Mathematics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Questions and Answers > MATH 451 Shadow Price. (All)
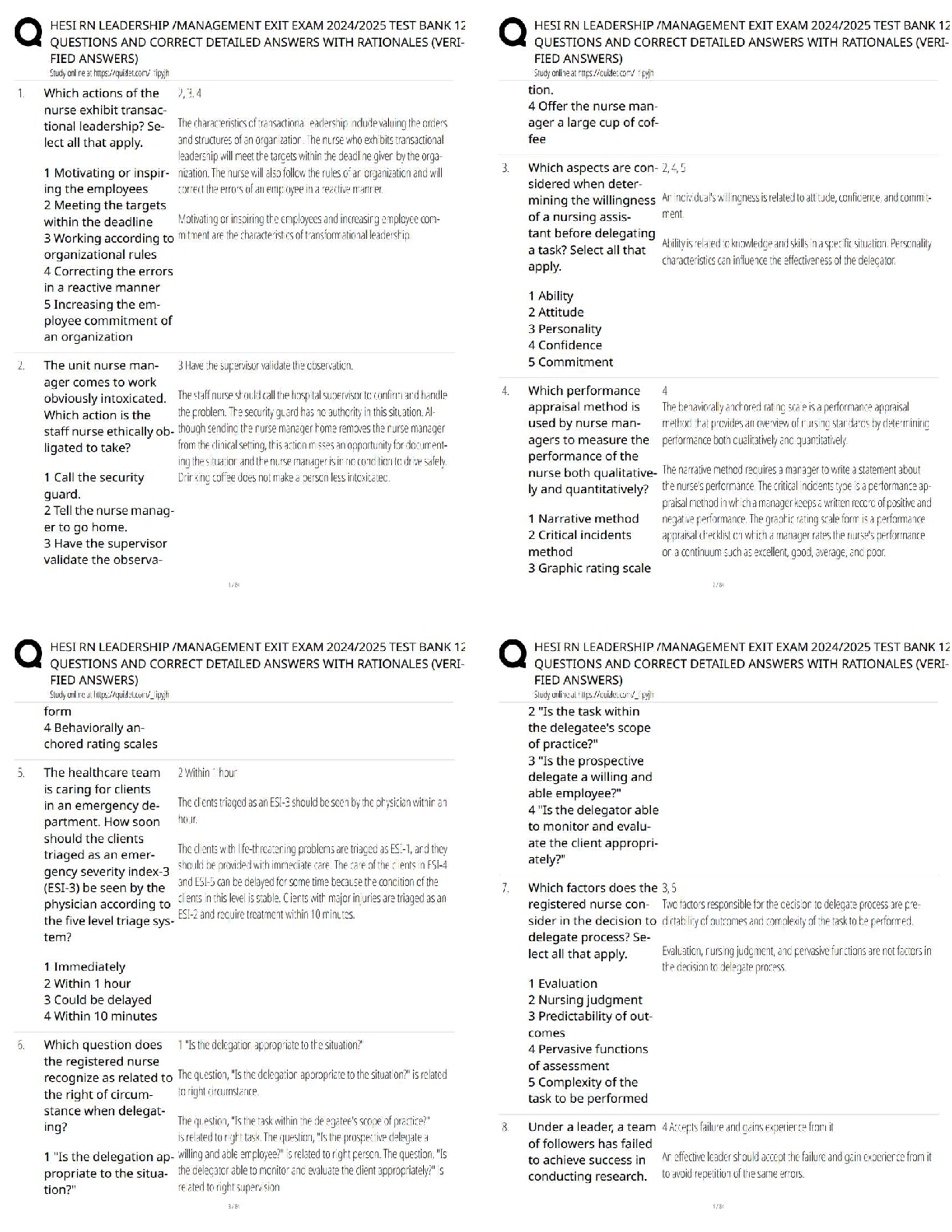
Questions and Answers > MATH 451 Shadow Price.
Document Content and Description Below
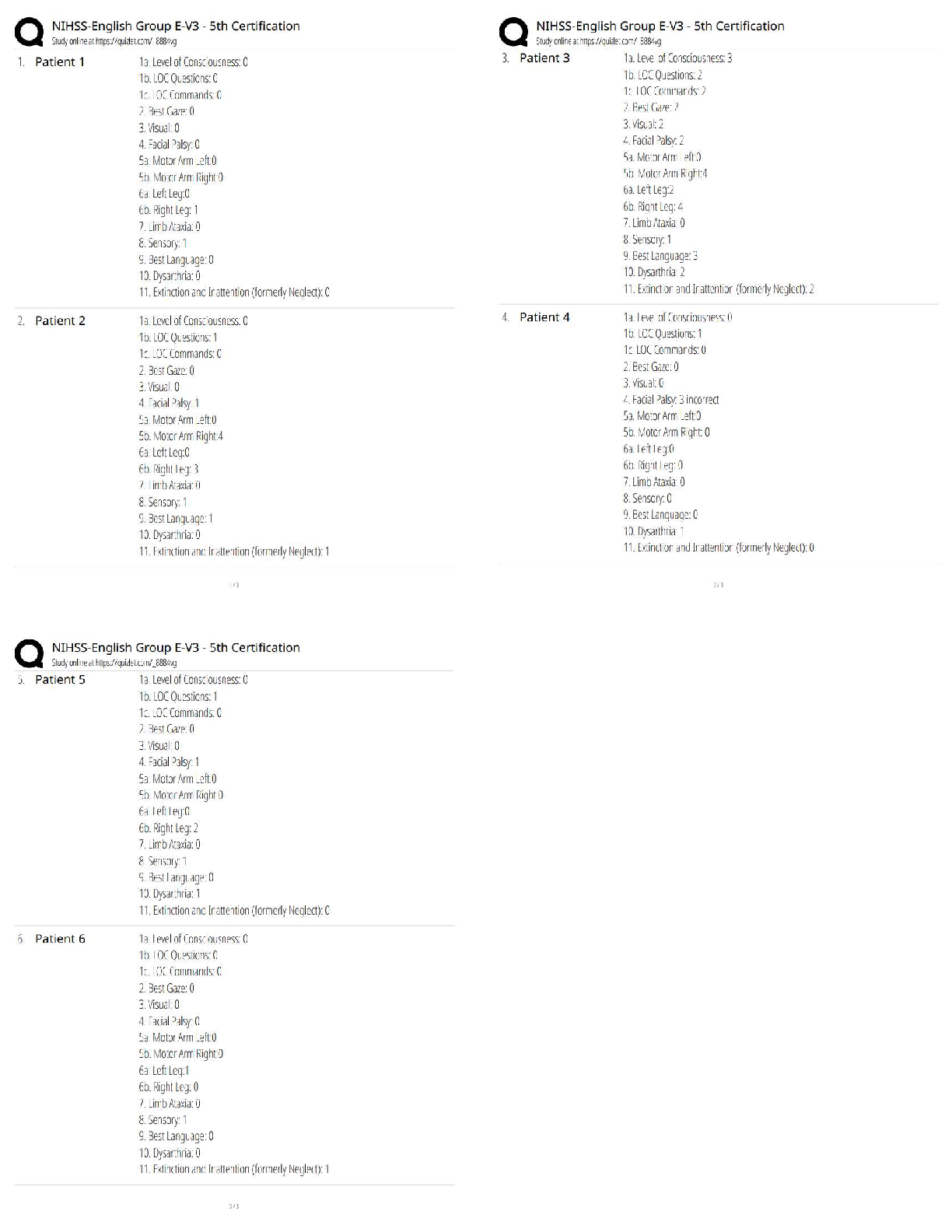
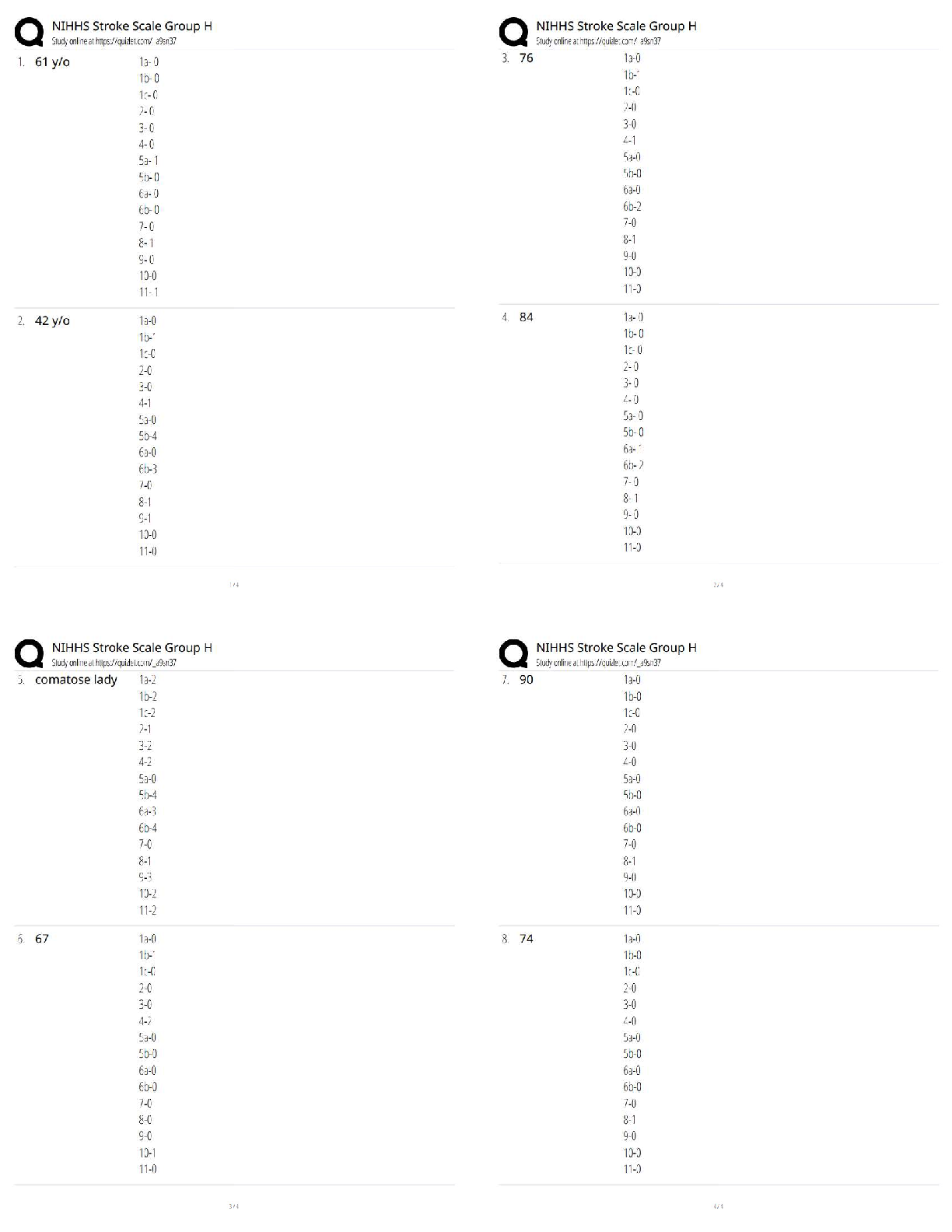
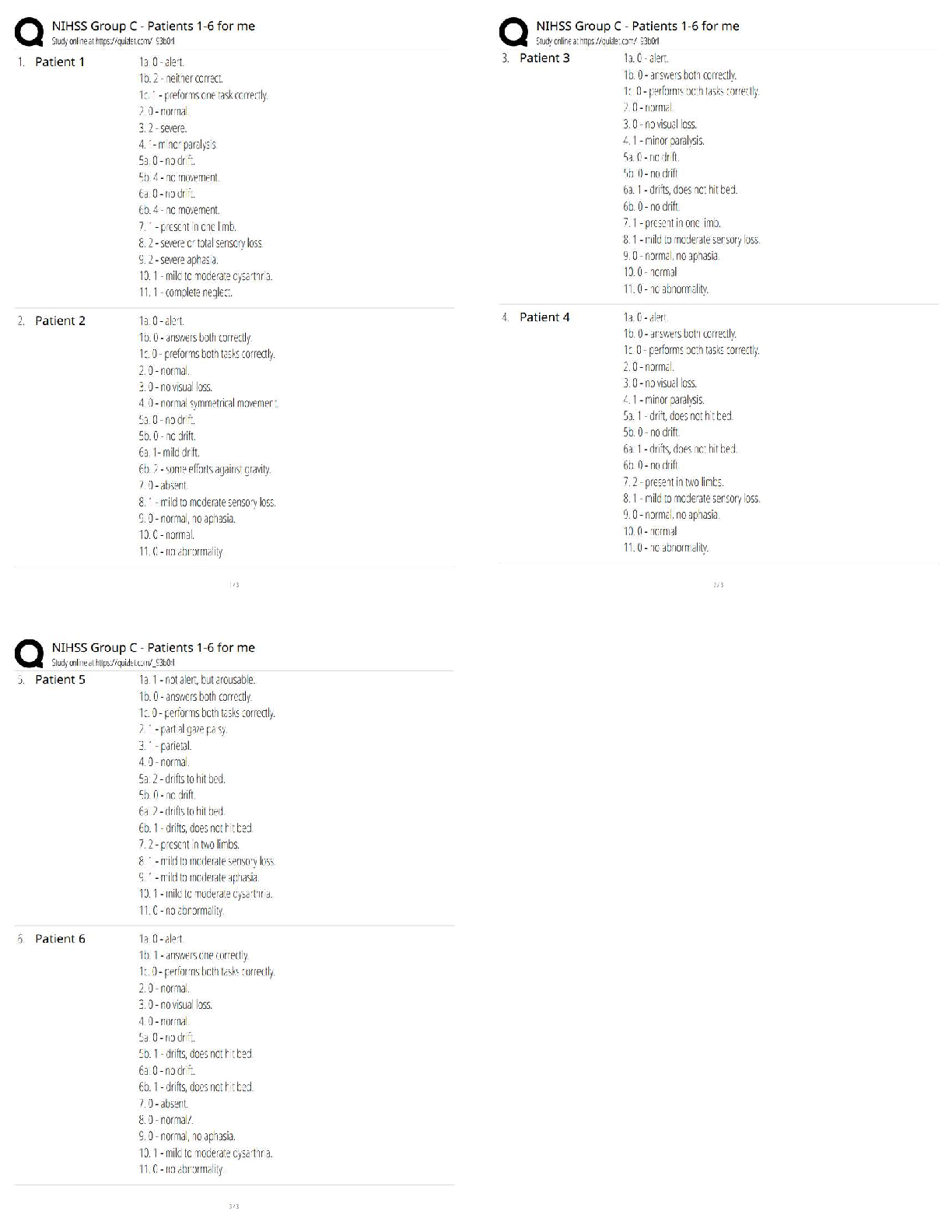
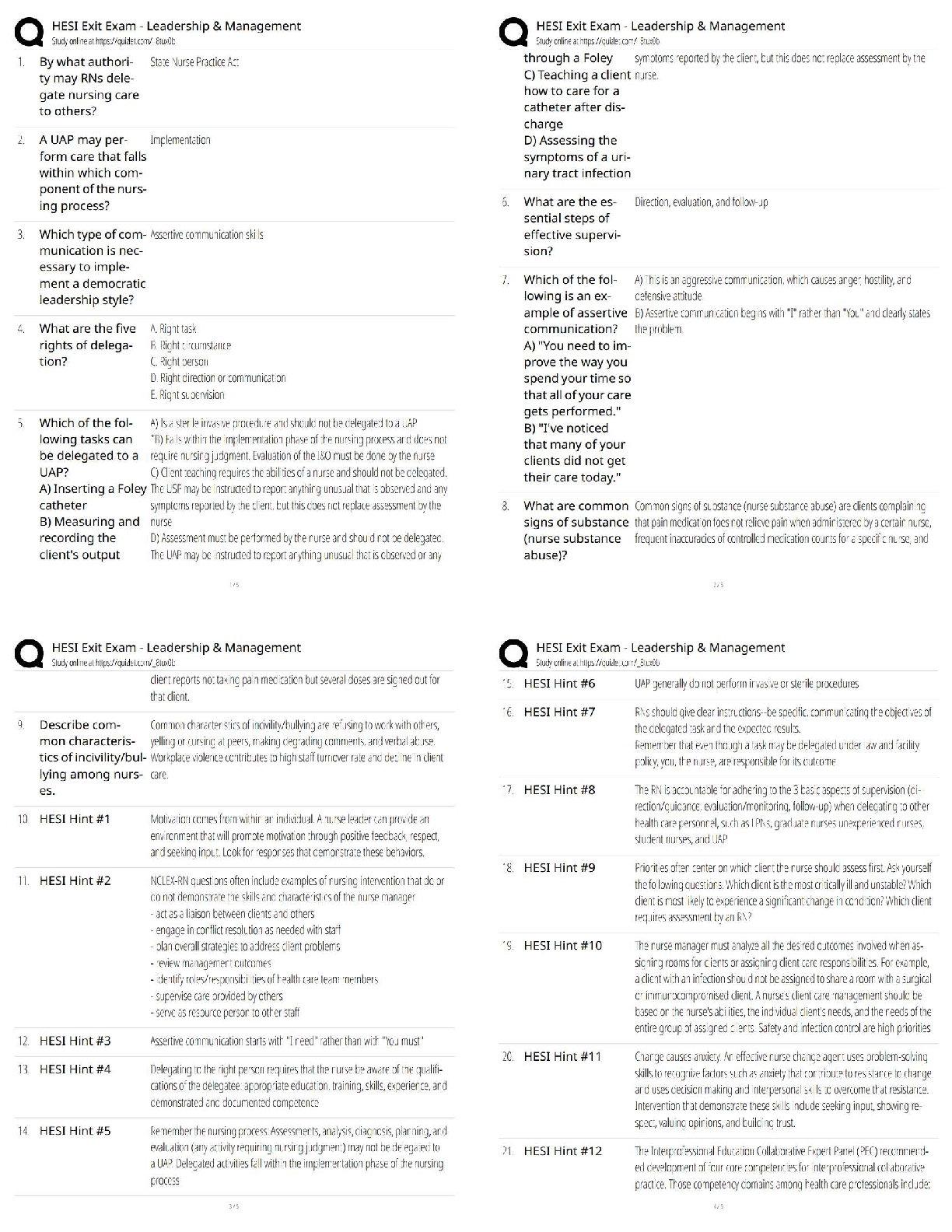
MATH 451 Shadow Price Introduction With changes to the constraints in a decision model, the profit will vary. The profit from one variable may increase, while the other decreases. The change in th ... e profit can be represented as an amount per hour. The change is the shadow price. Learning Materials What is shadow price? By definition, the shadow price is the magnitude of the change in the objective function value for Profit and Shadow Price Realistically, the profit will not continue to increase by the shadow price without limits. Increasing and Decreasing the RHS Increasing the right-hand side (RHS) of a ≤ constraint endlessly will eventually make it a Example In a furniture store problem: Maximize profit = $7T + $5C subject to constraints 3T + 4C ≤ 2,400 (carpentry time) binding 2T + 1C ≤ 1,000 (painting time) binding C ≤ 450 (maximum chairs allowed) T ≥ 100 (minimum tables required) T and C ≥ 0 (nonnegativity) Optimal Solution The optimal solution is to produce 320 tables and 360 chairs for a maximum profit of $4,040. . Sensitivity Report Here is the Sensitivity Report for the furniture store problem. Understanding the Results The shadow price for the carpentry hours of $0.60 measures the impact on profit for a unit Revised Scenario Revise the RHS constraint for the carpentry hours to increase from 2,400 to 2,600 hours. The What happens when RHS exceeds the allowable increase in the optimal solution? Has the constraint become a redundant constraint? In the given Constraints portion of the sensitivity report, what is the shadow price for testing hours? 6.25 27.5 0 200 Increasing the RHS of a ≤ constraint __________ will make it a redundant constraint. endlessly slightly relatively moderately The shadow price remains valid if the RHS changes remain in the __________. (Choose 2) allowable increase and decrease values same scope allowable range constraints A shadow price of $0.30 for an assembly constraint indicates the __________ will increase $0.30 for each additional hour of assembly. (Choose 2) profit objective function value objective function coefficient (OFC) total cost Which of the following is true about the shadow price for a resource? It measures the range of variability of a resource's constraint. It measures the impact on profit for a one-unit change in a resource's usage. It measures the allowable increase in a resource. It measures the maximum usage possible for a resource. What is the allowable increase for the assembly hours in the given Constraints portion of the sensitivity report? 560 200 400 350 Question 2 Additional nonelectronic components add __________ contribution to the profit. a significant little zero an insignificant The shadow price is the __________ of the change in the objective function value for a 1-unit increase in the RHS of a constraint. amount unimportance insignificance total Increasing the RHS of a ≤ constraint __________ will make it a redundant constraint. slightly relatively moderately infinitely If the right-hand side (RHS) of a constraint exceeds the allowable increase in the optimal solution, what happens to the shadow price? It does not change. It increases up to the change in the constraint's RHS value. It is reduced by the amount of the excess in the constraint's RHS value. It becomes 0. If a resource has a shadow price of $3.60 and the use of that resource is increased by 100 hours, which is within the acceptable range, what would be the profit increase? $36.00 $100.00 $3,600.00 $360.00 Which of the following best describes shadow price? The magnitude of the change in the objective function value for a one-unit increase in the right-hand side (RHS) value of a constraint The effect of the optimum amount used of a resource in relation to the right-hand side (RHS) constraint The magnitude of a resource constraint in relation to the cost of one unit of the resource The alternative price derived from a change in the objective function value for a one-unit increase in the right-hand side (RHS) value of a constraint A change in profit can be represented as __________. an amount per resource a misuse of a constraint only an increase a resource use over a constraint's right-hand side (RHS) value Summary The shadow price is the change in the objective function value when there is a change to a righthand side (RHS) constraint by 1 unit. The shadow price from the optimal solution is valid for a range of change in the RHS constraint’s value. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

THIS BUNDLE CONTAINS: Colorado Technical University MATH 451 Units Quizzes&Exams for Essentially the Entire Course Needs.
Questions and Answers > Colorado Technical University MATH 451-1404B-Transportation Model Questions and Answers > Colorado Technical University MATH 451-1404B-Minimal Spanning Tree Questions and...
By QuizMaster 3 years ago
$38
16
Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 02, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 02, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
151