Statistics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Exam Version 2 Commerce 2QA3. Applied Statistics for Business McMaster Univers (All)
Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Exam Version 2 Commerce 2QA3. Applied Statistics for Business McMaster University - Midterm Exam. Score 100%
Document Content and Description Below
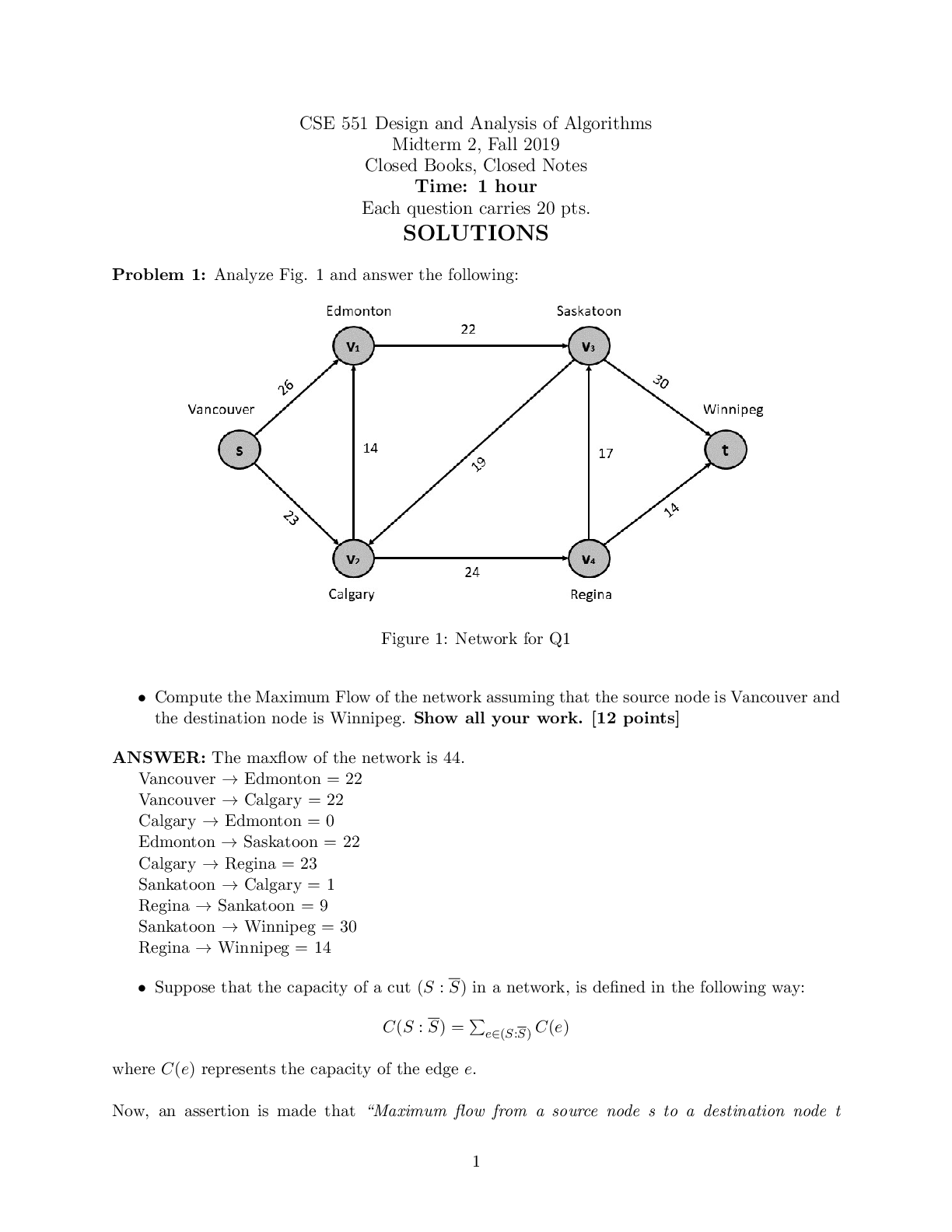
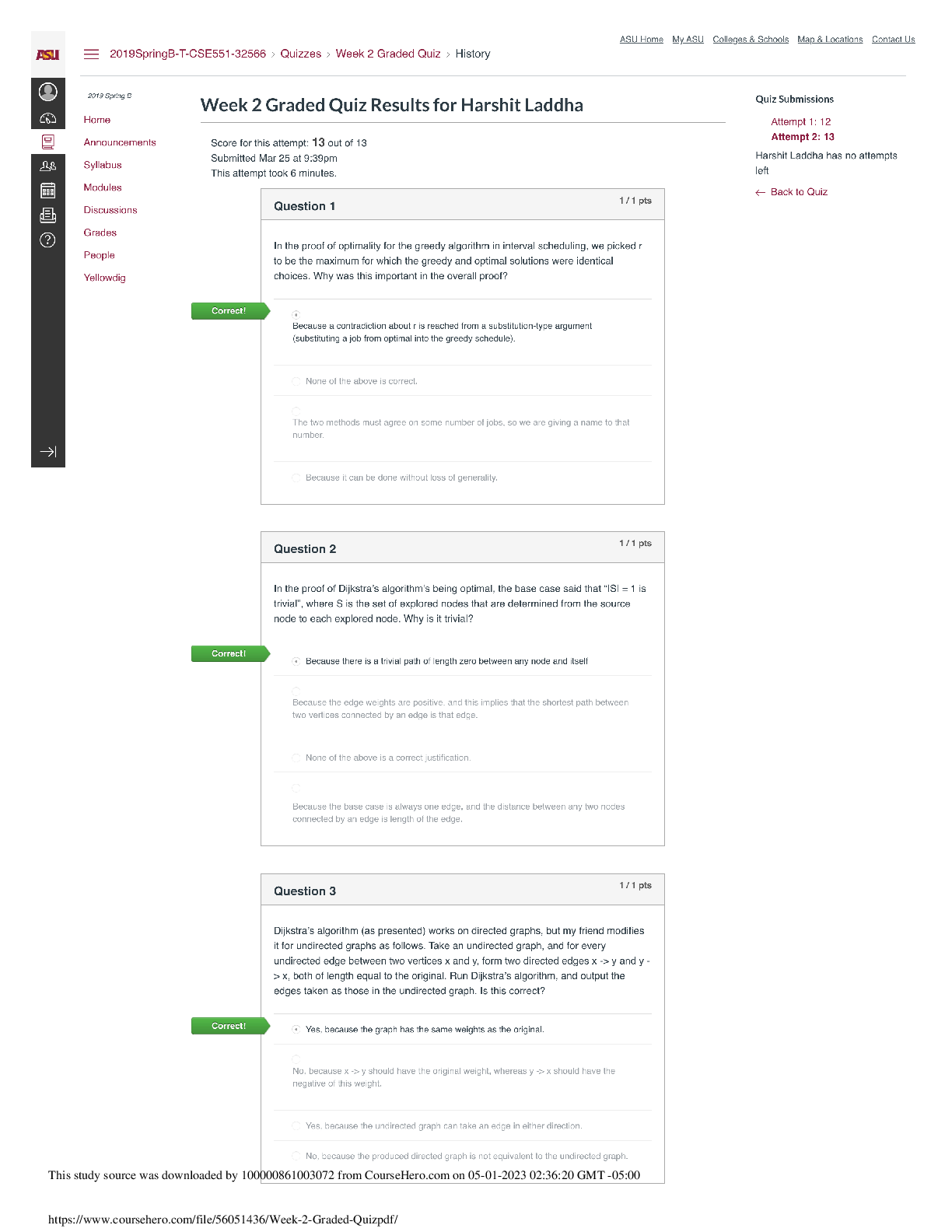
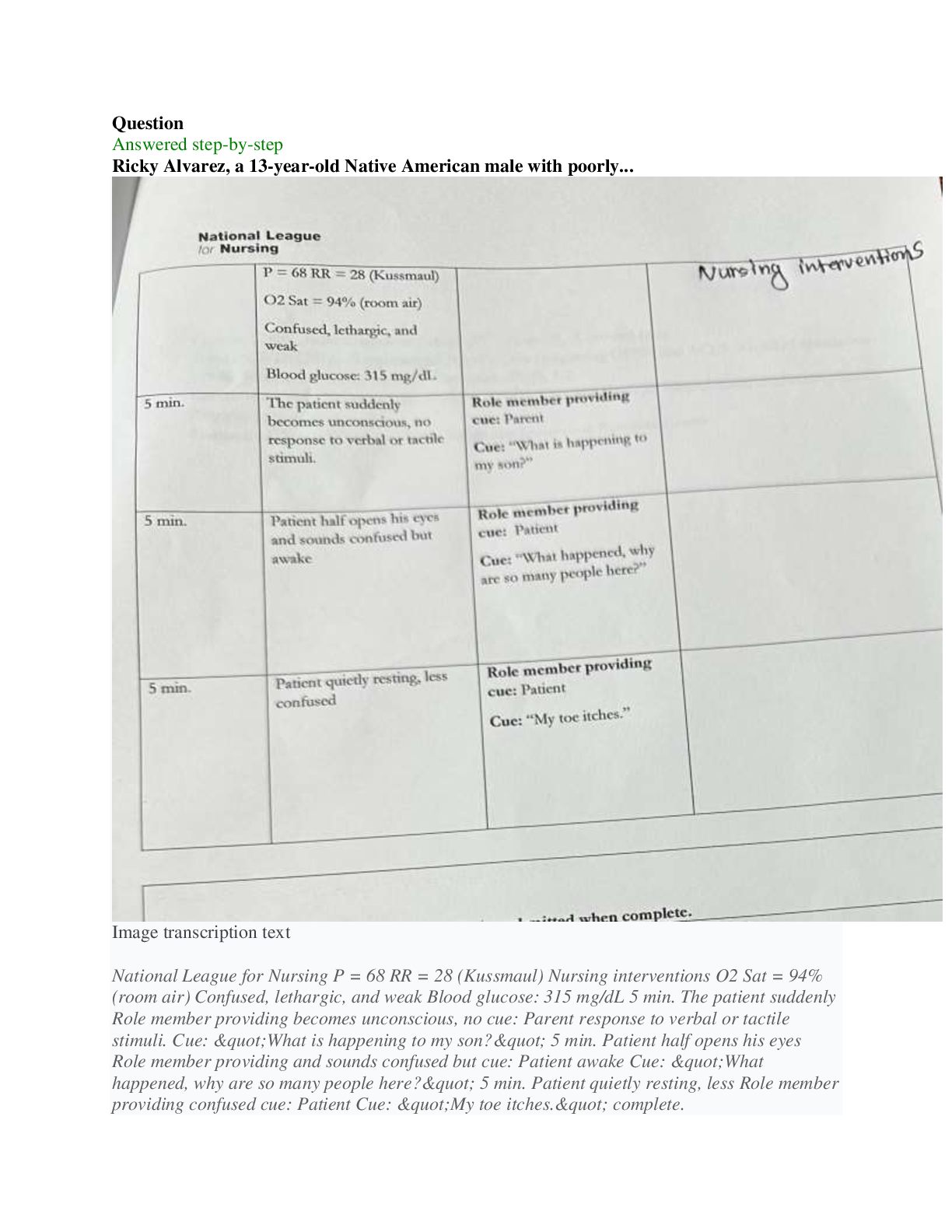
Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Exam Version 2 Commerce 2QA3 Applied Statistics for Business McMaster University - Midterm Exam Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 3 of 23 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (30 marks) ... • There are 30 questions. • Read each question carefully and give your answer in the OMR sheet. • Do not forget to write and fill up bubbles for your ID on the OMR sheet • Only the OMR sheet will be scanned and graded Chapter 1 1. Which one is not true? A) When a company’s accounts are audited, the auditor usually uses “statistical audit” instead of going through every item – for example, invoices. B) One reason to analyze data is to discover the truth. C) Usually retirements and resignations are decisions made by employees. We can use statistics to calculate probabilities for retirements and resignations from past records. D) Private organizations must use statistics more than government organizations in making decisions. Chapter 2 2. A Consumer Reports Health study on diabetes drugs takes into consideration cost. Cost is A) cross-sectional data B) time series data C) nominal data D) quantitative data 3. Which one is not true? A) Don’t label a variable as categorical or quantitative without thinking about the data and what they represent. B) A quantity or amount adopted as a standard of measurement, such as dollars, hours, or grams is called ordinal variable. C) The same variable can sometimes take on different roles. D) Categories are often given numerical labels. 4. The human resources department at McMaster University recently conducted an employee satisfaction survey of 100 of its employees. Data were collected on such variables as age, gender, marital status, current salary, level of overall satisfaction on a scale from 1 to 5, number of years with the company, and job title. Which of the variables would be classified as nominal data? A) gender, marital status, and job title B) age and gender C) age and number of years with the company D) age www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 4 of 23 E) level of overall satisfaction Chapter 3 5. Find a wrong statement. A) In practice, we usually obtain a statistics from a sample and use it to estimate a population parameter. B) Even if a survey is given to multiple random samples, the samples will differ from each other and so, therefore, will the responses. These sample-to-sample differences can happen only when errors are present in the process. C) What fraction of the population you sample doesn’t matter. It’s the sample size itself that’s important. D) Deliberate randomization is one of the great tools of Statistics. 6. Through their Roper Reports Worldwide, GfK Roper conducts a global consumer survey to help multinational companies understand different consumer attitudes throughout the world. Within 30 countries, the researchers interview 1000 people aged 13-65. Their samples are designed so that they get 500 males and 500 females in each country. Find the correct statement. A) They are using a simple random sample. B) No, they cannot use a simple random sample because it would be nearly impossible to get exactly 500 males and 500 females from every country by random chance. C) Stratified sampling can be impossible to use. D) No sampling technique that we learned in class can be used. 7. We need to survey a random sample of the 300 passengers on a flight from Toronto to Delhi. Find an obvious incorrect sampling technique. A) Pick every 9th passenger as people board on the plane. B) From the boarding list, randomly choose five people flying economy class only. C) Randomly generate 25 seat numbers and survey the passengers who sit there. D) Randomly select a seat position (right window, right center, right aisle, etc.) and survey all the passengers sitting in those seats. 8. The Canadian Census collects demographic data for specific groups such as lone-parent families, seniors, and those from specific language groups via what is commonly referred to as the "Short Form." The Short Form questionnaire is issued to each household in Canada, and all Canadian residents are legally required to complete the form. In addition to the "Short Form," a more detailed (long) form, sent for completion to certain households only, used to be mandatory, but became voluntary since 2011 census. What are the impacts of the change from mandatory to voluntary participation in the longer census? www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 5 of 23 A) The move to voluntary completion of the more detailed form introduces response bias. The households that receive the extra form have the opportunity to be counted multiple times and end up overrepresented in the results. B) The move to voluntary completion of the more detailed form introduces voluntary response bias. In particular, since disadvantaged households may choose not to complete the form, the results may underrepresent those groups in Canadian society. C) The move to voluntary completion of the more detailed form adds validity to the census. In particular, people who provide inaccurate answers out of spite from being forced to participate will no longer be factored in. D) The move to voluntary completion of the more detailed form introduces nonresponse bias. Since the survey is longer, very few households if any will elect to complete it instead of the Short Form, severely impacting the results. Chapter 4 9. As part of the marketing group at a film studio, you are asked to find out the age distribution of the audience of the studio's latest family friendly film. With the help of 10 of your colleagues, you conduct exit interviews by randomly selecting people to question at 20 different movie theatres. From 478 responses, you construct the frequency/relative frequency table below. Identify wrong statement. A) About two thirds of the viewers were either 10 to 14 years old or older than 21 (34% and 35%, respectively). B) About 17% were 6 to 9 years old, about 10% were younger than 6, and only about 44% were between 15 and 21 years old. C) Certain age groups might have been more or less willing to answer questions. D) About 44% were 6 to 9 years old, about 10% were younger than 6, and only about 17% were between 15 and 21 years old. 10.The Centers for Disease Control lists causes of death in the United States during 1999. (Each person is assigned only one cause of death.) Find the correct statement. A) It is reasonable to conclude that heart or respiratory diseases were the cause of approximately 39% of U.S. deaths in 1999 because there is no possibility for overlap. B) 12 percent of deaths were from causes not listed here www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 6 of 23 C) It is not reasonable to conclude that heart or respiratory diseases were the cause of approximately 39% of U.S. deaths in 1999 because there is no possibility for overlap. D) When we represent this information with pie chart, we do not need use a category label “other.” 11.A business survey group asked 581 small business owners in February 2004 what steps they had taken in the past year to increase productivity. They found that 60% of small business owners had updated their computers, 53% had made other (noncomputer) capital investments, 37% hired part-time instead of full-time workers, 26% had not replaced workers who left voluntarily, 13% had laid off workers, and 9% had lowered employee salaries. Find correct answer: A) The sum of the percentages is greater than 100%, indicating that the survey of the small business owners was biased. B) Since there are only six categories, a pie chart is an effective display. C) A bar chart to display the results D) The sum of the percentages is greater than 100%, the categories must overlap, so a pie chart would be misleading. 12.A survey of the entering MBA students at a university classified the region of origin of the students, as shown in the table below. Marginal distribution of origin A) www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 7 of 23 B) C) Marginal distribution cannot be found using given information D) Both A and B 13.Suppose your city has a large hospital and a small hospital, each performing major and minor surgeries. You collect data to see how many surgical patients have their discharges delayed by postsurgical complications, and find the results shown in the table. Find a wrong statement. A) Overall, for 11.3% of patients was discharge delayed. B) Yes, the overall percentage for major surgeries was greater. C) Overall, 12.3% were the discharge delay rates at each hospital. D) The small hospital advertises that it has a lower rate of postsurgical complications. Chapter 5 14.The histogram shows the December charges (in $) for 5000 customers from one marketing segment from a credit card company. (Negative values indicate customers who received more credits than charges during the month.) www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 8 of 23 Find the correct statement. A) The mean is larger because the distribution is left skewed. B) The median is larger because the distribution is left skewed. C) The mean is larger because the distribution is right skewed. D) The median is larger because the distribution is right skewed. 15.The marketing team at an internet music site wants a better understanding of who their customers are. They send out a survey to 25 customers asking for demographic information. One of the variables is the customer's age. For the 25 customers, the ages and summary statistics are shown to the right. Choose a correct boxplot using the quartiles given in the problem statement. A) B) C) www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 9 of 23 D) None of the above 16.An online company surveyed its readers about the reliability of portable music players. From the data gathered, the failure rates (in %) of 17 different models, shown below, were obtained. An appropriate graphical display will be A) B) C) D) www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 10 of 23 Chapter 6 17.The scatterplot of the housing cost index versus the median family income for 10 states is shown on the right. The correlation is 0.658. Which of the following best describes the relationship between the housing cost index and median family income by state? A) There is no association. B) There is a strong association but it is not linear. C) There is a moderate positive linear association with a few outliers. D) There is a moderate negative linear association with a few outliers. 18.The correlations between Age and Income as measured on 300 people is r = 0.79. Just reading this statement can we say that there are no outliers in the scatterplot of Income vs. Age. A) Yes, because since the correlation is under 0.95, there is a strong possibility that at least one outlier is in the data set. B) No, because the correlation alone cannot indicate the presence of outliers. C) Yes, because a data set with extreme outliers cannot have a correlation as high as 0.79. D) No, because since all conditions and assumptions of finding the correlation coefficient have been met, there cannot be any outliers. Chapter 7 19.The accompanying scatterplot shows the growth (in % of Gross Domestic Product) of the developing countries vs. the growth of developed countries for a particular region. Each point represents one of the years from 1970 to 2007. www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 11 of 23 Explain the meaning of Upper R2 = .2 in this context. A) About 20% of the variation in the growth rates of developed countries is caused by the growth rates of developing countries. B) About 20% of the growth rates of developing countries are accounted for by the growth rates of developed countries. C) About 20% of the variation in the growth rates of developing countries is caused by the growth rates of developed countries. D) About 20% of the variation in the growth rates of developing countries is accounted for by the growth rates of developed countries. 20.During the 1990s, investors made investment decisions based on market performance. As the nature of investing shifted (more day traders and faster flow of information using technology), the relationship between market performance (Return) in percent and money flowing (Flow) into mutual funds ($ million) shifted. The least squares linear regression is shown below. Complete parts a through d. (You may assume that the assumptions and conditions for regression are met.) Interpret the slope in the linear model. Choose the correct answer below. A) Fund Return increases by $782 million for every 1% decrease in money Flow. B) Fund Return increases by $782 million for every 1% increase in money Flow. C) Money Flow increases by $782 million for every 1% decrease in fund Return. D) Money Flow increases by $782 million for every 1% increase in fund Return. 21.Use the advertised prices for a used car of a particular model to create a linear model for the relationship between a car's Year and its Price. www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 12 of 23 You have a chance to buy one of two cars. They are about the same age and appear to be in equally good condition. Would you rather buy the one with a positive residual or the one with a negative residual? Which statement is incorrect in this context? A) You would rather buy the car with negative residual B) Negative residual indicates that the actual price is lower than the predicted price. C) Checking residual is important because the two cars have the same predicted price, since they are the same age and condition, so the one with the lower actual price is a better purchase. D) Checking residual cannot give you any clue about correct decision. Chapter 8 22.A consumer organization estimates that over a 1-year period 20% of cars will need to be repaired once, 10% will need repairs twice, and 1% will require three or more repairs. What is the probability that a car chosen at random will need some repairs? A) 0.69 B) 0.89 C) 0.31 D) 0.001 23.You bought a new set of four tires from a manufacturer who just announced a recall because 1% of those tires are defective. What is the probability that at least one of yours is defective? A) 0.042 B) 0.039 C) 0.01 D) 0.02 www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 13 of 23 24.You work for a large global management consulting company. Of the entire workforce of analyst, 42% have had no experience in the telecommunications industry, 13% have had limited experience (less than five years), and the rest have had extensive experience (five years or more). You are assigned to be part of a team of three analyst of a global management consulting company. What is the probability that both of your teammates have some telecommunications experience? A) 0.1764 B) 0.3364 C) 0.6975 D) 0.03364 25.A European department store is developing a new advertising campaign for their new Canadian location, and their marketing managers need to better understand their target market. Based on survey responses, a joint probability table that an adult shops at their new Canadian store classified by their age is shown in the table. Given this table, are age <20 and shopping at the department store independent? A) Yes, because there are no common outcomes. B) No, because the outcome of one influences the probability of the other. C) Yes, because the outcome of one does not influence the probability of the other. D) No, because there are outcomes that are common between them. Chapter 9 26.Fuel economy estimates for automobiles built one year predicted a mean of 24.8 mpg and a standard deviation of 6.2 mpg for highway driving. Assume that a Normal model can be applied. Use the 68-95-99.7 Rule to find the correct answer. A) about 16% of autos should get more than 39 mpg. B) about 13.5% of autos should get between 31 and 37.2 mpg. C) the gas mileage of the worst 2.5% of cars is less than 2.4 mpg. D) the gas mileage of the worst 2.5% of cars is less than 10.4 mpg. 27.A salesman normally makes a sale (closes) on 80% of his presentations. Assuming the presentations are independent, the probability the first presentation he closes will be one of his first three attempts. www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 14 of 23 A) 0.02 B) 0.2 C) 0.89 D) 0.9920 28.A manufacturer of a robot used on production lines for car manufacturing tests the accuracy of the robot operation and finds that, on average, the accuracy becomes unacceptable after 4450 hours of operation. The manufacturer specifies that the robot must be serviced to maintain its accuracy after 900 hours of operation. What is the probability that the robot will become unacceptable before it's serviced? Assume an Exponential distribution for this "time to failure." The probability that the robot will become unacceptable before it's serviced is A) 0.36 B) 0.183 C) 0.2 D) 0.28 29.In an effort to check the quality of their cell phones, a manufacturing manager decides to take a random sample of 10 cell phones from yesterday's production run, which produced cell phones with serial numbers ranging (according to when they were produced) from 43005000 to 43005999. The manager noticed that the number of faulty cell phones in the production run of cell phones is usually small and that the quality of one day's run seems to have no bearing on the next day. If the mean number of faulty cell phones is 1.5 per day, what is the probability that no faulty cell phones will be produced tomorrow? A) 0.442 B) 0.223 C) 0.151 D) 0.332 30.A company's employee database includes data on whether or not the employee includes a dependent child in his or her health insurance. What are the possible values it (this variable) can take on? A) Yes or no B) any positive integer C) 1, 2, or 3 D) None of the above Extra Page www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 15 of 23 Extra Page www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 16 of 23 Commerce 2QA3 Tables and Formulae General Formulae Sample Mean = average of a data set, For population mean, we write µ. Population mean is the average of population data. Sample standard deviation, s = the individual data values, y the mean, When we use population data, we use σ to represent population standard deviation σ= Standard deviation = positive square root of variance. If we are using sample data, to calculate z we use sample mean and sample standard deviation Z= www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 17 of 23 Lower and Upper Fences for the Box Plot: Q1 - 1.5IQR, Q3 + 1.5IQR Chapter 6 r Chapter 7 www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 18 of 23 Chapter 8 www.degroote.mcmaster.ca P P ( ) 1 ( ) A A C Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 19 of 23 Chapter 9 Expected Value of a Discrete Random Variable: E X xPx Variance for a Discrete Random Variable: V X x E X 2 Px Number of experimental outcomes providing exactly x successes in n trial Binomial Probability Function )( ) (1 !( )! ! ( ) px p n x x n x n P x where: x = the number of successes p = the probability of a success on one trial n = the number of trials P(x) = the probability of x successes in n trials n! = n(n – 1)(n – 2) ….. (2)(1) Expected value for binomial probability distribution Ex μ = np Variance for the binomial distribution Var (x) = σ2 = np(1 - p) Poisson Probability function, ! ( ) ex f x x Expected value for Poisson probability distribution E(X)= λ www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 20 of 23 Variance for the Poisson distribution Var (x) = λ Uniform Probability Density Function f (x) = 1/(b – a) for a < x < b = 0 elsewhere where: a = smallest value the variable can assume b = largest value the variable can assume Expected value for x (uniform probability density function) E(x) = (a + b)/2 Variance of x (uniform probability density function) Var(x) = (b - a)2/12 Converting to the standard normal random variable y z For Normal Approximation of Binomial Distribution Mean = np and standard deviation = Continuity Correction Whenever we are calculating the probability that X is greater than or equal to a certain value, we subtract 0.5 in the calculation of z. When we are dealing with X less than or equal to a given value, we add 0.5. Exponential Probability Function f (x) e x for x > 0 where: 1/λ = expected or mean of the exponential distribution e = 2.71828 Exponential Distribution: Cumulative Probabilities How to calculate mean, variance and standard deviation using your calculator (It is just an example_ in the exam, data values will be different) The following data gives the lengths in cm of 30 pieces of iron rods 45, 55, 65, 60, 61, 68, 59, 54, 64, 70 To operate the statistic calculation Using CASIO fx-991MS calculator Press [ON] [MODE] [MODE] [1] (SD) [45] [M+] [55] [M+] [65] [M+] [60] [M+] [61] [M+] [68] [M+] [59] [M+] [54] [M+] [64] [M+] [70] [M+] www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 21 of 23 Find the mean (x) Press [SHIFT] [2] [1] (mean x) [=] (60.1) Find the variance Press [SHIFT] [S-VAR] [2] [x2] [=] (49.29) Find the standard deviation Press [SHIFT] [S-VAR] [2] [=] (7.020683727) Find the variance (Sample) Press [SHIFT] [S-VAR] [3] [x2] [=] Find the standard deviation (for sample) Press [SHIFT] [S-VAR] [3] [=] www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 22 of 23 www.degroote.mcmaster.ca Commerce 2QA3 Midterm Page 23 of 23 www.degroote.mcmaster.ca [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$5.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 14, 2023
Number of pages
23
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 14, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
87