Chapter 29--Hematological Dysfunction: Nursing Management
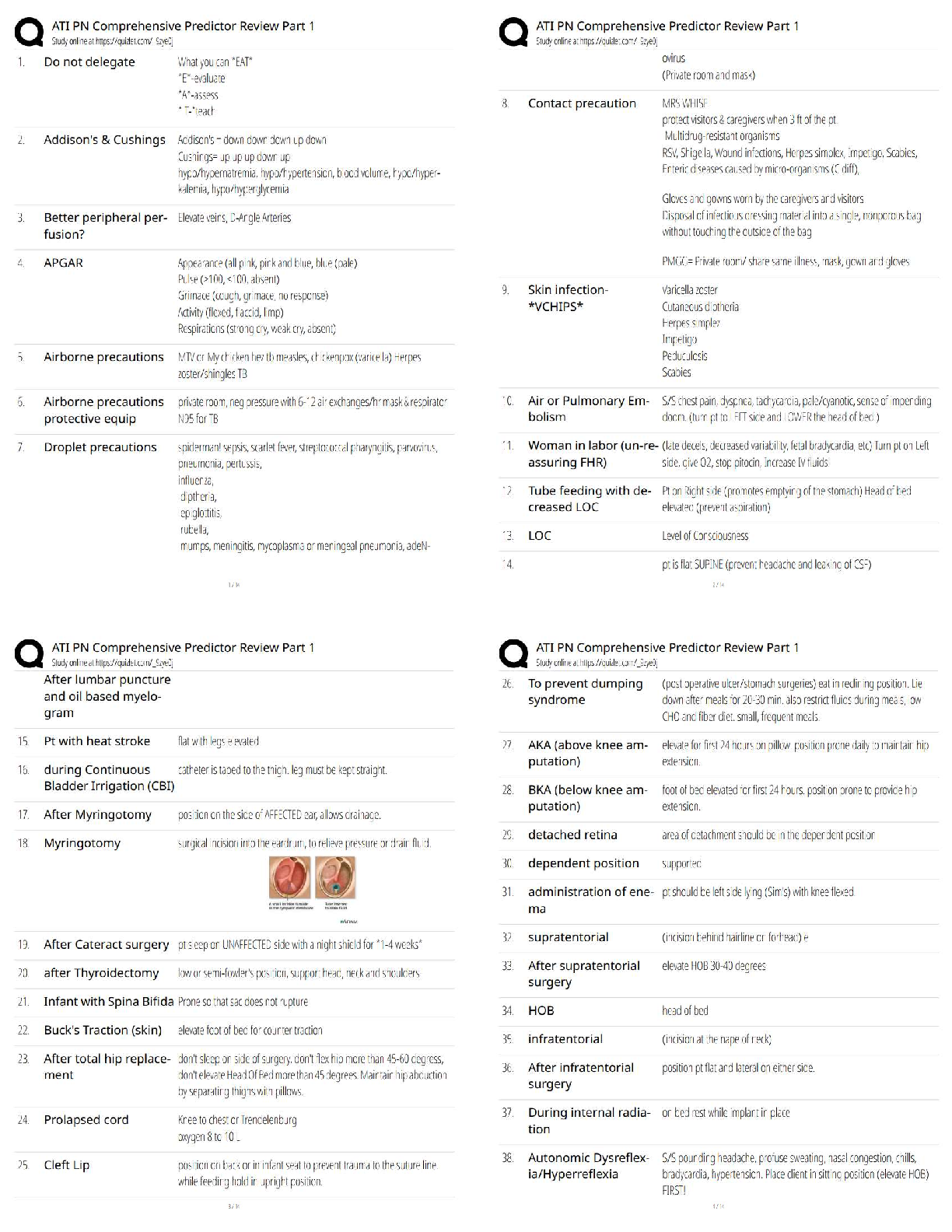
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. A client is diagnosed with anemia. The nurse realizes that which of the following could be the treatment for this client’s disorder?
1
...
Chapter 29--Hematological Dysfunction: Nursing Management
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. A client is diagnosed with anemia. The nurse realizes that which of the following could be the treatment for this client’s disorder?
1. Erythropoietin therapy
2. Leukemia
3. Poor nutrition
4. Trauma
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Anemias: Epidemiology
2. A client is diagnosed with alpha- and beta- defect thalassemia. The nurse realizes that this disease is common within which of the following cultural groups?
1. Persons from China
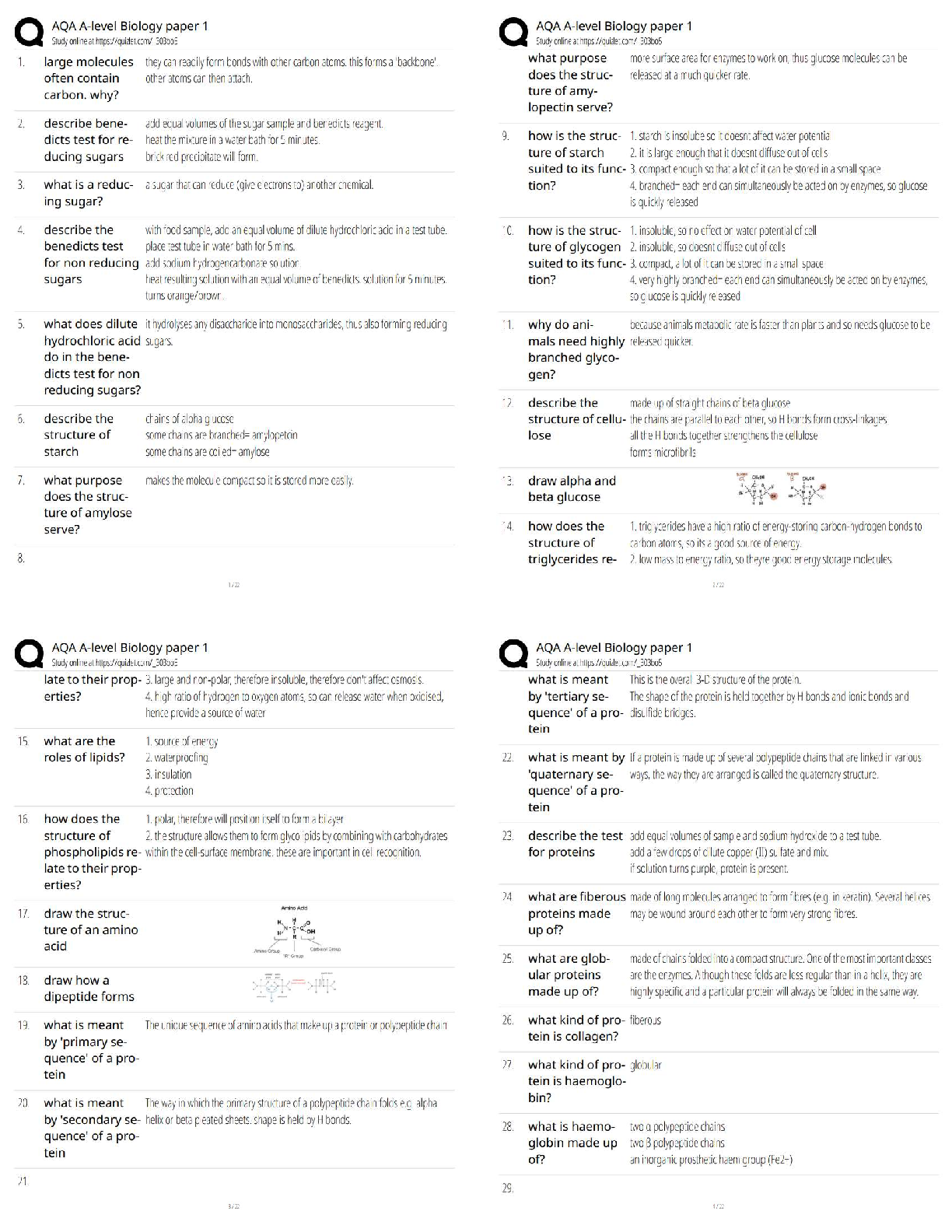
2. People of Mediterranean ancestry
3. African Americans
4. Persons from the Philippines
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Thalassemia: Epidemiology
3. The mother of a newborn is concerned since the baby is jaundiced. The nurse realizes that the infant should be assessed for which of the following anemias?
1. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
2. Hereditary spherocytosis
3. Sickle-cell anemia
4. Thalassemia
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Anemia: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
4. During the health history portion of the assessment, the client states, “I have sickle-cell trait.” The nurse realizes that:
1. precautions should be taken to prevent the cell from sickling.
2. the client is a carrier.
3. the client will show signs of the disease as she grows older.
4. the client will transmit the disease to any offspring.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Sickle-Cell Anemia: Etiology
5. A client diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia is recovering from a bone marrow transplant. Which of the following nursing interventions would not be appropriate for this client?
1. Assess for reactions to anesthesia.
2. Assess vital signs.
3. Maintain isolation precautions.
4. Obtain a low-pressure mattress to prevent skin breakdown.
.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Leukemia: Planning and Implementation
6. A client diagnosed with chronic disseminated intravascular coagulation is prescribed heparin. The nurse realizes that this medication is used to:
1. increase blood flow to the circulation.
2. increase blood clot formation.
3. decrease blood flow in the circulation.
4. decrease blood clot formation.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation: Pharmacology
7. The nurse should assess a client diagnosed with multiple myeloma for which of the following electrolyte imbalances?
1. Hypercalcemia
2. Hyperkalemia
3. Hypermagnesemia
4. Hypernatremia
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Multiple Myeloma: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
8. A client is receiving treatment for the diagnosis of hemophilia. Which of the following should the nurse assess in this client?
1. Appetite
2. Urine output
3. Muscle and joint pain
4. Respiratory rate
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Hemophilia: Assessment with Clinical Manifestations
9. A client is diagnosed with emphysema. For which of the following hematologic disorders should the nurse include in the assessment of this client?
1. Hemolytic anemia
2. Disseminated intravascular coagulation
3. Polycythemia
4. Hemophilia
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply REF: Polycythemia: Secondary Polycythemia
10. A client, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, is receiving the first phase of chemotherapy. The nurse realizes this client is in which phase of treatment for the disorder?
1. Induction
2. Consolidation
3. Maintenance
4. Central nervous system prophylaxis
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Pharmacology
11. The nurse is encouraging a client diagnosed with chronic leukemia to join a support group. Which of the following would a support group address?
1. Fatigue
2. Infection
3. Anxiety
4. Social isolation
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Box 29-6 Common Problems of Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
12. A client is diagnosed with stage II Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The nurse realizes that this diagnosis means the disease is:
1. terminal.
2. limited to lymph nodes on the same side of the diaphragm.
3. in the bone marrow.
4. easily treated.
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Box 29-8 Staging Hodgkin's and NHL
13. A client is diagnosed with disseminated low-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Which of the following treatments would be indicated for this client?
1. Administration of CHOP
2. Radiation therapy
3. Bone marrow transplant
4. Watch and wait
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze
REF: Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Planning and Implementation
MULTIPLE RESPONSE
1. A client is diagnosed with G6PD anemia. Which of the following medications should the nurse instruct the client to avoid? (Select all that apply.)
1. Acetaminophen
2. Aspirin
3. Chloroquine
4. Nitrofurantoin
5. Sulfonamides
6. Vitamin K
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Box 29-1 Medications that Heighten the Hemolytic Affects of G6PD
2. A client diagnosed with sickle-cell anemia is experiencing vaso-occlusive crisis. Which of the following interventions would be appropriate for this client? (Select all that apply.)
1. Administering oxygen
2. Decreasing hydration
3. Managing pain
4. Promoting activity
5. Encouraging rest
6. Restricting calories
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Sickle-Cell Anemia: Planning and Implementation
3. A client is having diagnostic tests to determine the cause of anemia. The nurse realizes that these tests will focus on which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
1. Presence of bleeding
2. Fluid balance
3. Disorders that cause red blood cell destruction
4. Cardiac functioning
5. Disorders that reduce the production of red blood cells
6. Digestion
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Anemias: Pathophysiology
4. A client tells the nurse that he is anemic because of a “poor diet.” Which deficiencies cause nutritional anemias? (Select all that apply.)
1. Iron deficiency
2. Folic acid deficiency
3. Vitamin C deficiency
4. Vitamin D deficiency
5. Vitamin A deficiency
6. Vitamin B-12 deficiency
PTS: 1 DIF: Analyze REF: Nutritional Anemias
5. Which of the following should the nurse instruct a client who is receiving treatment for the diagnosis of leukemia? (Select all that apply.)
1. See a dentist regularly.
2. Increase fluids.
3. Report any fatigue to the physician.
4. Expect to have frequent coughs and colds.
5. Use a sunblock when outdoors.
6. Report gastrointestinal distress to the physician.
PTS: 1 DIF: Apply
REF: Box 29-5 General Nursing Care for Patients with Leukemia
[Show More]