Statistics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Research Paper > The-Normal-Distribution-Estimation-Correlation-1 (All)
Research Paper > The-Normal-Distribution-Estimation-Correlation-1
Document Content and Description Below
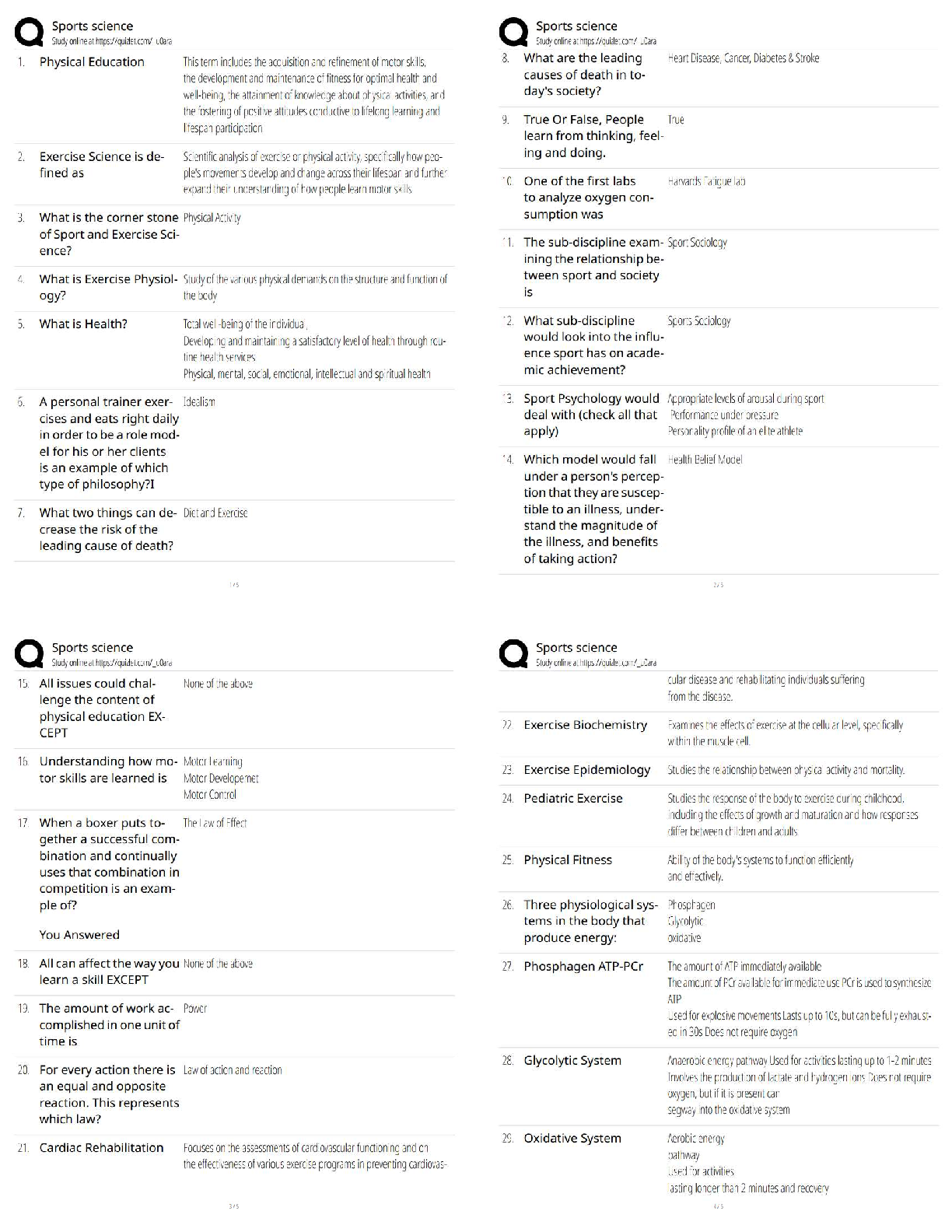
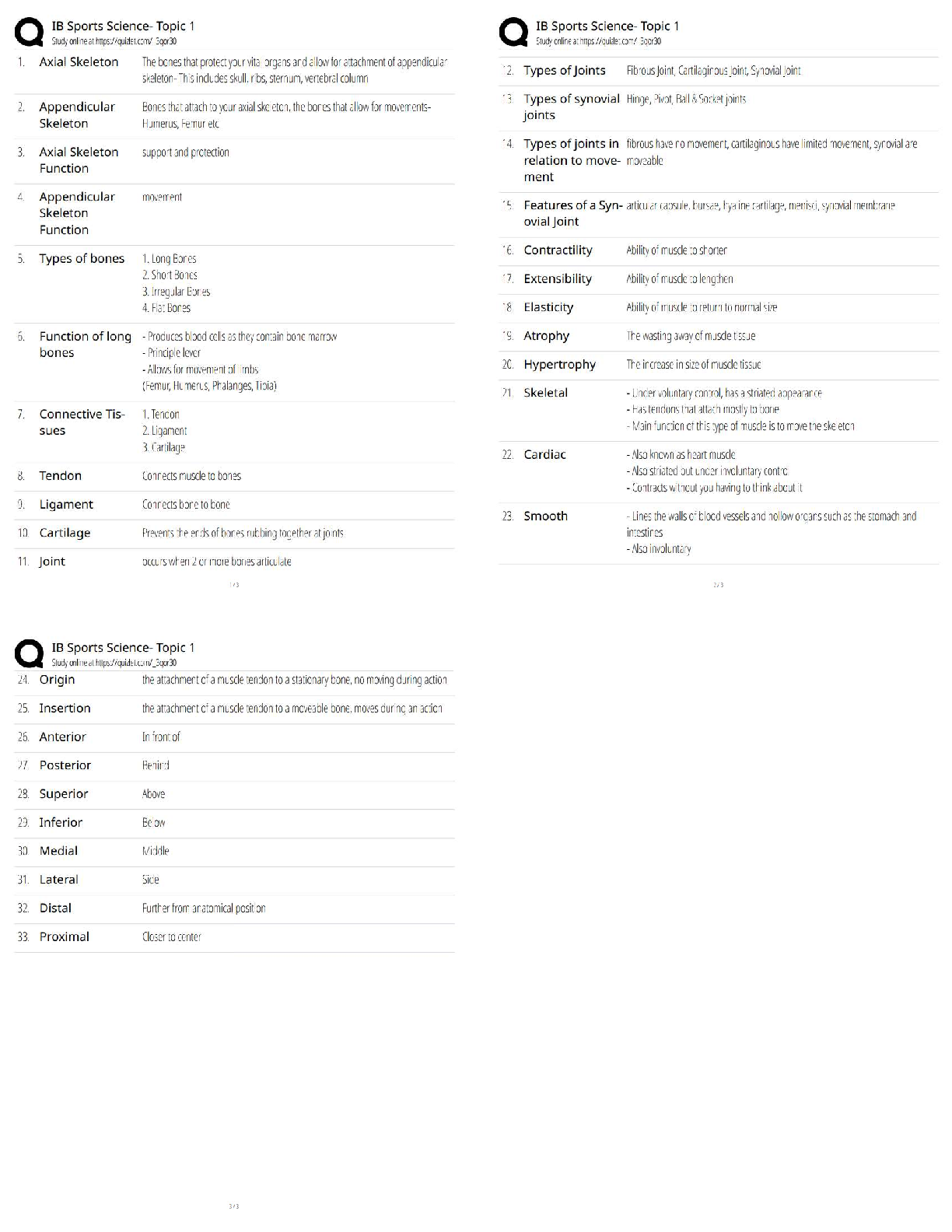
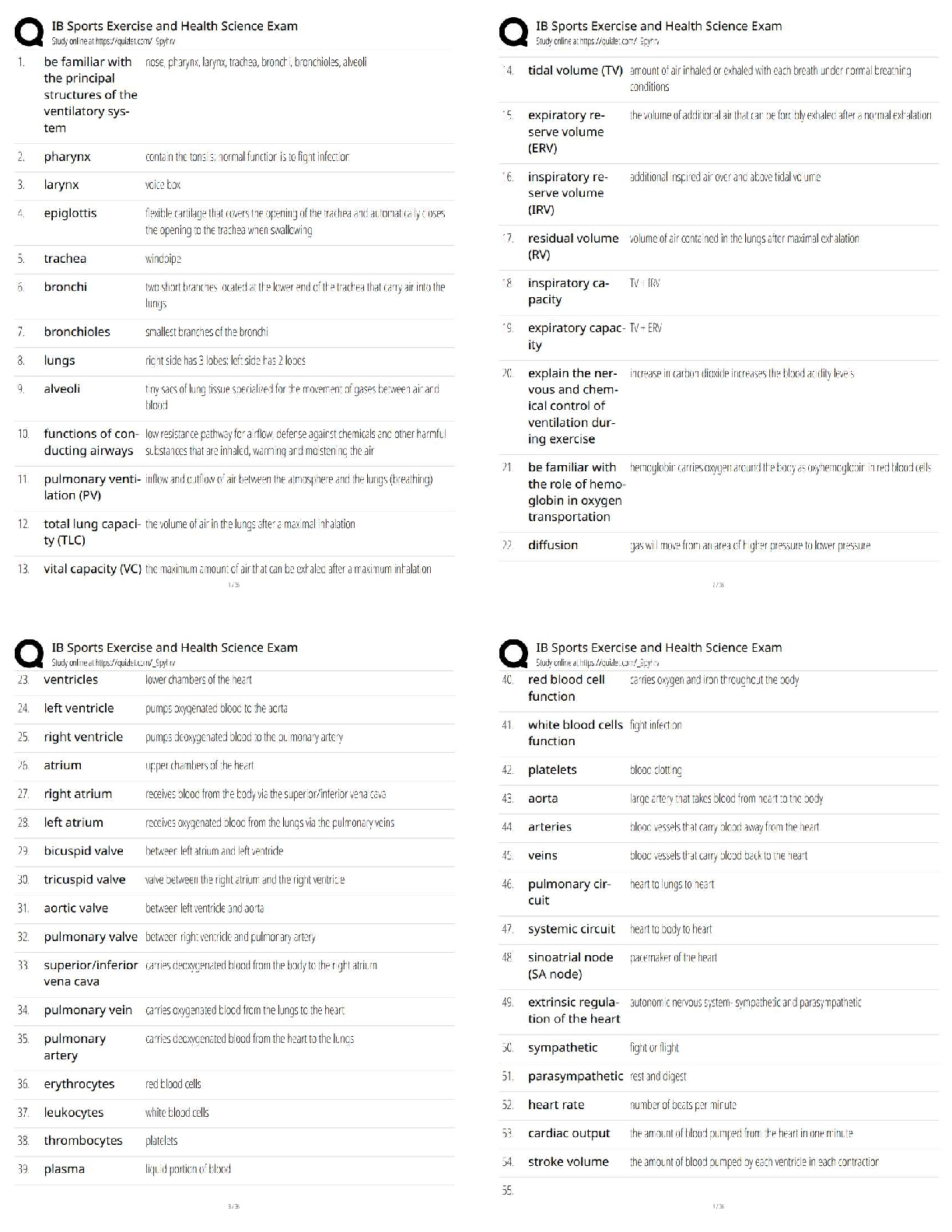
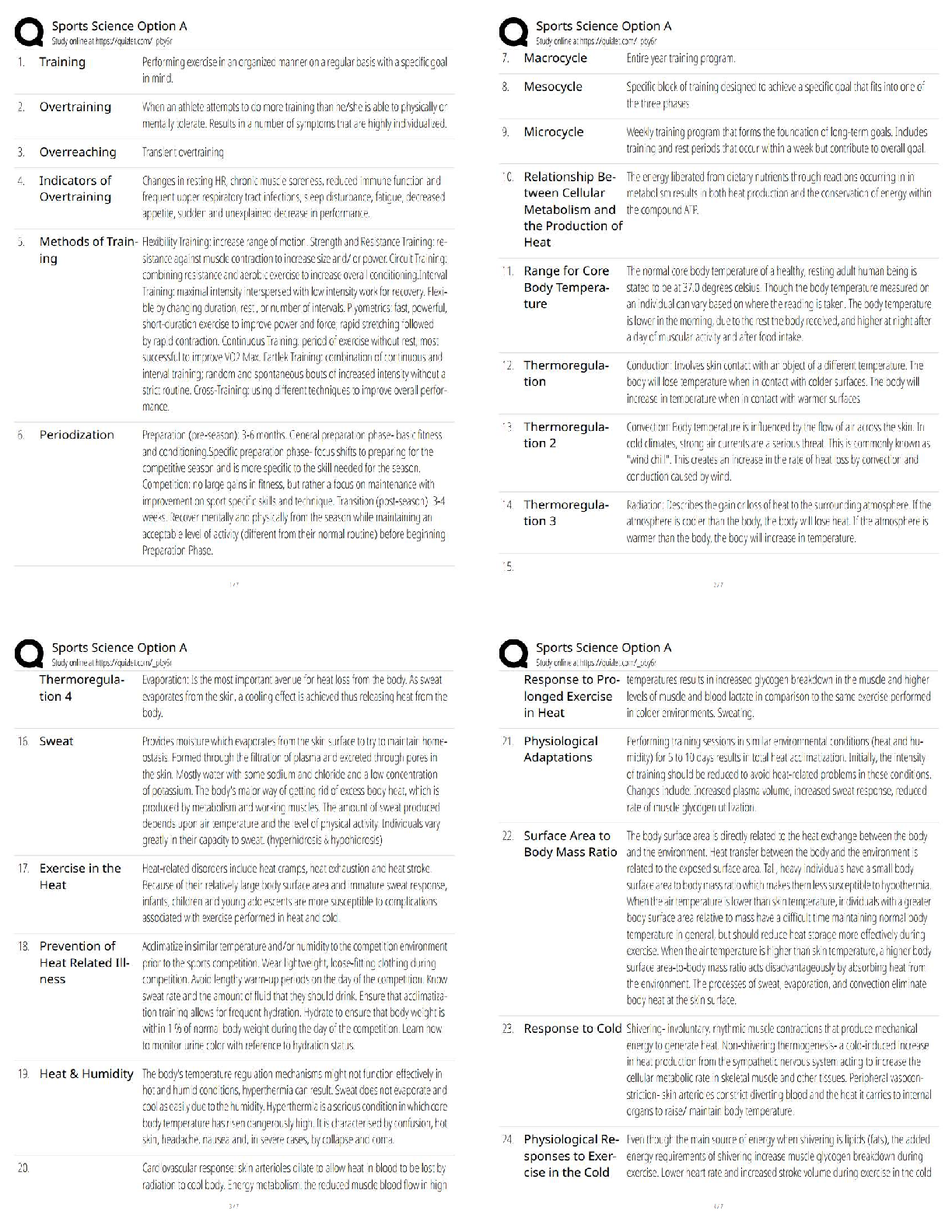
Research Paper > The-Normal-Distribution-Estimation-Correlation-1 The-Normal-Distribution-Estimation-Correlation-1 THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION DEFINITION: A continuous random variable X is said to ... be normally distributed if its density function is given by: for and for constants µ and σ, where Notation: If X follows the above distribution, we write The graph of the normal distribution is called normal curve. Properties of the normal curve: 1. The curve is bell-shaped and symmetric about a vertical axis through the mean µ. 2. The normal curve approaches the horizontal axis asymptotically as we proceed in either direction away from the mean. 3. The total area under the curve and above the horizontal axis is equal to 1. -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 DEFINITION: The distribution of a normal random variable with mean zero and standard deviation equal to 1is called a standard normal distribution. If , then X can be transformed into a standard normal random variable through the following transformation: If X is between the values , the random variable Z will fall between the corresponding values: Therefore, Examples: 1. Let Z be a standard normal random variable. That is, . Find the following probabilities: (see the z-table for the probabilities) A. B. C. D. 2. Let Z be a standard normal random variable. That is . Find the value of a. A. B. C. 3. Let X be a normal random variable with . Find the following probabilities: A. Therefore, the B. Therefore, the C. Therefore, the 4. Given a test with a mean of 84 and a standard deviation of 12. A. What is the probability of an individual obtaining a score of 100 or above in this test? B. What score includes 50% of all the individuals who took the test? C. If 654 students took the examination, then how many students got a score below 60? Solution: Given: µ=84, σ=12 A. Therefore, the probability of an individual obtaining a score of 100 or above on this test is 0.0918 or 9.18%. B. In notation form, the statement is equivalent to: Finding the corresponding z-score of the probability 0.50, z = 0.00 From the transformation formula, Therefore, the score that includes 50% of those who took the exam is 84. C. Given: µ=84, σ=12, N= 654 The number of students who got a score lower than 60 is equal to the product of the probability and the total number of students. Exercise 6.2 1. Let Z be a standard normal variable. Find the following probabilities: a. b. c. d. 2. Given a normal distribution with µ= 82 and find the probability that X assumes a value a. Less than 78 b. More than 90 c. Between 75 and 80 3. The mean weight of 500 male students at a certain college is 151 pounds. And the standard deviation is 15 pounds. Assume that the weights are normally distributed. a. How many students weigh between 120 and 155 pounds? b. What is the probability that a randomly selected male student weighs less than 128 pounds? ESTIMATION [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 10, 2021
Number of pages
16
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 10, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
56






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)