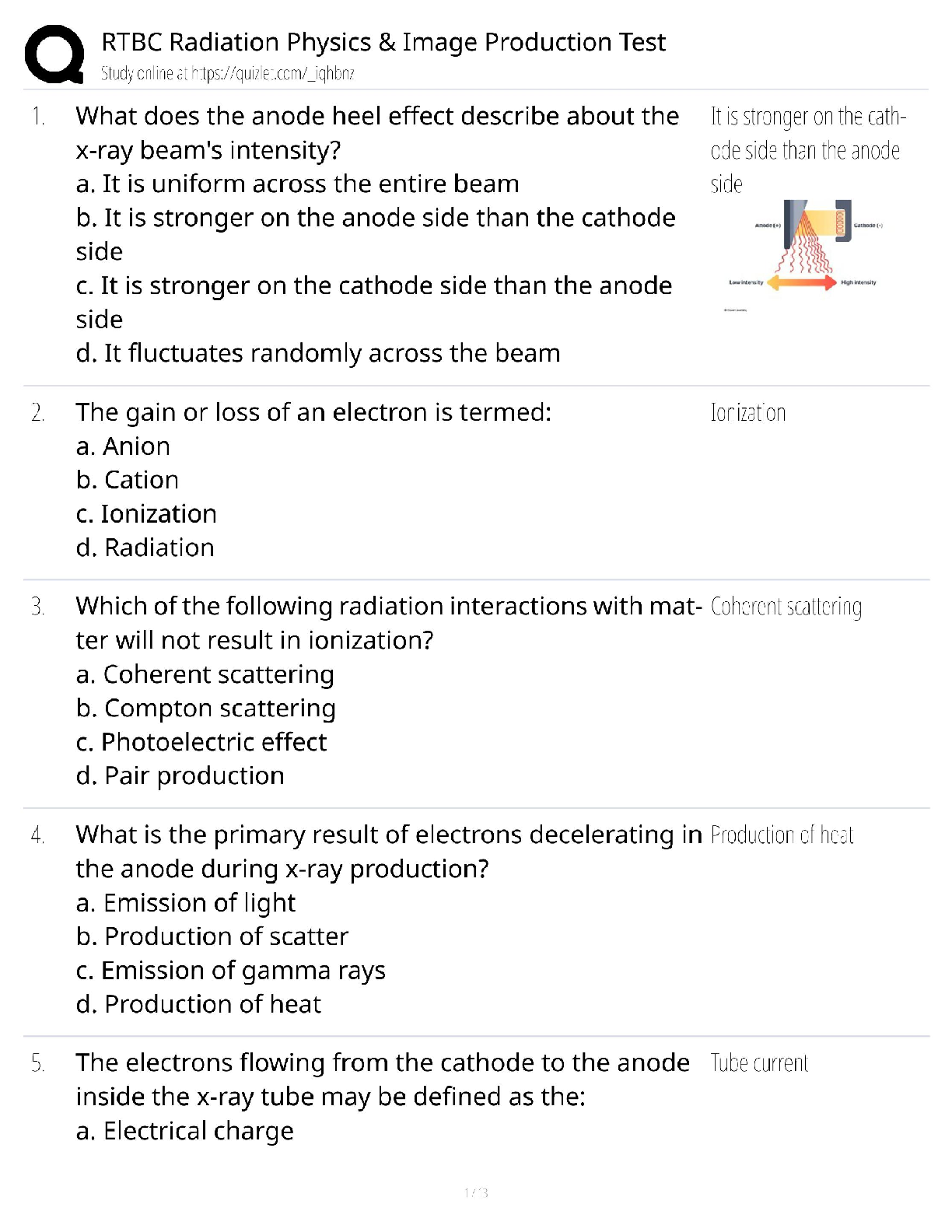
Identify, define and apply the concepts of the following terms
Healthy People 2020
o Provides science-based national objectives and goals across all life stages, esp. reducing rate of fetal
& infant deaths, rate of
...
Identify, define and apply the concepts of the following terms
Healthy People 2020
o Provides science-based national objectives and goals across all life stages, esp. reducing rate of fetal
& infant deaths, rate of maternal mortality, reducing preterm births, reducing C-section births among
low-risk women.
o To have healthy moms & babies the mom needs to maintain a healthy lifestyle and needs to have
access to medical care. RN responsibility is to both mom and fetus – 2 pts
o EMTLA – emergency medical treatment & labor act – ensures that anyone coming to the hospital
(ER) uninsured will be treated
Problems with the US Healthcare system- define and solutions
o Expensive, inaccessible (lack of money, transportation, childcare, physicians refusing to take
Medicaid)
US has higher cost of healthcare than the next 12 countries on the list. Physician involvement
with nurse practitioners is required in all states except 16 (costly). Most insurance will not
reimburse mid wives or nurse practitioners fully.
o Vulnerable populations: women, pregnant, minorities, incarcerated, homeless, etc.
o Info on the internet helpful for pts to become involved in their own care
o Infant mortality may be affected by financial, educational, sociocultural, and behavioral factors.
Barriers to care must be removed and services modified to meet needs.
Trends in Fertility and Birth rate
o Low Birth weight & preterm birth – increases risks for morbidity & mortality
o Morbidity and Mortality both maternal and infant – incidence higher in AA babies. Factors: limited
maternal education, young maternal age, unmarried status, poverty, lack of prenatal care, smoking,
poor nutrition, alcohol use, maternal health conditions.
Maternal mortality rate small, but a problem b/c most are preventable (usually HTN,
infection, hemorrhage, CV disease – major cause)
o Obesity – more than 1/3 women in US obese; racial disparity, increases risk from HTN & diabetes;
also decreased fertility, congenital anomalies, miscarriage, fetal death
Trends in Nursing Practice
o Specialization, advanced degrees, certification programs
o Nurses in advanced practice may provide primary care
Standards of Practice and Legal Issues
o Legislation enacted for mothers/babies to stay in hospital at least 48 hrs after vag birth & 96 after
cesarean if desired
o AWHONN (Association of Women Health Care & Neonatal Nursing) publishes standards of practice &
education for perinatal nurses: “Standards & Guidelines for Professional Nursing Practice in the Care
of Women & Newborns),” including an evidence-based approach to practice
Must document! RN can be sued by pts for up to 18 yrs & 3 mos after delivery
o “Failure to rescue” - a death after a treatable complication. RN failed to recognize or act on early
signs of distress. Must identify complication through careful surveillance and put appropriate
measures in place through quick action.
1
o Sentinel event – “unexpected occurrence involving death or serious physical or psychological injury,
or risk thereof. Serious injury specifically includes loss of limb or function.” - any maternal death
related to process of birth, perinatal death unrelated to congenital condition, infant discharge to
wrong family, severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, etc.
Chapter 2 – Community Care and Culture
Identify Family
Primary unit of socialization – whoever the pt considers to be family (nuclear, extended, multigenerational,
no-parent, married-blended, cohabiting parent, single parent, homosexual)
Identify cultural factors and the implications for nursing; define culture
Using childbearing beliefs and practices identify, define, and provide culturally appropriate care
Definitions
o Subculture – a group within a larger cultural system that retains its own characteristics
o Acculturation – changes that occur w/in a group when mixing or contacting other cultures – often in
times of crisis or change (like childbearing) a woman may rely on old cultural patterns even after
acculturation
o Assimilation – when cultural group loses identity & becomes part of dominant culture
o Ethnocentrism – the view that one’s own culture’s way of doing things is best
o Cultural relativism – the opposite of ethnocentrism
Culture has a direct effect on health
Nurse’s role: develop cultural competence and integrate it into the nursing care plan, often considering
health promotion rather than illness care
Some main differences:
o Childbearing beliefs & practices
o Personal space
o Time orientation
o Family roles
Important to recognize disparity between nurse’s culture & pt’s culture, educate & promote healthy
behaviors in cultural context that has meaning for pts, apply abstract cultural knowledge in a practical way,
have respect for differences (including nontraditional & alternative), recognize importance of culturally
different communication styles, problem-solving techniques, concepts of space & time, and desire to be
involved with care decisions
Communication often the most challenging part obstacle for nurses working with people from other
cultures. Use translators/interpreters when necessary
Review pg. 27 (K)
Identify, define and provide appropriate nursing care to vulnerable Populations
Vulnerable populations are groups who are at higher risk for development of physical, mental, or social
health problems, with racial and ethnic disparities existing for a number of health conditions and services
o Women in general
o socioeconomically disadvantaged
o racial & ethnic minorities (poverty, higher rates of chronic disease, preterm labor, LBW)
o adolescent girls (risky behaviors, misinformed)
o older women (chronic illness)
[Show More]
.png)













.png)