Statistics > EXAM > Statistics Modeling and Finance QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 100% CORRECT (All)
Statistics Modeling and Finance QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
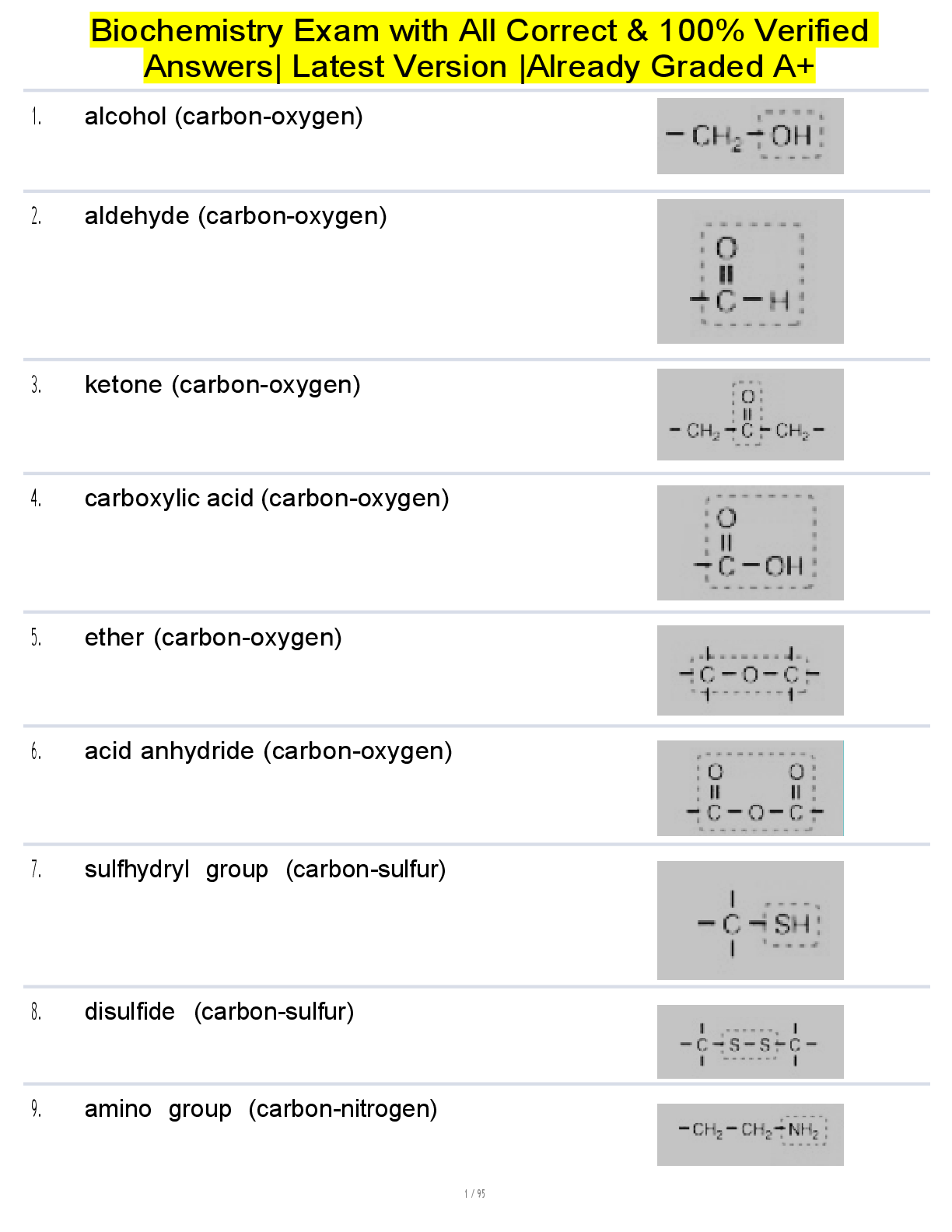
Statistics Modeling and Finance QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 100% CORRECT Opinion Correct answera view, judgment, or appraisal formed in the mind about a particular matter. descriptive statistics Correct ... answerA branch of statistics concerned only with characterizing, or describing, a set of numbers. The measures used to characterize a set of data (e.g., average, maximum, coefficient of dispersion) or charts and tables depicting the data. inferential statistics Correct answerThe process of drawing conclusions about population characteristics through analysis of sample data. graph Correct answerA chart or visual representation of data relying on references to two axes, which may be either numerical or categorical in scale. For example, a scatter plot is a graph referencing two numerically scaled axes, whereas a bar chart is a graph referencing one numerical axis and one categorical axis. Graphic analysis Correct answerQuantitative techniques used to identify and measure adjustments to the sale prices of comparable properties; a variant of statistical analysis in which an appraiser interprets graphically displayed data visually or through curve fit analysis. Graphs can also be used to support and exhibit value trends for comparison elements in qualitative analysis. variable Correct answerIn statistics, a characteristic or attribute of an item, service, or individual that can change from observation to observation. For example, improved living area is a characteristic of a house that can change with each observation. dependent variable Correct answerThe variable being estimated (outcome or response variable) in a predictive model such as a multiple linear regression equation. Trend Correct answerA series of related changes brought about by a chain of causes and effects. Trends are forecast through economic base analysis, statistical analysis, market analysis, and analysis of economic indicators and surveys. Random Relationship Correct answerSometimes variables are not related. There is no causal effect exerted by the independent variable on the dependent variable. A scatter diagram will also reveal if there is no relationship. Negative Relationship Correct answerScatter diagrams can also record negative relationships. We said that a positive correlation trends up and to the right. A negative relationship moves up and towards the left. That would mean a higher amount of one variable would lead to a lower price in the other variable. Your stock went from $125 to $97.25 in three years. What is the average percent change per year? Correct answer-7.4% "Quantitative techniques used to identify and measure adjustments to the sale prices of comparable properties; a variant of statistical analysis in which an appraiser interprets graphically displayed data visually or through curve fit analysis" is the definition of _____________ analysis. Correct answerGraphic A chart or visual representation of data relying on references to two axes, which may be either numerical or categorical in scale" is the definition of Correct answergraph A(n) _______________ is defined as "a characteristic or attribute of an item, service, or individual that can change from observation to observation." Correct answervariable "The process of drawing conclusions about population characteristics through analysis of sample data" defines ___________ statistics. Correct answerinferential All the charts and graphs in the course were prepared using Correct answerMicrosoft Excel Central tendency Correct answerThe central point, or representative value, around which items cluster in a frequency distribution. The measures of central tendency (called averages) are the mean, the median, and the mode. mean Correct answerA measure of central tendency. The sum of values for a variable in a sample or population divided by the number of items in the sample or population. The arithmetic average. Universe Correct answerIn statistics, a population or entire body of data; used to distinguish between a population and a sample obtained from the population. Population is a more generally used term. Sample Correct answerIn statistics, a subset of a population selected for analysis. parameter Correct answer1. A constant or value used to index a function, such as use of degrees of freedom to derive an appropriate t-statistic or F-statistic function. Aggregate Correct answerThe sum of all the observations within a population; e.g., the aggregate sale price of all the houses sold in a given community. median Correct answermeasure of central tendency identified as the middle value in an ordered array of numerical values mode Correct answerA measure of central tendency consisting of the numerical value or categorical characteristic that occurs most frequently in a sample or population. The ________ is most affected by extreme values. Correct answermean The _______ describes the central position in an array. Correct answermedian Central tendency is part of ________________ statistics. Correct answerdescriptive "The listing of a set of observations, such as sales ratios, in a specific order, e.g., alphabetical, alpha-numeric, chronological, order of magnitude" is the definition of Correct answerarray "In statistics, a population or entire body of data" is the definition of Correct answeruniverse universe Correct answerIn statistics, a population or entire body of data; used to distinguish between a population and a sample obtained from the population. Population is a more generally used term. sample Correct answerIn statistics, a subset of a population selected for analysis. random sample Correct answerIn statistics, the result of a sample selection process where all the numbers of a population or population stratum have the same probability of being selected. Bias Correct answerIn statistics, a systematic error. A statistic is biased if it systematically differs from the population parameter being estimated, such as the average sale price. An example in appraisal valuation modeling would be if the model results in consistently overvalued or undervalued properties. stratified random sample Correct answerA statistical sample in which the population is divided into one or more essential subgroups or strata, with random samples drawn from each subgroup. nonprobability sample Correct answerA sample produced by an unscientific, non-random selection process; for example, a nonprobability sample may be a sample based upon an appraiser's judgment about which cases to select or based on a convenience sample. Range Correct answerIn statistics, the difference between the highest and lowest values in a set of numbers. Deviation Correct answerThe amount a variable's value differs (i.e., deviates) from the mean or some other benchmark. average absolute deviation Correct answerThe sum of the absolute deviations divided by the number of observations. Absolute deviation Correct answerThe difference between an observation and the measure of central tendency (such as the arithmetic mean or median) for that array, without regard as to the sign (positive or negative) of the difference. standard deviation Correct answerThe square root of the variance. The sample standard deviation is the square root of the sample variance and the population standard deviation is the square root of the population variance; i.e., the square root of the sum of the squared deviations from the mean divided by either the population size or by the sample size minus 1. Degrees of freedom Correct answerIn statistics, the number of values in a calculation of a statistic that are free to vary. For example, if a sample of size four adds up to a sum of 50, only three of the sample values can vary. Once the three varying sample items values are ascertained, the fourth sample item value will be known with certainty and must be equal to the unique number required to equate to a sum of 50. Therefore, the degrees of freedom in this example is n - 1 = 3. normal distribution Correct answerA theoretical distribution often approximated in real-world situations. It is symmetrical and bell-shaped. normal curve Correct answerA symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that represents the distribution of a population of certain types of measurements or the frequency distribution of all possible means in large samples that may have been drawn from an unknown population distribution. Also known as a normal distribution or normal probability distribution. In a normal distribution, approximately ____ % of the observations fall within two standard deviations (+ or -) from the mean. Correct answer95 "A sample produced by an unscientific, non-random process", for example a sample based on an appraiser's judgment or a convenience sample is a ____________ sample. Correct answernonprobability The deviation as shown on a chart would be measured by the difference from the observation to the mean measured by a line that runs __________to the line of the mean. Correct answerperpendicular "A theoretical distribution often approximated in real-world situations. It is symmetrical and bell-shaped" is the definition of Correct answernormal distribution A random sample is not Correct answerbiased "The difference between the highest and lowest values in a set of numbers" defines Correct answerrange An appraiser calculates the mean of a set of numbers, and then subtracts the mean from each number, adds up these differences without regard to sign, and divides this sum by the number of items. What has the appraiser calculated? Correct answeraverage deviation In statistics, "a systematic error" is called Correct answerbias In a normal distribution, approximately ____ % of the observations fall within one standard deviation (+ or -) from the mean. Correct answer68 Measures of dispersion would include all of the following EXCEPT mode standard deviation range average deviation Correct answerMode The difference between an observation and the measure of central tendency for that array, without regard as to the sign of the difference, is the Correct answerabsolute deviation A large sample consists of ______ or more observations. Correct answer30 Which of the following can be used in the analysis of dispersion? Correct answerRange confidence interval Correct answerIn statistics, the specification of a zone within a population, based on a sample mean and its standard error, within which the true mean most probably lies. Standard error Correct answerThe standard deviation of a regression coefficient estimate. Also, the standard deviation of regression errors (residuals). Forecasting Correct answerTo estimate, calculate, or indicate in advance. Forecasts made by appraisers are based on past trends and the perceptions of market participants concerning their continuation or alter [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 21 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 16, 2022
Number of pages
21
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 16, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
58