FSU ANT2301: Exam 1 (Thomas FA17)
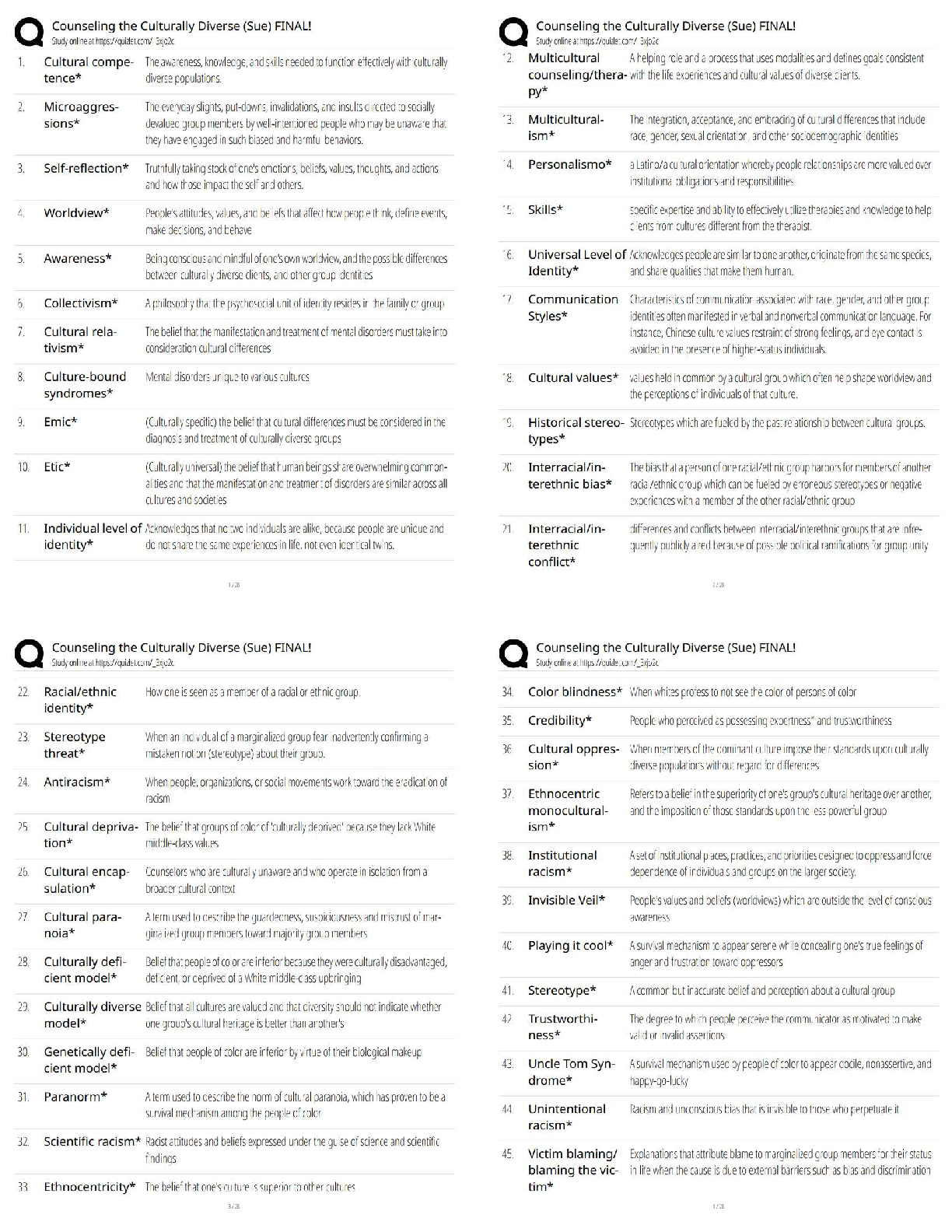
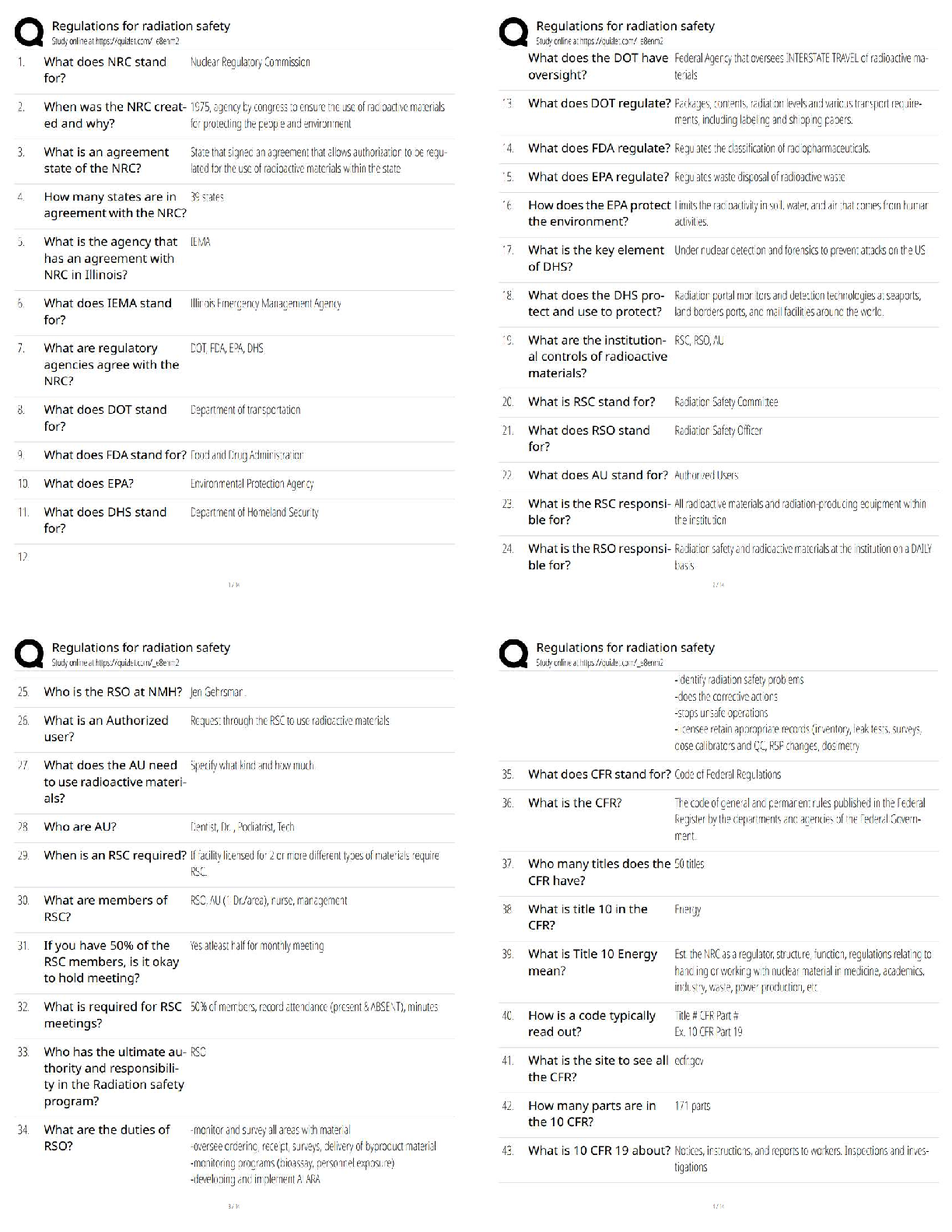
What is anthropology? - ✔✔the study of human beings
anthropos means? - ✔✔human being
logia means? - ✔✔study of
What are the subfields of anthropology? - ✔✔Archeological, Cultural, Li
...
FSU ANT2301: Exam 1 (Thomas FA17)
What is anthropology? - ✔✔the study of human beings
anthropos means? - ✔✔human being
logia means? - ✔✔study of
What are the subfields of anthropology? - ✔✔Archeological, Cultural, Linguistic, Physical
(Biological)
*NO F*CKING DINOSAURS*
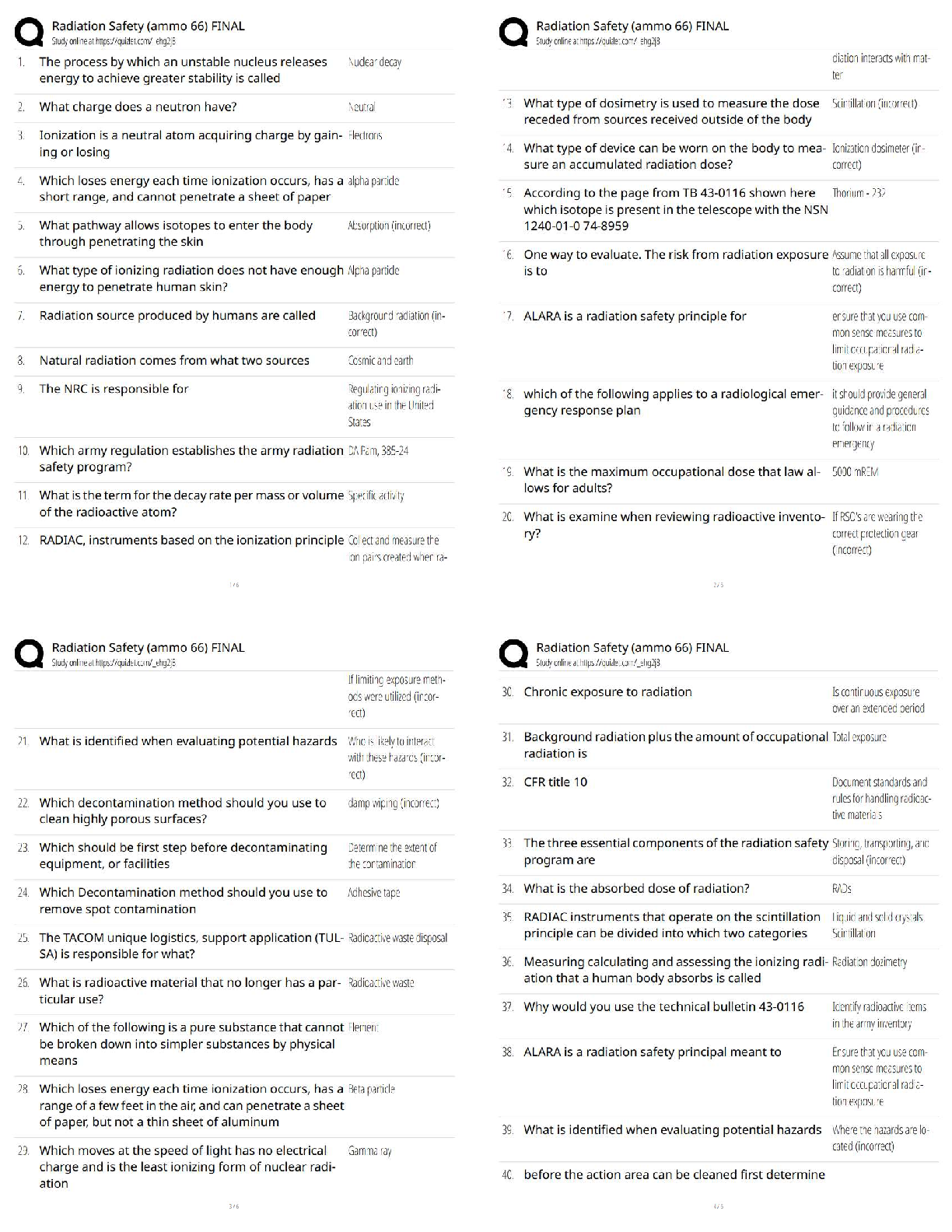
What is Cultural Anthropology? - ✔✔- The study of cultures and societies of human beings and
their very recent past.
- Traditional cultural anthropologists study living cultures and present their observations in an
ethnography.
What is Archaeology? - ✔✔The study of past societies and their cultures, especially the material
remains of the past, such as tools, food remains, and places where people lived.
What is Linguistic Anthropology? - ✔✔The study of language, especially how language is
structured, evolution of language, and the social and cultural contexts for language.
What is Physical Anthropology? - ✔✔- A.k.a biological anthropology
- The study of human evolution and variation, both past and current.
Evolutionary Theory? - ✔✔tries to explain human biology (anatomy, brains, psychology,
behavior...) through evolution and natural selection.
Evolutionary biology shows that the human genotype is the result of? - ✔✔those ancestors who
reproduced with greater frequency than others
Current behavior is probably a result of? - ✔✔selective forces that occurred in the Pleistocene
Naturalistic fallacy - ✔✔- the error deriving what ought to be from what is
- creating an evolutionary explanation of a behavior in humans does not justify the behavior or
make it universal
Genetic determinism - ✔✔- idea that behavior is unalterable, programmed, and unchangeable
- this idea is untrue; we are not saying that because a behavior may be selected for, it is
inevitable or acceptable.
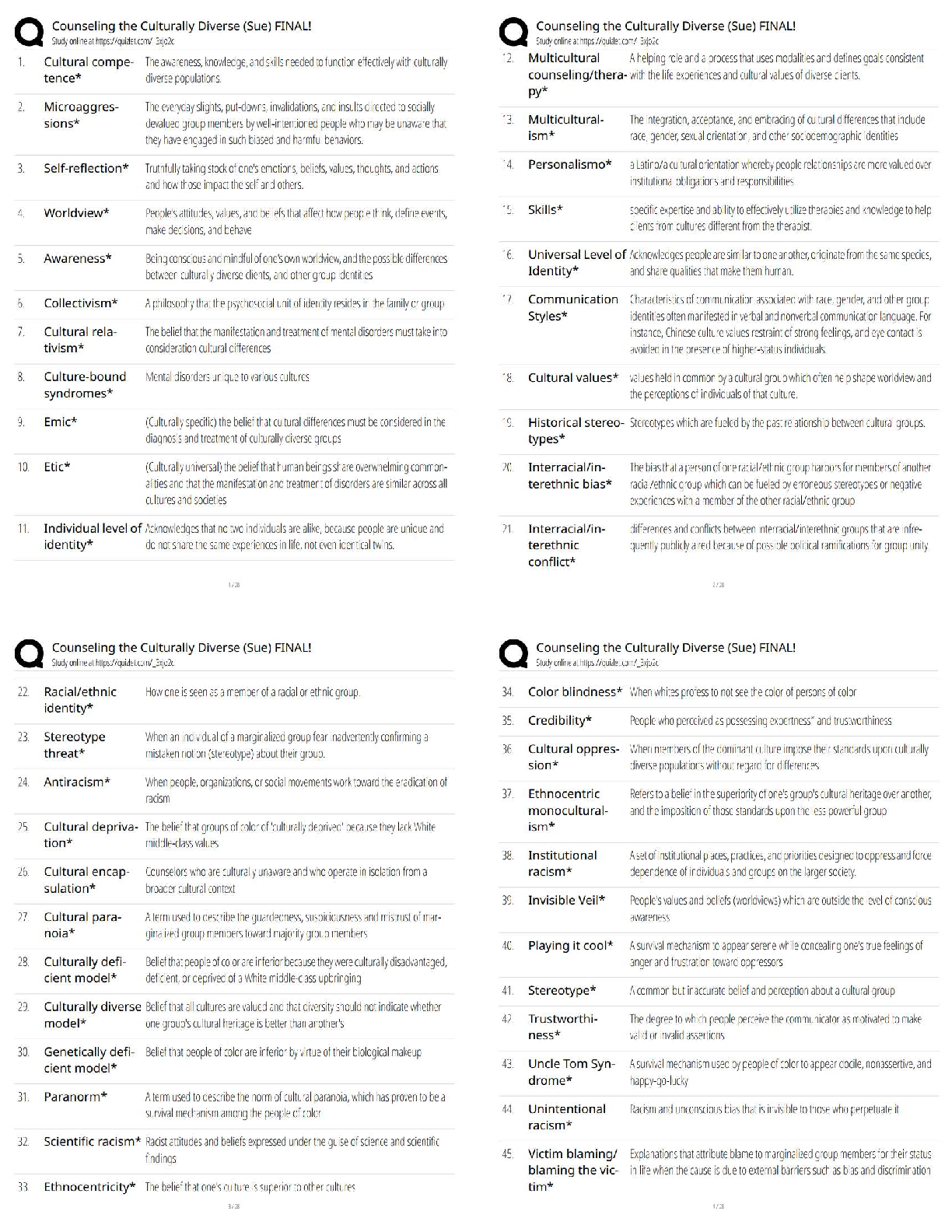
What is sexuality? - ✔✔- how people experience and express themselves as sexual beings
Biological, Social and Philosophic aspects of sexuality - ✔✔- biological: encompass sexual
intercourse and sexual contact in all its forms
- social: covers the cultural, political and legal aspects
- philosophic: spans the moral, ethical, theological, spiritual or religious aspects
Prehistoric Sexuality - ✔✔earliest evidence appears after the increase in symbolic thought
accompanying early modern humans
ex. Venus of Willendorf, Hohle-Fels (thicc statues w/ big titties)
Ancient Mediterranean Sexuality - ✔✔- concept of what activities and sensations are "sexual" is
historically determined
- in ancient writings and art accounts of: STDs, Menstruation, Circumcision, Contraception.
The Hebrews (1000 - 200 BC) - ✔✔Hebrew Bible had rules about sexual behavior, tales of
sexual misconduct, tales of marital love, acknowledges the importance sexuality in marital
relations
The Greeks (1000 - 200 BC) - ✔✔- Distinguish between love and sex (Aphrodite/Eros)
- One of the few major civilizations to institutionalize gays (Pederasty)
- Men and the male form were idealized (everyone loved some dick)
The Romans (500 BC - AD 700) - ✔✔- marriage and sexual relations were viewed as a means to
improve one's economic/social standing
- few restrictions regarding sexuality
India (Beginning about 400 BC) - ✔✔- Hinduism (karma)
- Patriarchal social system
- Kama Sutra (sex, love, family)
China (Beginning about 200 BC) - ✔✔- Tao (yin & yang)
- sexuality is a natural procreative process
- Yin and yang equally necessary, therefore men and women more equal
- Polygamy
Moche, Peru (100 - 800 AD) - ✔✔-
[Show More]
.png)








.png)











.png)