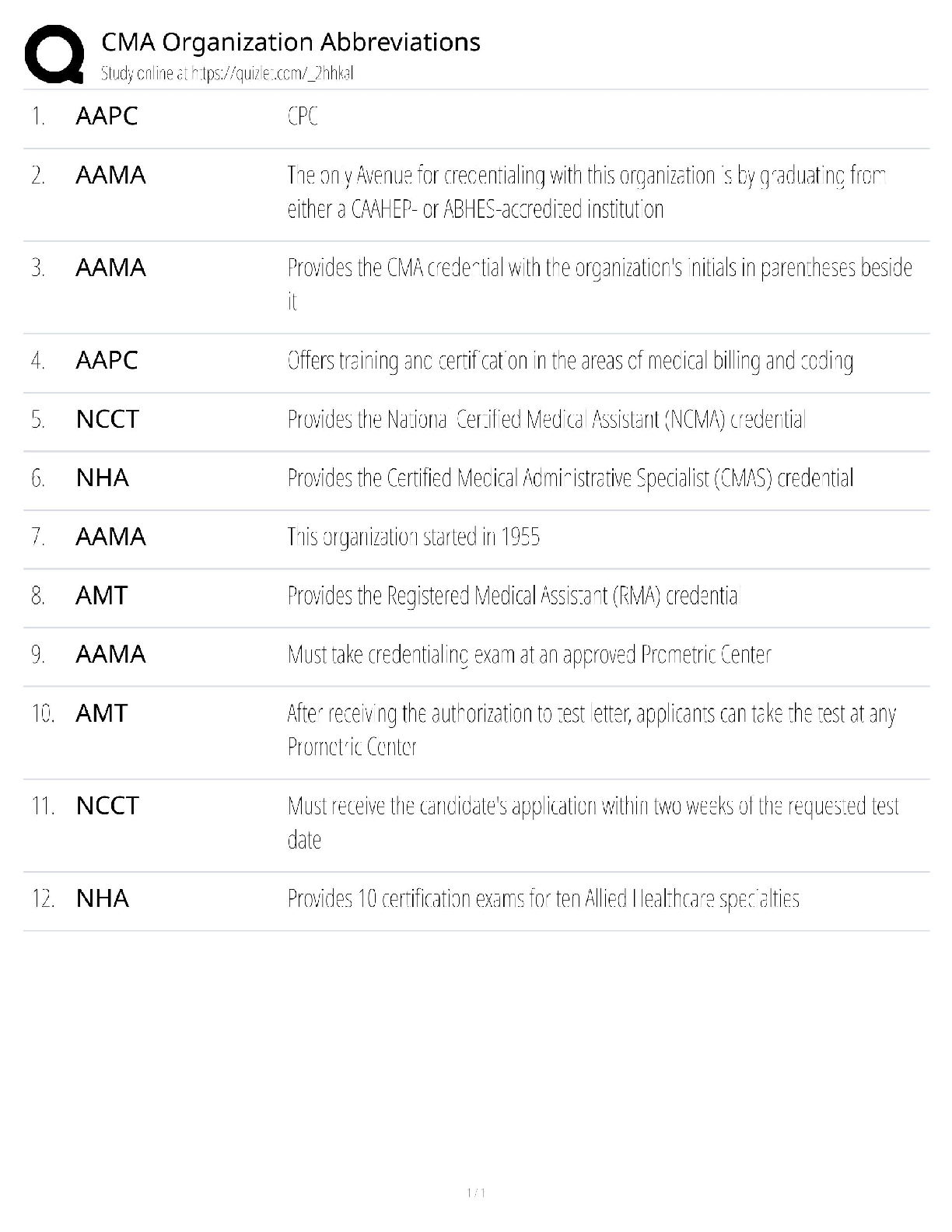
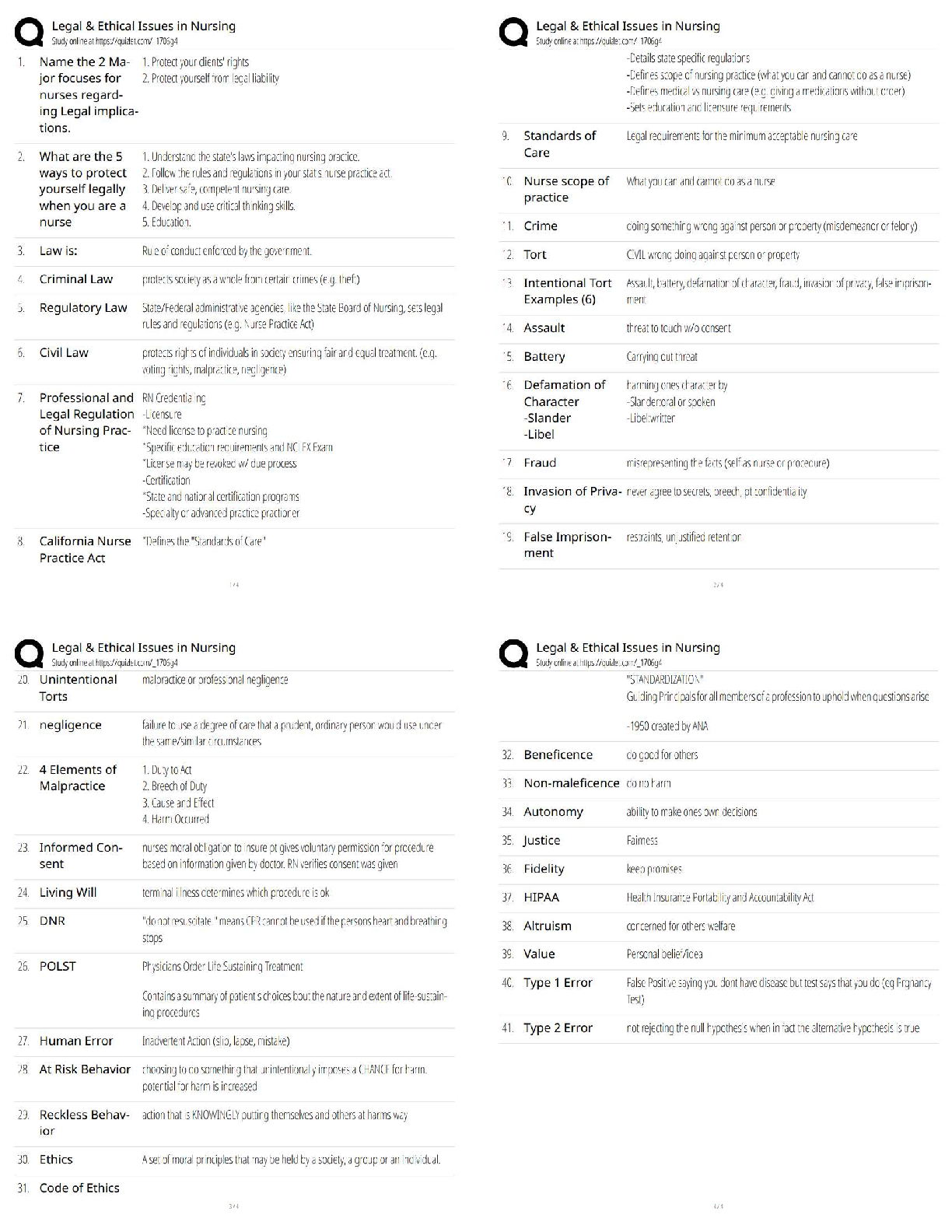
OSI vs TCPIP, Troubleshooting Methodology CAT Ratings IEEE standards, connector types, commands, ports, Top Exam questions and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+ What layer(s) of the OSI Model ... make up the Application layer in the TCP/IP Model? Session, Presentation, and Application What layer(s) of the OSI Model make up the Link in the TCP/IP Model? Physical and Data Link What layer(s) of the OSI Model make up the Transport layer in the TCP/IP Model? Transport What layer(s) of the OSI Model make up the Internet layer in the TCP/IP Model? Network What are the layers of the OSI Model? Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application What are the Layers of the TCP/IP Model? Link, Internet, Transport, Application What is the third step of the troubleshooting methodology? Establish a theory of probable cause What is the fourth step of the troubleshooting methodology? Test the theory to determine cause Put these steps in order: 1. Test the theory to determine cause 2. Establish a plan of action to resolve the problem and identify potential effects. 3. Implement the solution or escalate as necessary. 4. Establish a theory of probable cause 5. Verify full system functionality, and if applicable, implement preventive measures. 6. Identify the problem 7. Document findings, actions, and outcomes. 6, 4, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7 What cat rating and network application does the below describe? Frequency 16MHz Capacity 10 Mbps Max Distance 100m (328ft) Cat 3 and 10BASE-T What cat rating and network application does the below describe? Frequency 100MHz Capacity 100 Mbps Max Distance 100m (328ft) Cat 5 and 100BASE-TX What cat rating and network application does the below describe? Frequency 100MHz Capacity 1 Gbps Max Distance 100m (328ft) Cat 5e and 1000Base-T What cat rating and network application does the below describe? Frequency 250MHz Capacity 1Gbps Max Distance 100m (328ft) and Capacity 10Gbps Max Distance 55m (180ft) Cat 6 and 1000BASE-T or 10GBASE-T What cat rating and network application does the below describe? Frequency 500MHz Capacity 10Gbps Max Distance 100m (328ft) Cat 6A and 10GBASE-T What cat rating and network application does the below describe? Frequency 600MHz Capacity 10Gbps Max Distance 100m (328ft) Cat 7 and 10GBASE-T IEEE 802.___ is a series of standards for Wi-Fi 802.11 IEEE 802.__ standard for the Logical Link Control (LLC) sublayer is used with other 802 protocols, such as 802.3 (Ethernet) and 802.11 (Wi-Fi). 802.2 IEEE 802.__ is based on the Ethernet networking product. This standard specifies protocols that implement the functions of the MAC sublayer, plus signaling and media specifications at the Physical layer. 802.3 802.11___ Year Released: 1999 Frequency: 5Ghz Max Data Rate: 54Mbps 802.11a 802.11___ Year Released: 1999 Frequency: 2.4Ghz Max Data Rate: 11Mbps 802.11b 802.11___ Year Released: 2003 Frequency: 2.4Ghz Max Data Rate: 54Mbps 802.11g 802.11___ Year Released: 2009 Frequency: 2.4Ghz & 5GHz Max Data Rate: 600Mbps 802.11n 802.11___ Year Released: 2014 Frequency: 2.4Ghz & 5GHz Max Data Rate: 1.3Gbps 802.11ac What RG rating is a drop cable for modern Cable Access TV (CATV) and broadband cable modems? RG-6 What RG rating is a drop cable for older CATV/cable modem installs and CCTV network cabling RG-59 Coax cable is usually terminated by using ___ connectors crimped to the ends of the cable. BNC ____ cable is made of two conductors that share the same axis Coax A PC is classed as ___ equipment, as are most data terminals and other devices that interact with users. DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) ___ equipment is defined as those items that provide an interface between DTE equipment and other communications systems or networks (for example, modems). DCE (Data Circuit-terminating Equipment) _____ is used for Ethernet twisted pair cabling. RJ-45 ____connectors are used for telephone systems—for example, to connect a modem to a phone jack. RJ-11 ___ is an early bayonet-style connector that uses a push-and-twist locking mechanism. ST (Straight Tip) ___ is a push/pull design, allowing for simple insertion and removal. It can be used for single- or multimode. It is commonly used for Gigabit Ethernet. SC (Subscriber Connector) ___ is a small-form-factor connector with a tabbed push/pull design. LC (Lucent or Local Connector) ___ is a small-form-factor duplex connector with a snap-in design used for multimode networks. Mechanical Transfer Registered jack (MTRJ [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$6.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 13, 2023
Number of pages
6
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 13, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
100