NCTI End Didactic Study Guide 2023 LATEST UPDATE
$ 11

Database Implementation (INF3707) | Score 100% / New Version / 2025 Update – SQL, Constraints & Transactions
$ 13

OxfordAQA Physics (9630) International AS PHYSICS 9630 – Electricity, oscillations and waves Mark Scheme. 2021 ASSESSMENT MATERIALS MARK SCHEME and QP
$ 12
.png)
WGU C720 PA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ALREADY PASSED
$ 15
.png)
University of Texas - MSCI 353Homework+4+answer+key ALL ANSWERS CORRECT
$ 7
 (1) (1).png)
ATI MENTAL HEALTH PROCTORED RETAKE 2019 - Reliable with Verified Questions & Answers
$ 12

H - Cambridge BEC Wordlist
$ 7.5

NSG 211 Patho Module 10 b study notes
$ 10

A-level COMPUTER SCIENCE 7517/1 Paper 1 Mark scheme June 2022 Version: 1.0 Final *226A7517/1/MS* MARK SCHEME – A-LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE – 7517/1 – JUNE 2022 2
$ 8

AQA June 2022 Question Paper A-level PHYSICS Paper 3 Section A 7408/3A
$ 7

Anti-Harassment and Non- Discrimination Training (2022/2023) Already Passed
$ 10.5
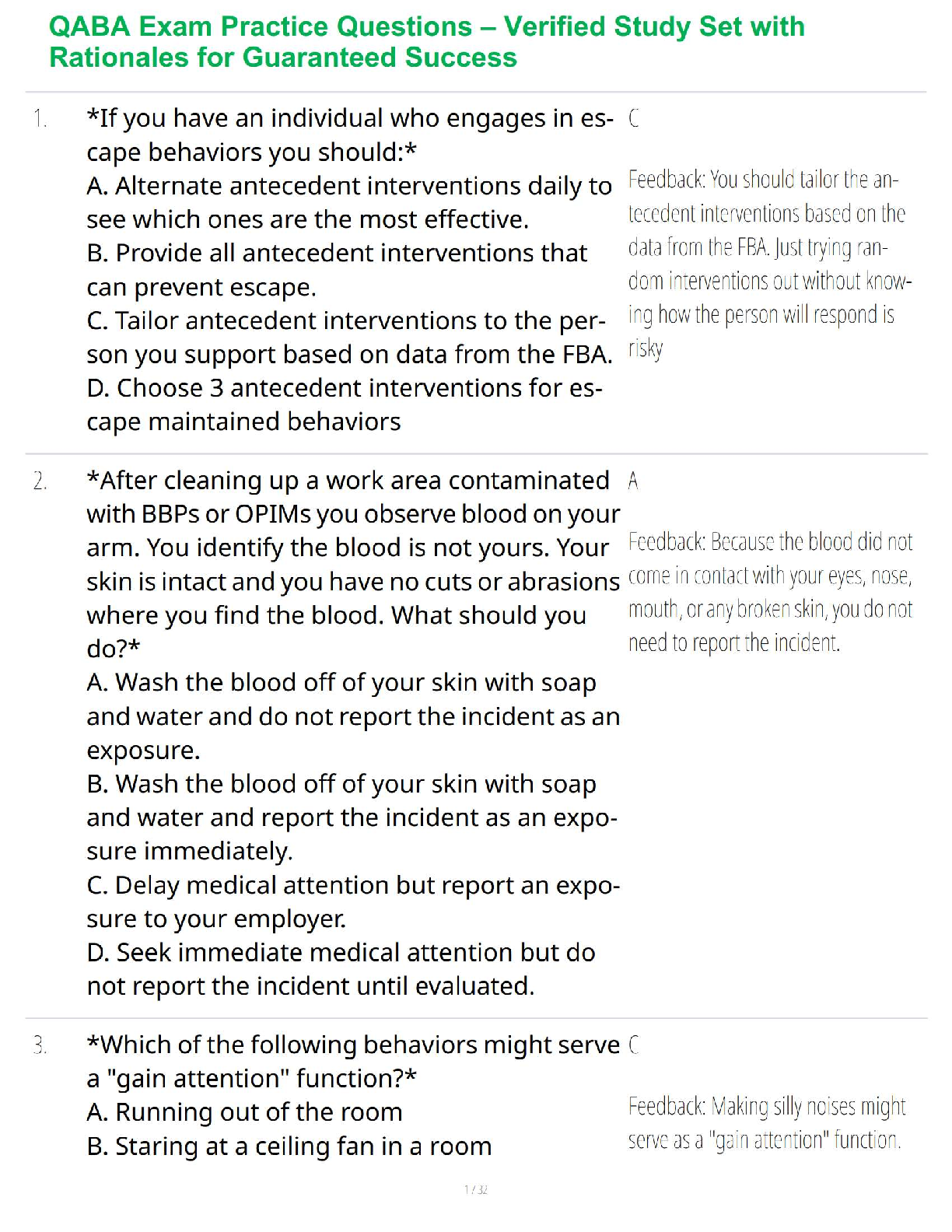
QABA Exam Practice Questions – Verified Q&A & Guaranteed Behavior Analyst Certification Success
$ 37.9

2023 BIOLOGY EXAM 3 REVIEW AND EXAM GUIDE TIPS
$ 12.5

A Level Further Mathematics B (MEI) Y432/01 Statistics Minor June 2023 QP
$ 4

Pathophysiology Module 3 Exam Review Portage LEARNING
$ 8

A Level Chemistry A H432/02 Synthesis and analytical techniques June 2024 QUESTIONS & MARK SCHEME
$ 6

NREMT Paramedic Questions and Answers Rated A+
$ 10

eBook [PDF] for Practice Makes Perfect_ Spanish Conversation, Premium 4th Edition by Jean Yates
$ 30

(LU) ENGI 428 CNC & Programming Logic Chips - Midterm Exam Review 20242025
$ 11

ATI RN COMPREHENSIVE PREDICTOR EXAM 2023 (EXTRACTED FROM ACTUAL EXAM)
$ 31
.png)
WGU C846 - ITIL v4 Questions and Answers 100% Pass
$ 10

EXERCISE AND MENTAL HEALTH MODULE II||APPLICABLE||RATED 100%
$ 9

CTS Practice Exam Questions with Verified Solutions
$ 13.5

Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE AS (8FM0/27) Further Mathematics Advanced Subsidiary Options 27:Decision Mathematics 1(Part of Options D,F,H & K ) Question paper+mark scheme Friday 17 may 2024
$ 7

OCR AS LEVEL 2022 PHYSICS A MARK SCHEME -H156-01 PAPER 1-H156/01: Breadth in physics
$ 11.5

ATI PEDIATRIC PROCTORED Exam (Forms A, B, C & Retake) | Updated Version | Verified Questions with Correct Answers & Detailed Rationales | 100% Accurate | Rated A+ Q&A Study Resource with Detailed Explanations
$ 15
.png)
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE Further Mathematics Advanced Subsidiary Further Mathematics options 28: Decision Mathematics 2 (Part of option K only) 8FM0/28
$ 8

H005-01 OCR AS LEVEL 2022 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY MARK SCHEME PAPER 1
$ 3

A Level Further Mathematics B (MEI) Y435/01 Extra Pure June 2023 QP
$ 4

March USA Past Paper SAT QAS
$ 7

Summary Pedagogy and Professional Responsibilities: PPR EC-12 (160) Exam.
$ 9
 – Chest Pain Complete Latest Solutions.png)
Case study i-human Florence Blackman (66 yo female) – Chest Pain Complete Latest Solutions
$ 18
MAS 209
$ 14.5

(Full Stack JavaScript) Dynamic User Interface Interactions Knowledge Assessment Q & S 2024
$ 11

A Level Further Mathematics B (MEI) Y436/01 Further Pure with Technology June 2023 QP
$ 4
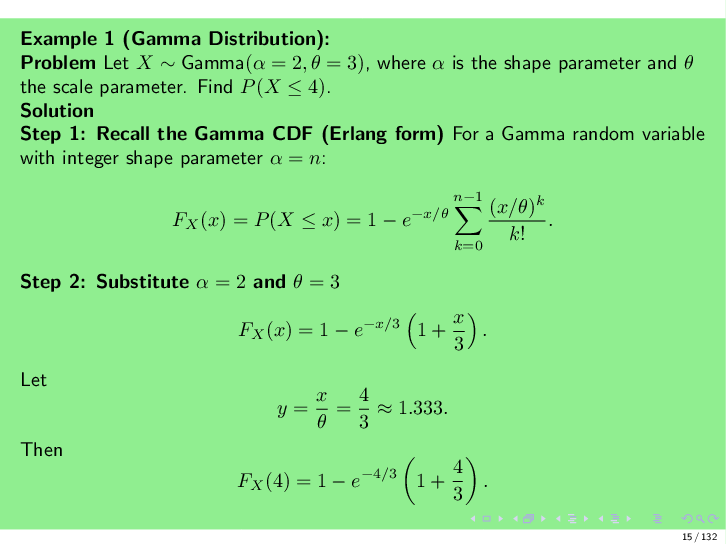
MAS-209-NOTE-pdf-pdf
$ 13

AQA GCSE FRENCH Listening Higher Tier Theme 2 Local, national, international and global areas of interest 2021 ASSESSMENT RESOURCE
$ 7

PSYCHOLOGY DEVELOPMENT MIDTERM EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2024
$ 13

CCS CPT CODING LESSON 3 ASSESSMENT QUESTION WITH CORRECT ANSWERS
$ 4

Advanced Complex Analysis A Comprehensive Course in Analysis, Part 2B Barry Simon
$ 12

CSE 598 Week 2 Quiz Hash Functions | Arizona State University
$ 10

ISYE 6414 (Statistical Modelling and Regression Analysis) Week 11 Homework Simulation | Georgia Institute of Technology – Expert Solutions & Verified Answers
$ 12
.png)
Photosynthesis Lab(The best document you can get on Photosynthesis)
$ 12

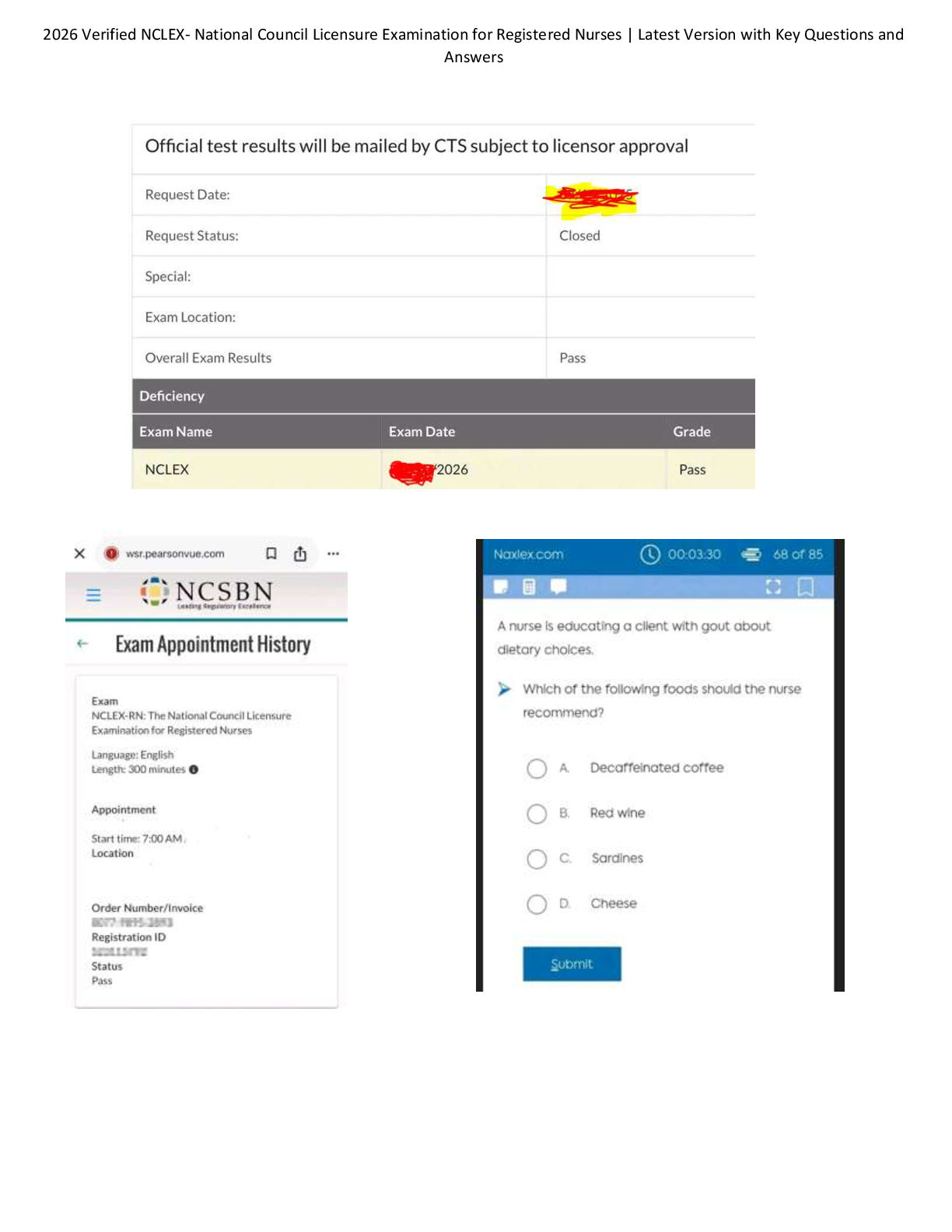
NCLEX RN NEWEST 2025, 2024, AND 2023 (3-LATEST VERSIONS) TEST BANK ACTUAL EXAM 2500 QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS WITH RATIONALES (VERIFIED ANSWERS)/ RN NCLEX TEST BANK|GRADED A+|BRAND NEW!!
$ 20.5

MATH 225N Week 6 Assignment Understanding Confidence Intervals (A)_ Already Graded A.
$ 16

C_SAC_2102 SAP Analytics Cloud Certification 2024 / Exam Prep & Test Bank / 300+ Questions & Answers / Pass Guaranteed