NUR 2092 - Final Exam Concepts
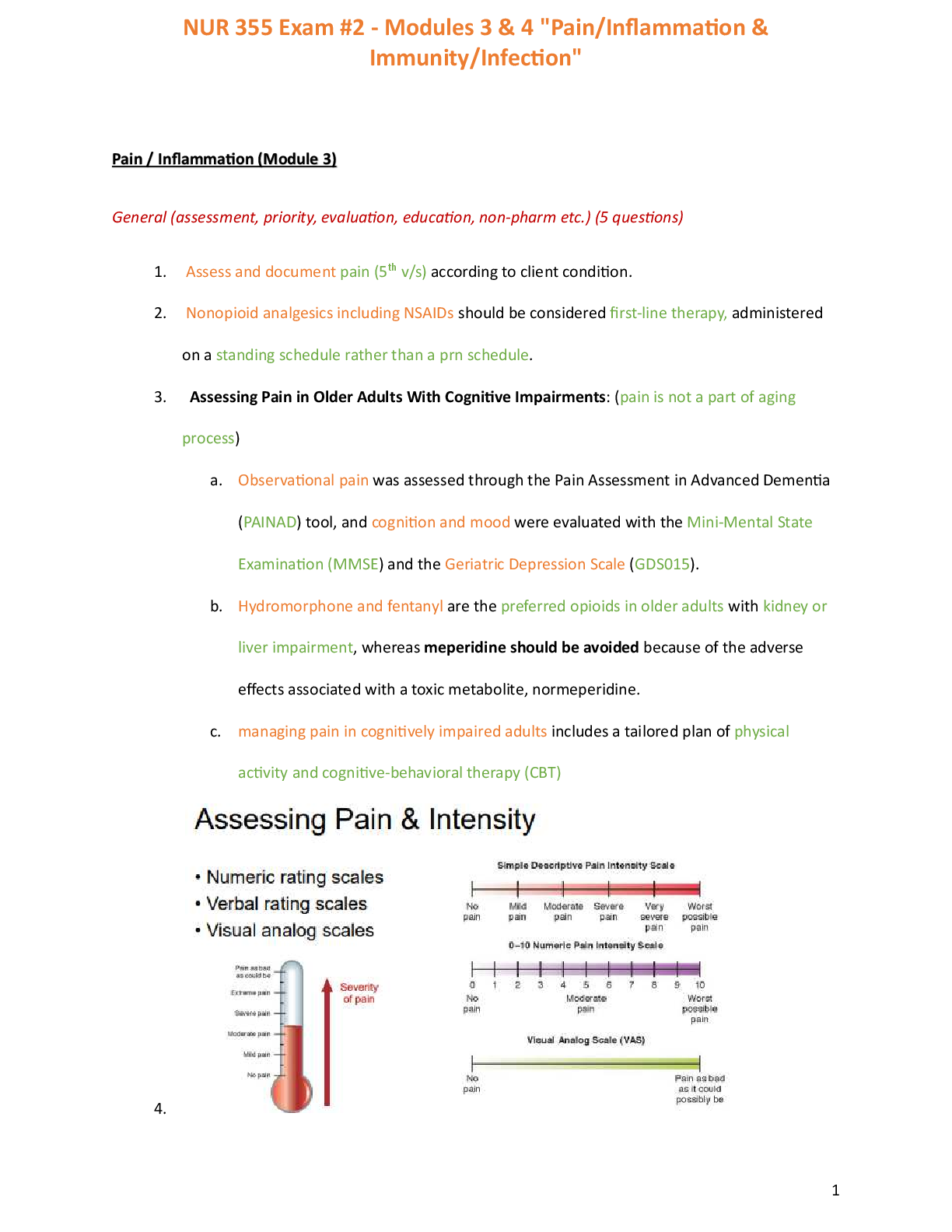
1. Know the difference between subjective and objective data.
• Subjective: What a person says about themselves
o Example: “My BP was 118/90 yesterday” and pain
• Objective: What you
...
NUR 2092 - Final Exam Concepts
1. Know the difference between subjective and objective data.
• Subjective: What a person says about themselves
o Example: “My BP was 118/90 yesterday” and pain
• Objective: What you observe through measurement, inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation
o Examples: Meter readings, vital signs, and measurements
2. Barriers to communication. What are they?
• The use of jargon
• Emotional barriers and taboo
• Lack of attention, interest, distractions, or irrelevance to the receiver
• Difference in viewpoint
• Physical barriers to non-verbal communication
• Physical or mental disabilities (Physical: Hearing problems. Mental: Down Syndrome)
• Language differences and difficulty understanding unfamiliar accents
• Cultural difference.
3. Traps of interviewing-Chapter 3
• Providing false assurance or reassurance
• Giving unwanted advice
• Using authority
• Using avoidance language
• Distancing
• Using professional jargon
• Using leading or bias questions
• Talking too much
• Interrupting
• Using “why” questions
4.Open ended questions vs closed ended questions. Know the difference and when to use them during the interview process.
• Open ended: Questions asking for narrative information
o When to use them:
Use it to begin the interview
Introduce a new section of questions
Whenever the person introduces a new topic
• Closed (direct) questions: Asking for specific information. Elicit a short, one- or two-word answer, a “yes” or “no” or a forced choice.
o Used in an emergency to obtain information quickly
5. Components of a Health History -Chapter 4.
• Biographical data
• Source of history
• Reason for seeking care
• Present health or history of present illness
• Past health
• Family history
• Review of systems
• Functional assessment including activities of daily living
6. General survey and what it consists of.
• Initial inspection
• Observe posture
• Hygiene
• Facial expression
• Assess breathing
• Behaviors
• Body language
o Appearance
o Body Structure and mobility
o Behavior
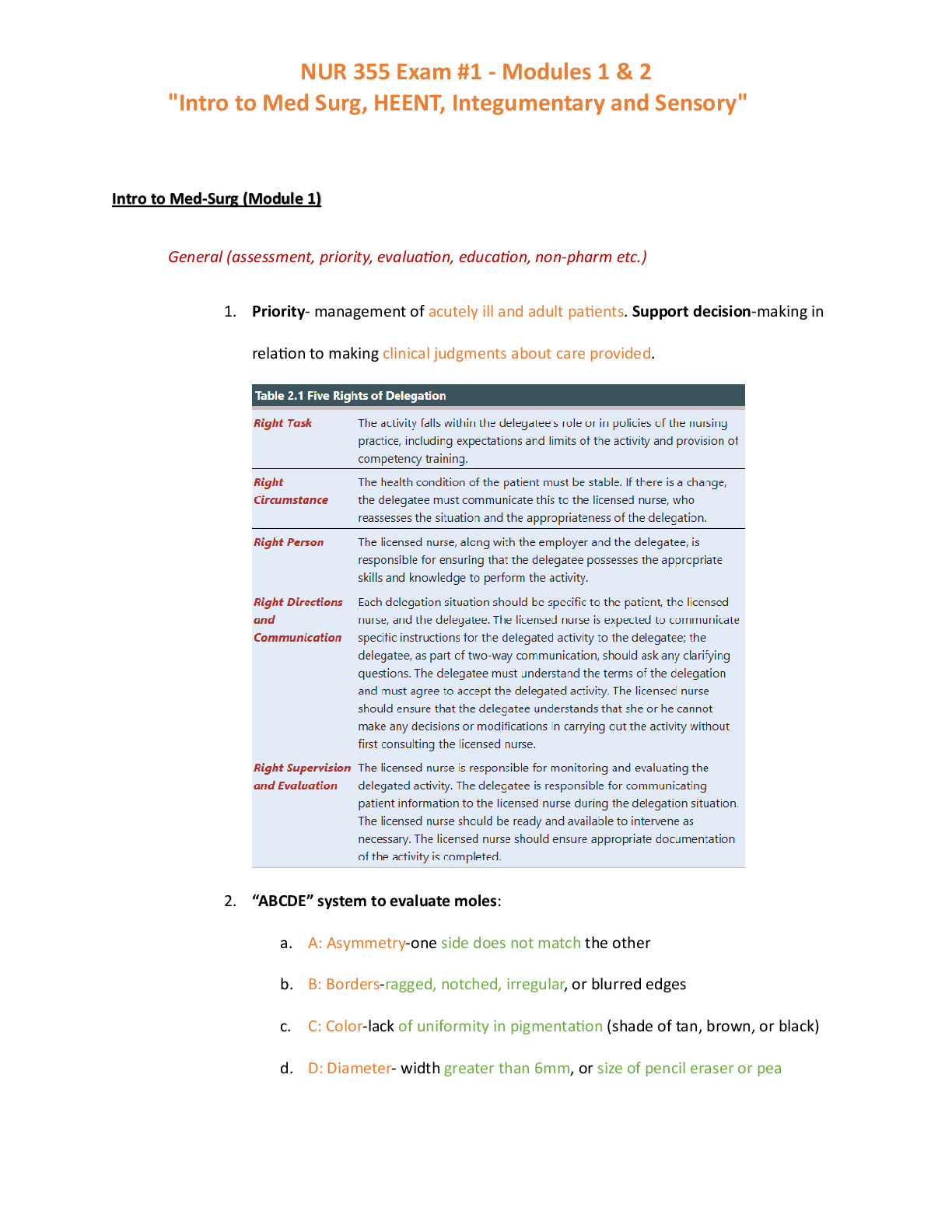
7. Skills requisite of physical exam. Chapter 8. Know the correct order for assessment. (Inspection, palpation etc). Know the different order for abdominal exam.
• Order:
o Inspect – individual as a whole
o Palpation - touch
o Percussion – tapping for underlying structures
o Auscultation - listening
Abdomen:
• Inspect
• Auscultation
• Percussion
• Palpation
8. Know the normal range of respirations. Above and below that range, what's it called?
• Normal Range: 12-20(21)
• Dyspnea: Shortness of breath; < 12
• Tachypnea: Abnormally rapid breathing; >21
9. Lung sounds- Know difference between normal vs abnormal and where they are heard.
• Normal – pattern changes without our awareness in response to cellular demands
o Bronchial sometimes called tracheal or tubular
o Bronchovesicular
o Vesicular
• Abnormal
o Crackles or rales – periphery only – fluid in airways – high pitched, heard during inspiration
o Wheezing – mucous noise during inspiration or expiration – louder during expiration
o Rhonchi – rumbling, course sound, like a snore, heard during inspiration and expiration
10. Characteristics of pulse and how to document it.
• Rhythm: Normal regular, even tempo
o Rating:
Force:
• 3+: Full, bounding – anxiety, exercise – increased stroke volume
• 2+: Normal
• 1+: Weak, thread – low stroke volume
• 0: Absent
11. Blood pressure cuff sizes and impact on blood pressure readings.
• Cuff sizes:
o Too small: Falsely high BP due to extra pressure to compress artery
o Too large: Falsely low BP due to not being able to cut off blood vessel properly
12. Changes in blood pressure in the elderly caused by what?
• African American’s, menopause, older age due to hardening of vessels, higher blood pressure
• BP dependent on
o Cardiac output – heart pumps more blood into blood vessels – pressure on container walls increase
o Peripheral vascular resistance – vessels become smaller pressure to push becomes greater
o Volume of circulating blood – blood tightly packed into arteries – more blood more pressure
o Viscosity – thickness
o Elasticity of vessel walls – stiff and rigid increased pressure is needed
13. Assessment of ALL pulses and their locations. (Apical, radial, popliteal, etc)
• Temporal
• Carotid
• Apical (5th ICS, L Mid clavicular)
• Brachial
• Radial
• Femoral
• Popliteal
• Posterior Tibial
• Dorsalis pedis
14. Carotid pulse- location and abnormality is called?
• Carotid is in the neck – groove between the trachea and sternomastoid muscle, medial to and along-side
• Abnormal pulse = 1+ weak, thread
• Below 60 = bradycardia
• Above 100 = tachycardia
15. How does the physical assessment differ of newborn , toddler, adolescent and elderly. What is important to consider with each stage? What to do differently when performing exam with each age group?
• Newborn – parent bonding /coping
• Toddler – growth charts
o Prenatal status – L&D – complications – full term
o Accidents – injuries – illness – operations – allergies - medication
• Adolescent –
o HEEADSSS – Home – education – eating – activities – drugs – sexuality – suicide, depression - safety
• Elderly – past health for 5 years – chronic illnesses, hospitalizations, operations, last exam, current medication, bring in meds, ADL’s
16. Diastolic vs Systolic. Know the differences.
• Systolic: Pressure is maximum pressure felt on the artery during left ventricular contraction
• Diastolic: Pressure is the elastic recoil, resting, pressure that the blood exerts constantly between each contraction
17. What is PERRLA?
• Pupil
• Equal
• Round
• React
• Light
Continued...............................
[Show More]