OB Maternal Newborn ATI Proctored Notes
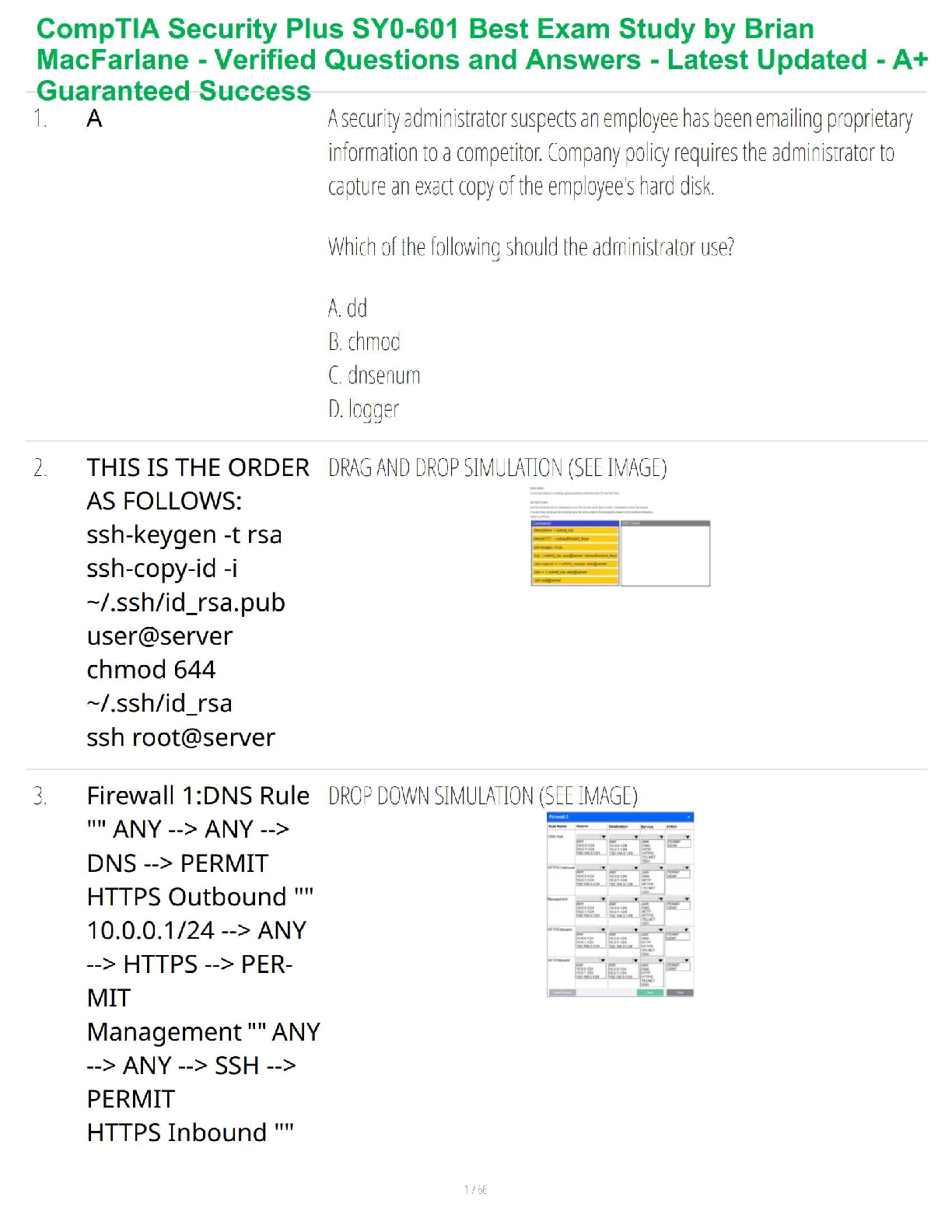
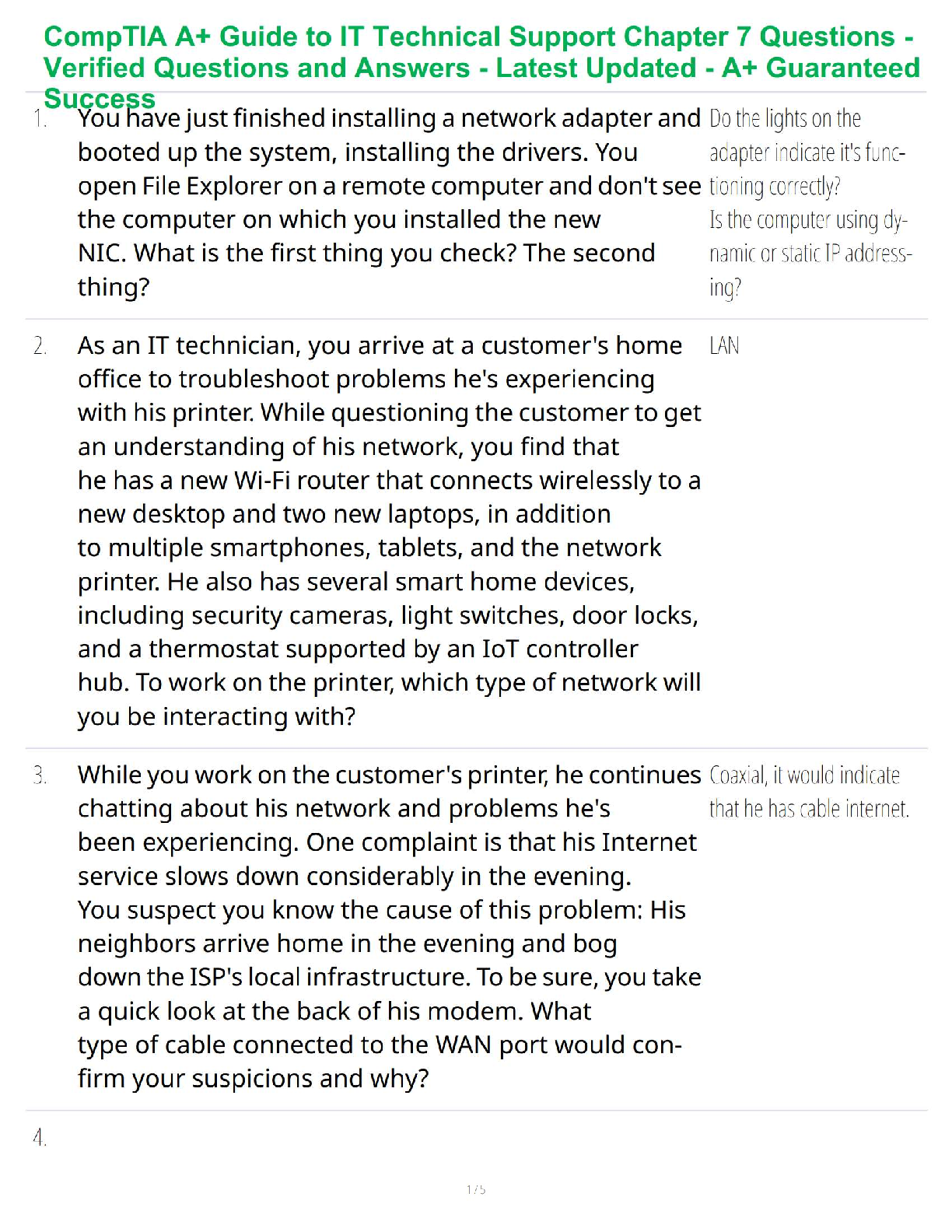
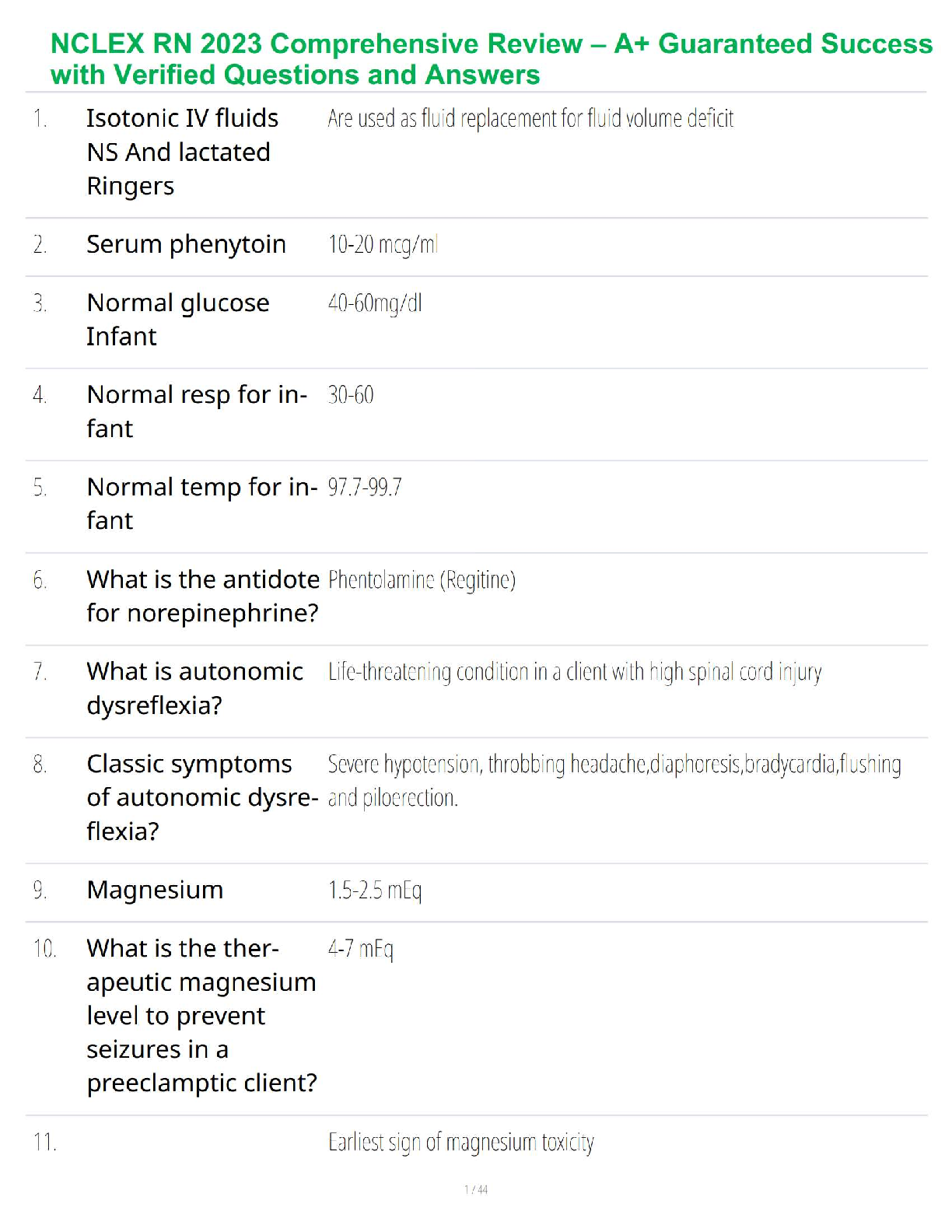
Video #1: Contraception & Infertility
Ø Diaphragms: client must be refitted for a diaphragm for the following conditions:
1.) Its been 2 years since she’s been fitted
2.) G
...
OB Maternal Newborn ATI Proctored Notes
Video #1: Contraception & Infertility
Ø Diaphragms: client must be refitted for a diaphragm for the following conditions:
1.) Its been 2 years since she’s been fitted
2.) Gained more than 15 pounds (7kg)
3.) Had a full term pregnancy
4.) Had a second term abortion
o When you use a diaphragm, you need to use spermicide with every act of coitus
(withdrawal of penis from vagina prior to ejaculation). Every time you withdrawl, instill
more spermicide
o Diaphragm must stay inserted for 6hrs after act of coitus
Ø Hormonal Contraceptives (Oral)
o Side effects: Chest pain, SOB, Leg pain (from a possible clot), headache or eye problems
(from a stroke or hypertension)
o Contraindications: Women with a history of blood clots, stroke, cardiac problems, smoker,
breast or estrogen related cancers (pill contains estrogen)
Ø Depo-Provera/Medroxyprogesterone
o Injectable progestin
o Can cause decreased bone mineral density or loss of calcium
§ Nursing action: Ensure patient has adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D
Ø IUD
o Increase risk for PID
o Can cause uterine perforation or ectopic pregnancy (increases risk for ectopic pregnancy)
o Look out for/Notify PCP:
§ Change in string length à IUD is moving and not in the right place
§ Foul smelling vaginal discharge
§ Pain with intercourse
§ Fever/Chills (infection)
Infertility is defined as an inability to conceive desire engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse for a
prolonged period of time or at least 12 months.
Ø Common factors associated with infertility include:
o Decreased sperm production (Sperm analysis)
o Endometriosis
o Ovulation disorders
o Tubal occlusions à If you test and use DYE (used in the fallopian tubes), make sure the woman
is not allergic to iodine or shellfish/seafood
Video #2: Signs of Pregnancy
Presumptive: Can be defined by things/reasons other than pregnancy
Ø Amenorrhea à Can be anorexic or exercising too much
Ø Fatigue à Didn’t sleep well
Ø Nausea/Vomiting à Sick
Ø Urinary Frequency à UTI
Ø Quickening/Fluttering in stomach à Gas
Probable: Changes that make the examiner suspect a woman is pregnant (primarily related to physical
changes of the uterus).
Ø Abdominal enlargement: Related to changes in uterine size, shape, and position
Ø Hegar’s Sign: Softening and compressibility of the lower uterus Ø Chadwick’s Sign: Deepend violet bluish color of cervix and vaginal mucosa
Ø Goodell’s Sign: Softening of cervical tip
Ø Ballottement: Rebound of unengaged uterus
Ø Braxton Hicks Contractions: False contractions that are painless, irregular, and usually relieved
by walking
Ø Positive Pregnancy Test: Woman’s hormonal level may not be normal
Ø Fetal Outline:
Positive: Very distinct things.
Ø Fetal Heart Sounds
Ø Fetal Heart Beat can be heard
Ø Can see the baby with ultrasound
Ø Can feel movement in the uterus
Naegele’s Rule: LMP – 3 months + 7 days + 1 year
Cathy’s Rule: + 9 months + 1 week
Know how to find out GTPAL numbers
G= Gravidity (# of times a woman has been pregnant PLUS current pregnancy)
T= Term Births (How many baby’s were delievered at term 38 WEEKS OR MORE)
P= Preterm Births (Below 38 weeks)
A= Abortion (spontaneous or not) or miscarriages
L= Living children
Video #3: Weight Gain & Nutrition During Pregnancy AND Diagnostic Tests During Pregnancy
Weight Gain & Nutrition
Ø Normal weight gain = 25- 35 pounds
Ø Overweight person weight gain = 15- 25 pounds
Ø Underweight person weight gain = 28-40 pounds
Ø During 1st trimester à A woman should only gain 1-2 kg (2-4 pounds); A woman should not gain
1 pound per week.
Ø During 2nd trimester à 1 pound per week is normal; increase caloric intake by 340 calories per
day
Ø During 3rd trimester à 1 pound per week is normal ; increase caloric intake by 450 calories per
day
Ø If you are breastfeeding after pregnancy à You still need to eat an extra 300-400 calories per
day
Ø Intake of FOLIC ACID à Helps prevent Neural Tube Defects (NTD) à Sources: dark green leafy
veggies; orange juice
Ø Women should increase their fluid intake to 2-3L per day
Ø Women should limit their caffeine intake to à 300 mg per day
Ø No amount of alcohol is okay
Diagnostic Tests During Pregnancy
Noninvasive = Full Bladder
Invasive = Empty Bladder
Ultrasound à Bladder should be full to help sound waves resonate better
Amniocentesis à Bladder should be empty Biophysical Profile (BPP): Scored from 0-10
Ø Score between 8-10 à Healthy Baby
Ø Tests Measures 5 things
o Reactive HR (0/2)
o Breathing (0/2)
o Body Movement (0/2)
o Fetal Tone (0/2)
o Amniotic Fluid Volume (0/2)
Non-Stress Test (NST)
Ø Non-invasive
Ø Measures fetal well being within the last trimester of pregnancy
Ø Measures response of FHR to Fetal Movement
o Reactive: FHR accelerates during movement (normal; positive)
o Nonreactive: No accelerations during movement (not normal; negative)
§ If non-reactive, the DR will perform another test called: Contraction Stress
Test (CST) or a BPP
Video #4: Diagnostic Tests
Contraction Stress Test (CST)
Ø Induce contraction with administration of Pitocin/oxytocin or nipple stimulation
Ø During the contraction, monitor FHR for late decelerations
Ø Negative CST Response (no late decels; which is what you want)
Ø Positive CST (late decels happen; not a good thing)
Ø Risk
o Can send woman into PTL
Amniocentesis
Ø You want an empty bladder b/c you will poke into amniotic sac to test for genetic
abnormalities (levels of AFP aka alphafeto-protein)
o High AFP = NTD
o Low AFP = Chromosomal disorders such as down syndrome
Ø LS Ratio (Lecithin Sphingomyelin) à tests for fetal lung maturity
o Ratio of 2:1 = fetal lung maturity
o Ratio of 2.5:1 or 3:1 = fetal lung maturity for client with DM
Ø Done around 14 weeks
Ø Risks/Complications
o Amniotic Fluid Emboli (AFE)
o Hemorrhaging
o Infection
o Leaking of AF
o ROM
o Miscarriage
Chorionic Villus Samping (CVS) à Alternative to Amniocentesis
Ø Can be done between 10-12 weeks
Ø Also tests for genetic abnormalities by testing the placenta instead of the amniotic fluid
Ø Advantage à Can be done earlier
Bleeding and Complications During PregnancyVideo #5
Ø Ectopic Pregnancy à Ovum is planted outside of the uterus, often in the fallopian tube.
Need to know the symptom of unilateral stabbing pain in the lower abdominal quadrant
o If it burst the fallopian tube, it can be life threatening to the mom
Ø Gestational Trophoblasic Disease (GTD) à the proliferation and degeneration of trophoblastic
billi in the placenta that becomes swollen, fluid-filled, and takes on the appearance of grape-like
clusters or prune juice.
Ø Placenta Previa à Placenta previa occurs when the placenta abnormally implants in the lower
segment of the uterus near or over the cervical os instead of attaching to the fundus. PAINLESS
BRIGHT RED VAGINAL BLLEDING during the 2nd or 3rd trimester
o Very dangerous à May hemorrhage and may need to give blood
o Complete or Total: Cervix is completely covered by placental attachment
o Incomplete or Partial: Partially covered by the placental attachment
o Marginal or low-lying
Ø Abruptio Placenta: the premature separation of the placenta from the uterus, which can be a
partial or complete detachment.
o Sudden onset of intense localized uterine pain with dark, red, vaginal bleeding.
o Clinical Findings: Hypovolemic shock
Ø Yeast Infections are very common for pregnant woman
o Signs/Symptoms:
§ Cottage cheese discharge
§ Vulvar redness
§ White patches on vaginal wall
Ø Incompetent Cervix: Recurrent premature dilation of the dilation of the cervix or cervical
insufficiency (basically the cervix cant stay closed and will lead to a spontaneous abortion if not
taken care of). If woman has incompetent cervix, she will get a cerclage to help keep cervix closed
and from dilating and is removed at 37 weeks of gestation or when spontaneous labor occurs
Ø Hyperemesis Gravidarum à Nausea and vomiting that goes past 12 weeks. End up having
weight loss & electrolyte imbalances & dehydration.
o Nursing Interventions: IV Fluids, administration of B6, antiemetic medication
(Reglan or Zofran)
Video #6: Medical Conditions
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Ø Provider will prescribe FE supplements à Take FE Supplement that is rich in Vitamin C (i.e
orange juice)
Gestational Diabetes (GDM)
Ø If a patient has GDM during pregnancy, it increases her risk of developing DM after her pregnancy
Ø Poses risk to the fetus. Provider may want to do BPP or NST to monitor for complications
Ø Most oral anti-diabetic meds are contraindicated for pregnancy so woman will have to use insulin
to monitor sugar levels
Ø When to test: 24 – 28 weeks of gestation
o Start with 1 hour glucose tolerance test
§ No fasting required
§ Give pt 50g of oral glucose, then 1 hr later, test glucose levels
§ Positive screen of 130-140mg/dl or greater indicates need for additional testing (3
Hr OGTT)
o 3 Hr OGTT
§ Requires fasting
§ Avoid caffeine and smoking§ Will take fasting glucose level, then will be given 100g of glucose and will test
glucose at 1hr, 2hrs, and 3hrs
Gestational Hypertension (GHTN) à Caused by vasospasm contributing to poor tissue perfusion
Ø Spectrum of GHTN
o GHTN à after 20th week of pregnancy, if a woman has a BP over 140/90 recorded at least
twice, 4-6 hrs apart within a one week period of time, the patient is POSITIVE for GHTN.
There is NO PROTEIN in urine.
o Mild Preeclampsia
§ GHTN (BP 140/90)
§ Proteinuria (Level 1+)
§ Edema may not be present ATM
o Severe Preeclampsia
§ BP >/=160/100 + Proteinuria (Level 3+)
§ Creatinine levels will begin to rise and will be >1.2
§ May experience headache/blurred vision/hyperreflexia/peripheral
edema/Epigastric pain
o Eclampsia
§ Severe Preeclampsia + Seizures
o HELLP
§ Hemolysis: resulting in anemia and jaundice
§ Elevated Liver Enzymes: ALT & AST Levels will be high
• Manifestations: Epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting
§ Low Platelets: Platelet count <100k
• Manifestations
o Thrombocytopenia
o Abnormal bleeding and clotting time
o Bleeding gums
o Petechiae
o Possibly disseminated intravascular coagulopathy
Medications
Ø Antihypertensives
o Methyldopa
o Nifedipine
o Hydralazine
o Labetalol
o ** AVOID ACE inhibitors and ARBS
Ø Anticonvulsants
o Magnesium sulfate
§ Monitor patient for magnesium toxicity
§ S/s à No reflexes, reduces DTR, low urine output, RR low, LOC low, dysrhythmias
§ Antidote: Calcium Gluconate
Video #7: Early Onset of Labor
PTL
Ø Contractions or cervical changes that happen between 20-37 weeks. After 37 weeks, it will be
considered Full Term Labor
Ø May do a vaginal swab to check the fetal fibronectin to see if she is in PTL
o May administer Nifedipine (Calcium Channel Blocker) à Will relax muscles by suppressing
contractions by blocking calcium being transported to smooth muscles
o May administer Magnesium (check for toxicity) à relax smooth muscles of uterus o May administer Indomethacin à NSAID which inhibits prostaglandins à inhibits
prostaglandins à suppresses UCs
o May administer betamethasone à Steroid à Help promote fetal lung maturity
PROM
Ø Major cause of infection (especially if more than 24 hours goes by from when the
membrane ruptured and the time the baby is born)
o If membrane ruptures DR will order a Nitrazine paper test à Paper turns blue (pH
6.5-7.5)
o Positive ferning test can also indicate rupture of membrane
o If membrane does rupture, pt will be put on an antibiotic, betamethasone (develop
baby’s lungs)
o
Physiological Changes Preceding Labor
Ø Backache
Ø Weight Loss
Ø Lightening (Fetal head drops into the true pelvis)
Ø Contractions (True, not Braxton hicks)
Ø Bloody show
Ø Energy burst right before labor
Ø GI Changes (nausea, vomiting, indigestion)
Ø Rupture of membranes (check with nitrazine paper)
Tests Done
Ø Group B Strep
Ø Urinalysis (Protein, infection)
4 Stages of labor
Ø 1st à Onset of labor until complete dilation of cervix (10 cm)
o Has 3 phases
§ Latent
• 0-3 cm dilation
o Mother is talkative & eager
§ Active
• >3-7cm
o Mother is restless, anxious, and may feel helpless
§ Transition
• >7cm-10cm
o Mother is experiencing a lot of pain, has urge to push and may
feel like she is having a bowel movement (increased rectal
pressure)
Ø 2nd à Full dilation of cervix to birth of the baby
Ø 3rd à Birth of baby to delivery of placenta
Ø 4th à Delivery of placenta until mothers vitals are stable
Video #8 Pain Management & FHR Monitoring
Non-pharmacological methods
Ø Aromatherapy
Ø Imagery
Ø Music
Ø Effleurage: light, gentle circular stroking of the client’s abdomen with the fingertips in rhythm
with breathing during contractions Ø Sacral Counter-pressure: Consistent pressure is applied by the support person using the heel of
the hand or fist against the client’s sacral area to counteract pain in the lower back
Pharmacological Methods (Sedative & Opioid analgesics)
Sedative à puts baby at risk for respiratory depression
Opioid Analgesic à puts mom at risk for sedation, hypotension, and increased variability in FHR
Epidural Analgesia à Provides lack of sensation at level of the umbilicus to the thighs.
Ø Needs to be dilated at least 4cm or above
Ø Side effects include: maternal hypotension and fetal bradycardia.
Ø Nursing Interventions à Give IV Bolus to counteract hypotension; want to avoid supine
hypotension syndrome (avoid this by placing pt on her side and not on her back)
Spinal Block: provides lack of sensation from the nipples to the feet. Given for C-Sections.
Ø Side effects include: maternal hypotension and fetal bradycardia, potential headache from
leakage of CSF, and increase incidence of bladder and uterine atony.
Ø Nursing Interventions à Give IV Bolus to counteract hypotension; want to avoid supine
hypotension syndrome (avoid this by placing pt on her side and not on her back)
FHR Monitoring (VEAL à CHOP)
Ø 110-160 FHR BPM is normal
Ø Want variability (moderate), accelerations are okay
Ø Variable Deceleration à Cord Compression
o Interventions
§ Reposition client to side or knee chest position
§ D/c Pitocin
§ Administer O2
Ø Early decelerations are okay (Compression of fetal head during contraction)
Ø Late Decelerations à uteroplacental insufficiency (lack of fetal O2)
o Interventions
§ Assist mom to side laying position
§ Increase IV Fluids
§ Stop pitocin
§ Administer O2
§ Notify PCP
Ø DO NOT want late and variable decelerations.
Ø Fetal bradycardia may be r/t epidural or placental insufficiency (d/c oxytocin, put pt on side and
provide more O2 and notify PCP).
Ø Fetal Tachycardia à may indicate maternal infection. Give antipyretics and O2.
Ø (Prolapsed) Umbilical Cord Compression à Presenting part of the fetus head is crushing the
umbilical
o Interventions
§ Notify PCP and get help
§ Use steril gloved hand, insert 2 fingers into vagina and lift baby head off the cord to
stop compression
§ Reposition client to knee chest, or trendelenberg
§ Use a warm saline soaked sterile towel to ensure cord does not dry up
Ø Rhogam à administer within 72 hrs within giving birth if the mother is Rh- and the baby is Rh+
to prevent issues with their next pregnancy
Ø Fundal Height àImmediately after the deliver, the fundus should be firm and midline with the
umbilicus and approximately at the level of the umbilicus. At 12 hours post-partum it may go 1cm
above the umbilicus. Every 24 hrs after that, it should descend about 1-2cm. By 6th post partum
day, it should be halfway between the umbilicus and the symphysis pubis. By day 10, you should
not be able to palpate uterus. Video #9: Lochia à Discharge after women gives birth
3 types of Lochia
Ø Lochia Rubra à bright red bleeding; odor and may have clots (days 1-3 after women gives birth)
fleshy
o Bleeding should not be excessive; 1 saturated pad w/in 15 mins = excessive NOT OK
o Should not extend past 3 days. If it does, atony becomes a concern
Ø Lochia Serosa àSerosanguineous consistency + pinkish brown in color (day 4-10)
Ø Lochia Alba à Yellowish, white-creamy color with a fleshy odor. (day 11-6 weeks post partum)
Management After Birth
Ø Ice baths in the perineum area
Ø Sitz bath
Ø After birth; 2-3 days milk will come in. Before milk comes in, colostrum is what is being excreted
(thicker and yellow consistency. High fat content with antibiotics)
Ø Average blood loss during vaginal birth = 500ml
Ø Average blood loss for a c-section =1000ml
Uterine Atony à If woman is retaining urine, her bladder will be distended which will displace her
uterus.
Ø Intervention
o Have woman empty her bladder
Video #10: Baby Friendly Care
3 phases
Ø Dependent: Taking in phase
o First 24-48 hrs after birth
o Mom is eager to talk about birth experience
o Relies on others for assistance
Ø Dependent-Independent: Taking hold phase
o Day 2-3 and goes up to a few weeks
o Mother is focused on baby care
o Practicing skills and learning how to take care of baby
Ø Independent: Letting Go
o Its not all about how to take care of the baby
o Mother resumes her roles as a partner, individual, returns to work, etc
Discharge Teaching à Breast Engorgement & Post Partum Disorders
Ø Milk comes in 2-3 days after giving birth
o Breast Engorgement is common
§ Cold compress between feedings, warm shower prior to feeding to help with
circulation
§ Cold fresh cabbage leaves on the breast
§ Mild analgesics
o If she is not going to breast feed, do not promote milk flow
§ Cold compress, and tight bras are the interventions
Post-Partum Disorders
Ø Higher risk of getting DVT
Ø Pulmonary Embolism may occur à S/s à Chest pain, difficulty breathingØ PPH àDifferent types of lochia (COCA)
o Lochia rubra lasting longer
§ Culprit = uterine atony or retaining placental fragments
• Make sure bladder is empty
• Monitor pads and saturation
• If shes losing a lot of blood she will have tachycardia and hypotension
• Make sure to massage the fundus
o Medications used for PPH
§ Oxytocin/Pitocin (help contract uterus)
§ Methylergonovin à Methergine
§ Misoprostol à Cytotec
Ø Mastitis à infection of the breast
o S/S
§ Painful or tender localized hard mass
§ Reddened area on one breast
§ Flulike symptoms (chills/fatigue)
o Interventions to Prevent Mastitis
§ Wash hands prior to breast feeding
§ Keep breast nice and clean
§ Allow nipples to air dry
§ Make sure baby is taking in the entire nipple and areola into their mouth
§ Empty breast with each feeding
Video #11: Post Partum Depression Vs. Post Partum Blues & Newborn Assessment
Post Partum Blues
Ø Very common, can last up to 10 days (if extends over 10 days or symptoms get more severe,
assess for PPD)
Ø S/S
o Tearfulness
o Insomnia
o Lack of appetite
o Feeling of letdown
Post Partum Depression
Ø Occurs w/in 6 months of delivery and includes persistent feelings of sadness and intense
mood swings (10% of new moms)
Post Partum Psychosis
Ø Common with moms with h/x of bipolar disease
Ø S/S
o Disorientation
o Hallucination
o Obsessive behaviors
o Paranoia
Newborn Assessment (APGAR)
Ø 7-10 = No Distress
Ø 4-6 = Moderate Distress
Ø Under 4 = Severe Distress
Ø Score is based on 5 areas
o HR (0/1/2)
o RR (0/1/2)o Muscle Tone (0/1/2)
o Reflex Irritability (0/1/2)
o Color (0/1/2)
Video #12: New Ballard Scale
Ø Neuromuscular Maturity
o Full Term = Well Flexed
Ø Physical Maturity
o Preterm
§ Skin: Thinner/Transparent skin, may be sticky
• Lanugo
§ No plantar creases
§ No breast tissue/ not well developed
§ Boys àFlat/ Smooth scrotum
§ Female à prominent clitoris and flat labia
o Full Term
§ Skin: Thicker
• No lanugo
§ Plantar creases
§ Will have breast tissue (5-10mm in width)
§ Boys à Pendulum/Rugae scrotom
§ Girls à Labia will be more developed and will encompass clitoris
o Post-mature
§ Skin: Wrinkled, crack, leathery appearance
Ø Normal Deviations in Newborns
o Milia = small raised white spots on the nose or chin à will go away w/o treatment
o Mongolian Spots = bluish purple spots on their back or bottom
o Head = 2-3 cm larger than chest circumference; chest should be barraled shapped
§ Should have anterior and posterior fontanel; should be soft and flat
• Anterior = diamond shape, 5 cm in size
• Posterior= smaller in size, triangular shape
• If fontanel is bulging, it is NOT NORMAL
• Sunken is NOT NORMAL
§ Kaput Succidam & Cephalohematoma will resolve on their own
o Eyes = Blue or grey at birth; true eye color established in 3-5 months
o Ears = low set à may indicate down syndrome
o Epstein’s Pearls à small white cysts found at the gums and junctions of the soft and
hard pallets
§ Grey white patches on the tongue and gums IS NOT NORMAL. May be infection
Video #13: Reflexes (pg 159)
Ø Sucking & Rooting à Birth to 3-4 months but can last up to a year.
Ø Palmar Grasp à Birth to 6 months
Ø Plantar Grasp à Birth to 8 months
Ø Moro Reflex à Birth to 6 months
Ø Tonic Neck Reflex à Birth to 3-4 months
Ø Babinski Reflex à Birth to 1 year
Ø Stepping à Birth to 4 weeks Must keep baby warm. Baby can lose heat in 4 different mechanisms
Ø Conduction: Direct contact with a cooler surface
Ø Convection: Lose heat from cooler, environmental air (i.e fan)
Ø Evaporation: Lose surface liquid through vapor
Ø Radiation: Loss of heat from the body surface to another surface that is close by (window or
air conditioner)
Side Notes
Meconium should be passed within 24 hours after birth.
Prophylactic eye care à Erythromycin to prevent eye infection from chlamydia or gonorrhea
Vitamin K à Needed to prevent hemorrhaging given until they can produce their own
HEPB Vaccine is given at birth (immediately)
Be on lookout for hypoglycemia (S/s à jitteriness, twitching, high pitched cry, irregular
respirations, lethargy, cyanosis, eye rolling, seizures, blood glucose lvl will be under 40 mg/dl)
Video #14: Newborn Nutrition
Ø May lose 5-10% of body weight right after birth but should regain weight within 10-14 days
after they are born
Ø Breastfeeding is highly advised à reduces risk of infection, helps with brain growth, is
inexpensive and convenient, reduces instances of SIDS
o For the first 6 months of life, babies only need milk
o First food that is introduced (6 mo of age) FE fortified cereal (rice)
§ Do not introduce solids until 6 mo of age
o Breastfeeding is encouraged right after birth to begin breastfeeding
§ Can expect uterine cramps while breastfeeding (release of Pitocin; will help uterus
contract and reduce incidences of uterine atony)
§ Breastfeed 15-20 mins per breast
§ Empty the breast
§ Best indicator that baby is eating well
• Voiding 6-8 diapers per day
§ How to store breastmilk and formula
• Breastmilk
o Stored at Room temp under clean conditions up to 8 hrs
o Refrigerated in sterile bottles for 8 days
o Frozen for up to 6 months
o Deep freezer = 12 months
o Thawing milk à Thaw in fridge for 24 hrs (DO NOT MICROWAVE OR
REFREEZE)
§ Use portions of breast milk must be discarded. DO NO REUSE
§ How to store Formula
• Can be stored in fridge up to 48 hrs
• Discard any unused portion just like you would breast milk
Ø Always put baby to sleep on their back to reduce chances of SIDS
Ø Cord Care & Circumcision Care
o Umbilical Cord
§ Keep dry & above diaper
§ Sponge baths only until cord falls off (10-14 days after birth)
§ Monitor cord and make sure it is not moist, red, or house foul odor or purulent
drainage o Circumcision care
§ Clamp procedure
• Apply petroleum jelly with each diaper to prevent diaper from sticking to
penis
• Tub bath is not to be given until circumcision is completely healed
• Yellow film of mucus will form over glands by day 2, DO NOT wash off.
• May give baby acetaminophen
Ø Care Safety
o Rear facing careseat, middle seat until age 2
Video #15: Newborn Complications
Hypoglycemia à Glucose level < 40; GET BABY FOOD
Preterm Newborn
Ø At risk for complications
o Respiratory distress
o Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
o Necrotizing Enterocolitis (inflammatory disease of GI system)
o Hypotonic Muscles
Ø LGA
o Macrosomnic (large baby with organs that are not fully developed)
§ Born to mothers with diabetes
§ Suffer from hypoxia, hypoglycemia, or hypocalcemia (can cause tremors)
Ø Post-Term
o Lose subcutaneous fat
o Hair and nails may be long
o May have meconium staining on nails or umbilical cord
Ø Hyperbilirubinemia à Jaundice
o Physiologic Jaundice = Benign (occurs 24 hrs of age and resolves w/in 7 days)
§ Due to immaturity of baby liver
o Pathologic Jaundice = extends over 7 days. R/t blood group incompatibility r/t some kind
of infection
o Bilirubin Encephalopathy = very dangerous. r/t untreated hyperbilirubinemia. Levels
>25 mg/dl. Associated with cerebral palsy, epilepsy, mental handicap
o *Note time that jaundice set in to be able to differentiate types of jaundice
o Phototherapy is prescribed if bilirubin is
§ > 15mg/dl in newborn prior to 48 hrs of age
§ > 18 mg/dl in newborns prior to 72 hrs of age
§ >20 mg/dl at anytime then phototherapy is considered
§ Interventions
• Eyes mask over baby
• Keep newborn undressed
• Cover up genitalia on baby
• Avoid applying lotion (absorbs heat and can cause burn)
• Remove baby Q4 hrs, check eyes
• Reposition Q2 hrs
§ Effects
• Bronze discoloration & rash is not serious
• Monitor for dehydration (sunken fontanels, wet diapers)
• Make sure you feed baby frequently or provide formula to help excrete
bilirubin
[Show More]