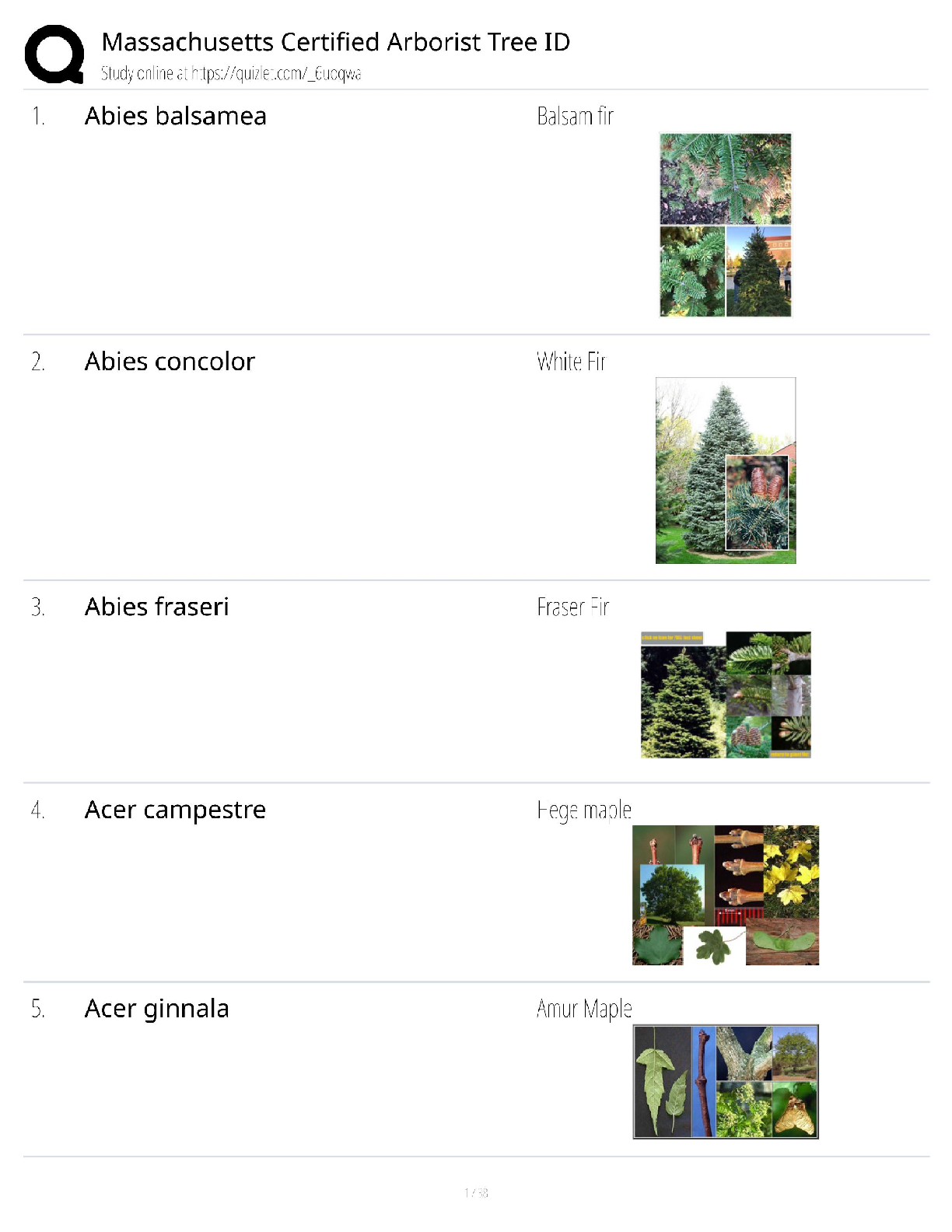
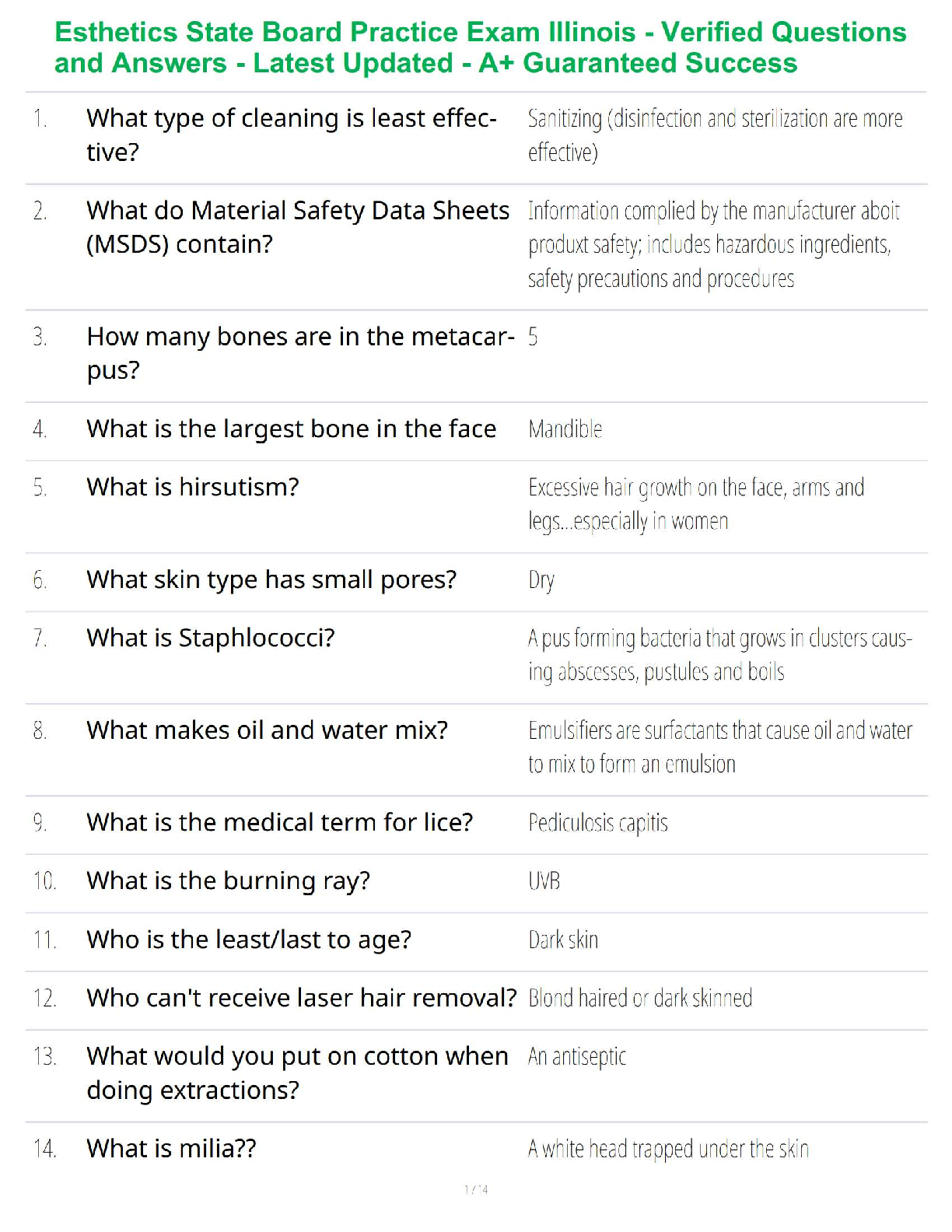
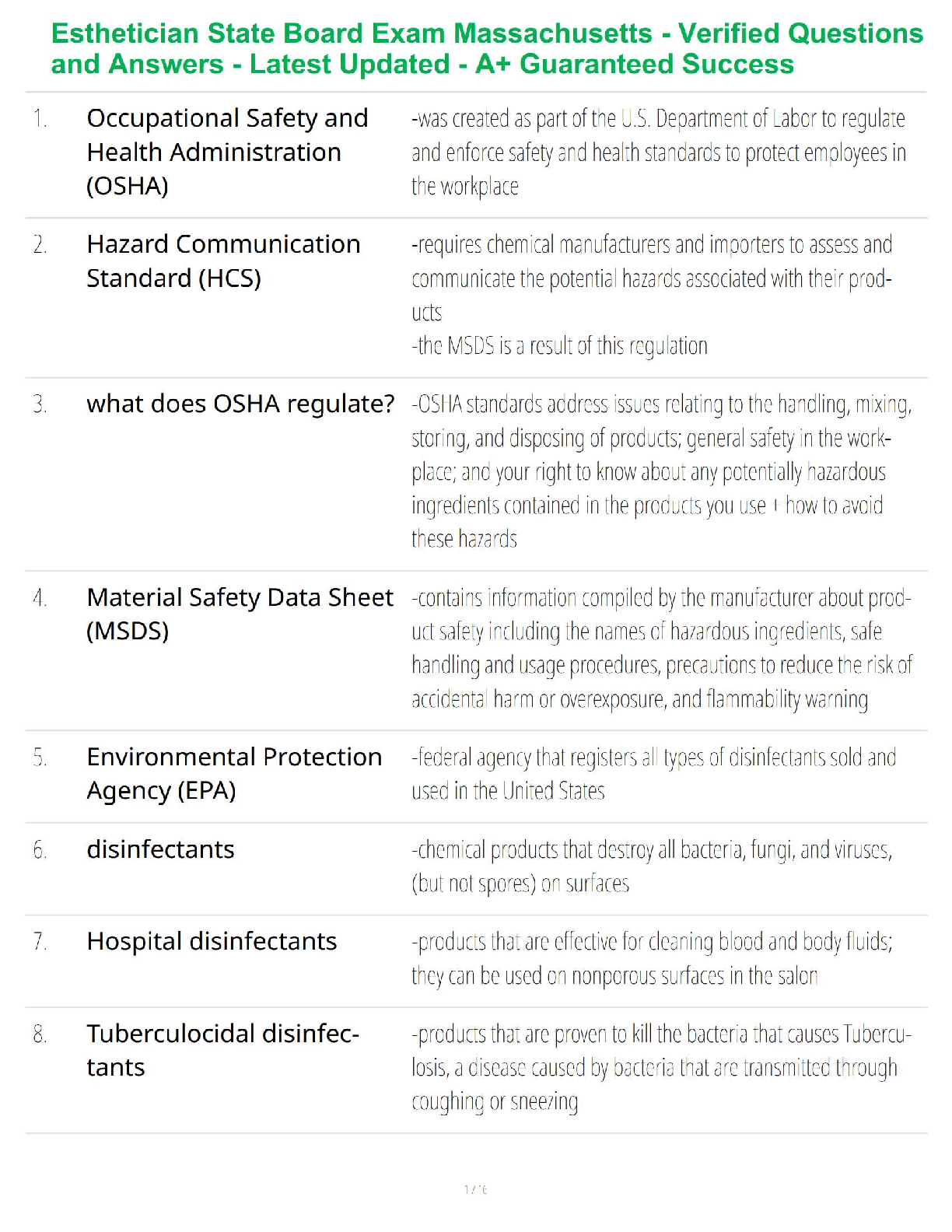
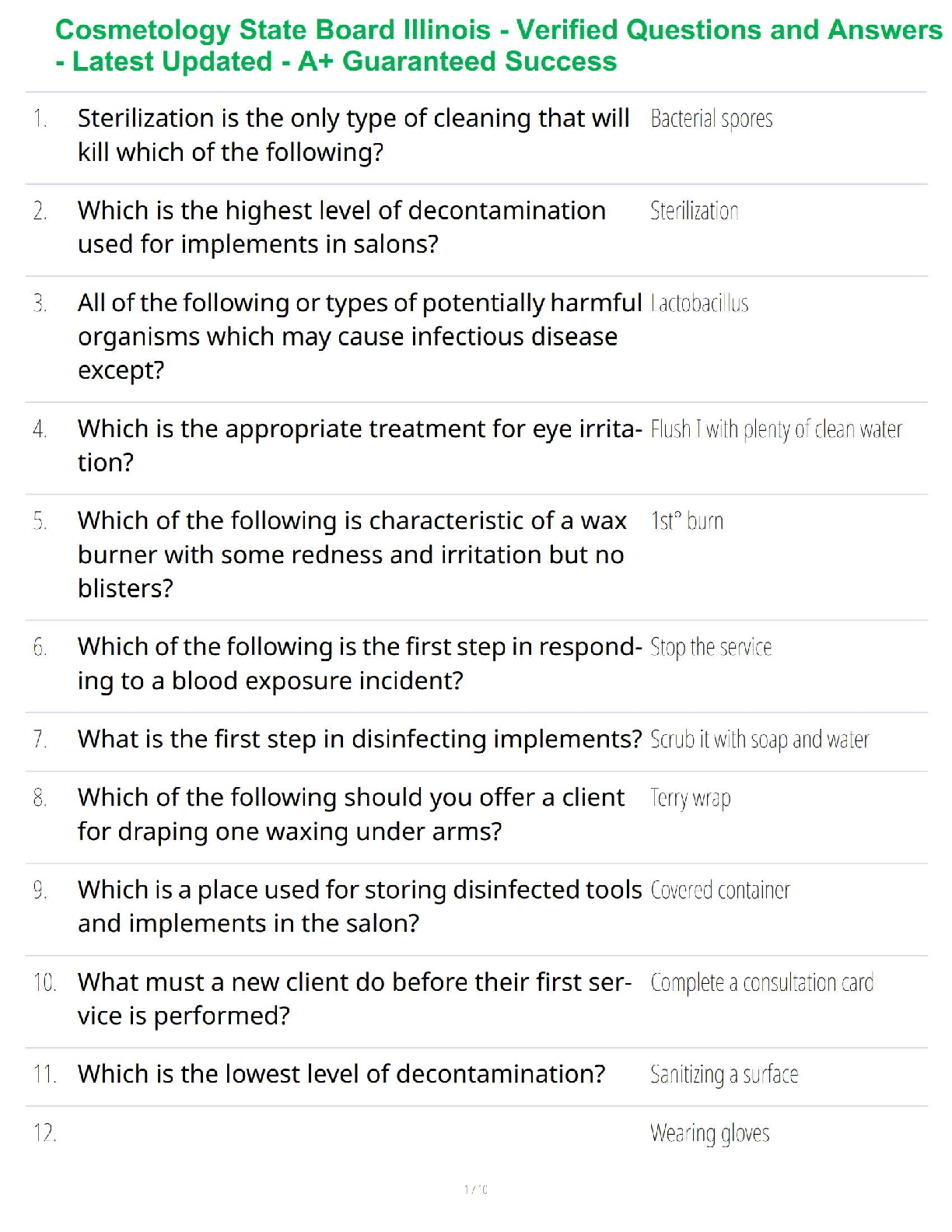
WGU c181 OA study guide
checks and balancesAns- each branch has a power to say no to the other 2 branches.
balancing out all 3 branches so 1 doesn't become more powerful
central ideas of federalist paper 51Ans-
...
WGU c181 OA study guide
checks and balancesAns- each branch has a power to say no to the other 2 branches.
balancing out all 3 branches so 1 doesn't become more powerful
central ideas of federalist paper 51Ans- that separation of powers and checks and
balances will prevent mob-rule. if powers distributed even between 3 branches
BiacameralAns- having two branches or chambers in the legislative branch
enumerated powersAns- Powers specifically given to Congress in the Constitution;
including the power to collect taxes, coin money, regulate foreign and interstate
commerce, and declare war.
Necessary and Proper Clause/Elastic ClauseAns- Constitutional clause that gives
congress the power to make all laws "necessary and proper" for executing its powers
FederalismAns- a form of government in which power is divided between the federal, or
national, government and the states( each state has different rules they have to follow
but then there are more rules that the whole country has to follow)
Federalist Paper #10Ans- No faction (group with a common political purpose) or interest
group can control or take over power. The 3 branches of government make sure that
does not happen
judical reviewAns- the right of the Supreme Court to determine if a law violates the
Constitution
Lemon v. Kurtzman (1971)Ans- 1971 must not discourage or advance religion and does
not entangle the government with religion.
Citizens United v. Federal Election CommissionAns- ruled that individuals, corporations,
and unions could donate unlimited amounts of money to groups that make independent
political expenditures. (ex. super PACS)
Sherbert v. Verner (1963)Ans- a lady declined a job because the job conflicted with her
religion. it was forcing her to give up her religious beliefs because they wouldn't give her
unemployment benefits
Tinker v. Des Moines (1969)Ans- Students have the right to symbolic speech at school
as long as it is not disruptive
District of Columbia v. Heller (2008)Ans- Individuals have a right to own a loaded
handgun at home for self defense
McDonald v. Chicago (2010)Ans- The right of an individual to "keep and bear arms"
cannot be ban by
[Show More]
.png)









.png)