MSMIT CSC550Week1_hw
Chapter 2_Problems
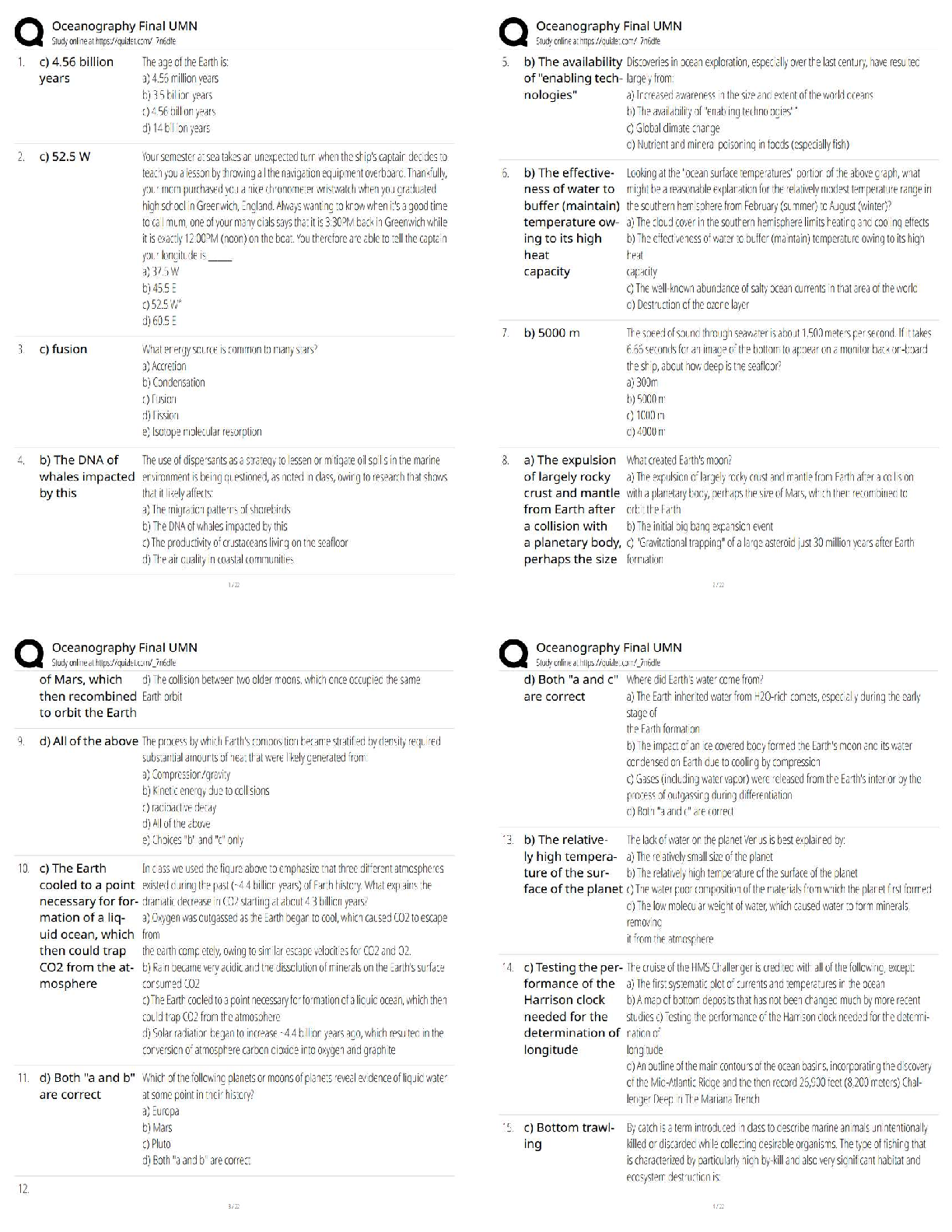
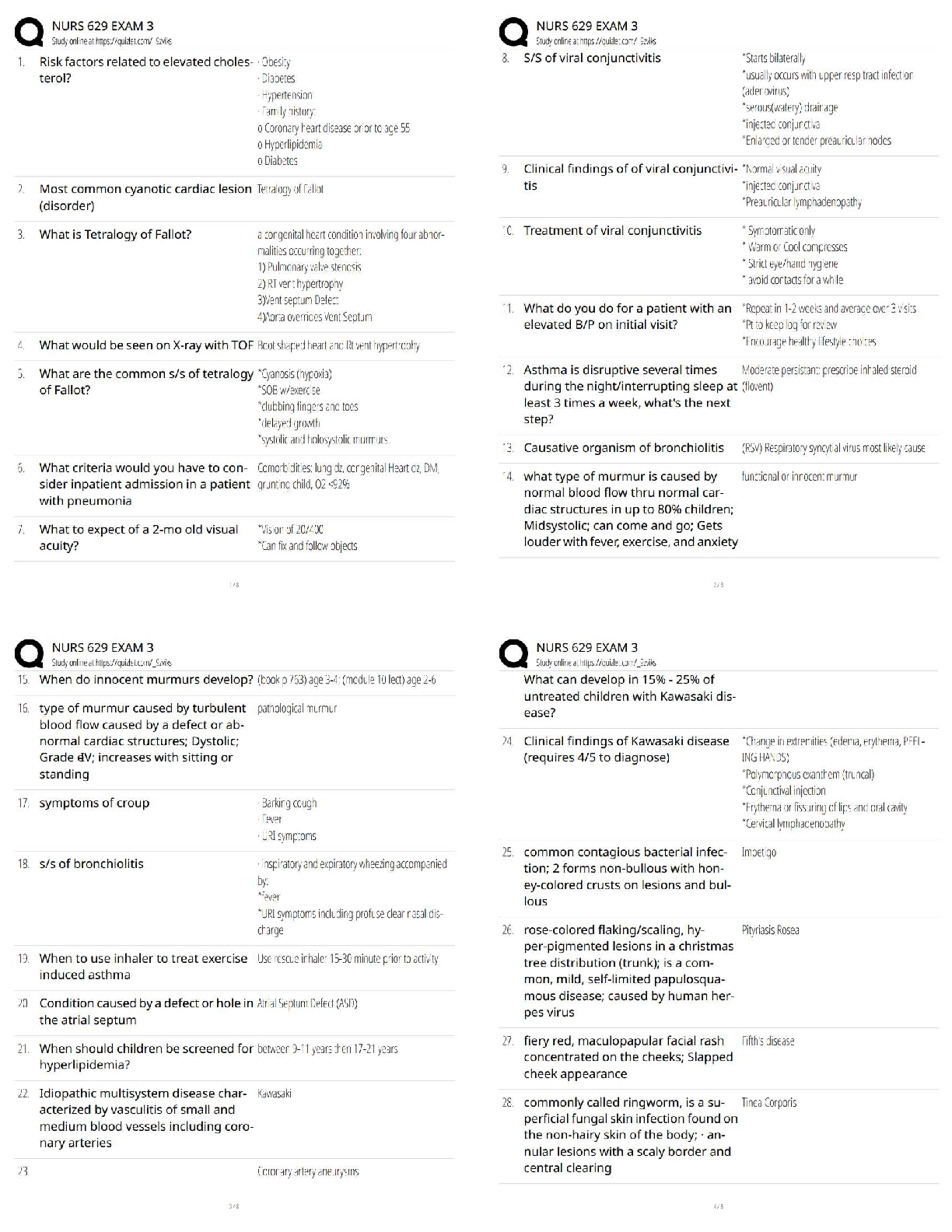
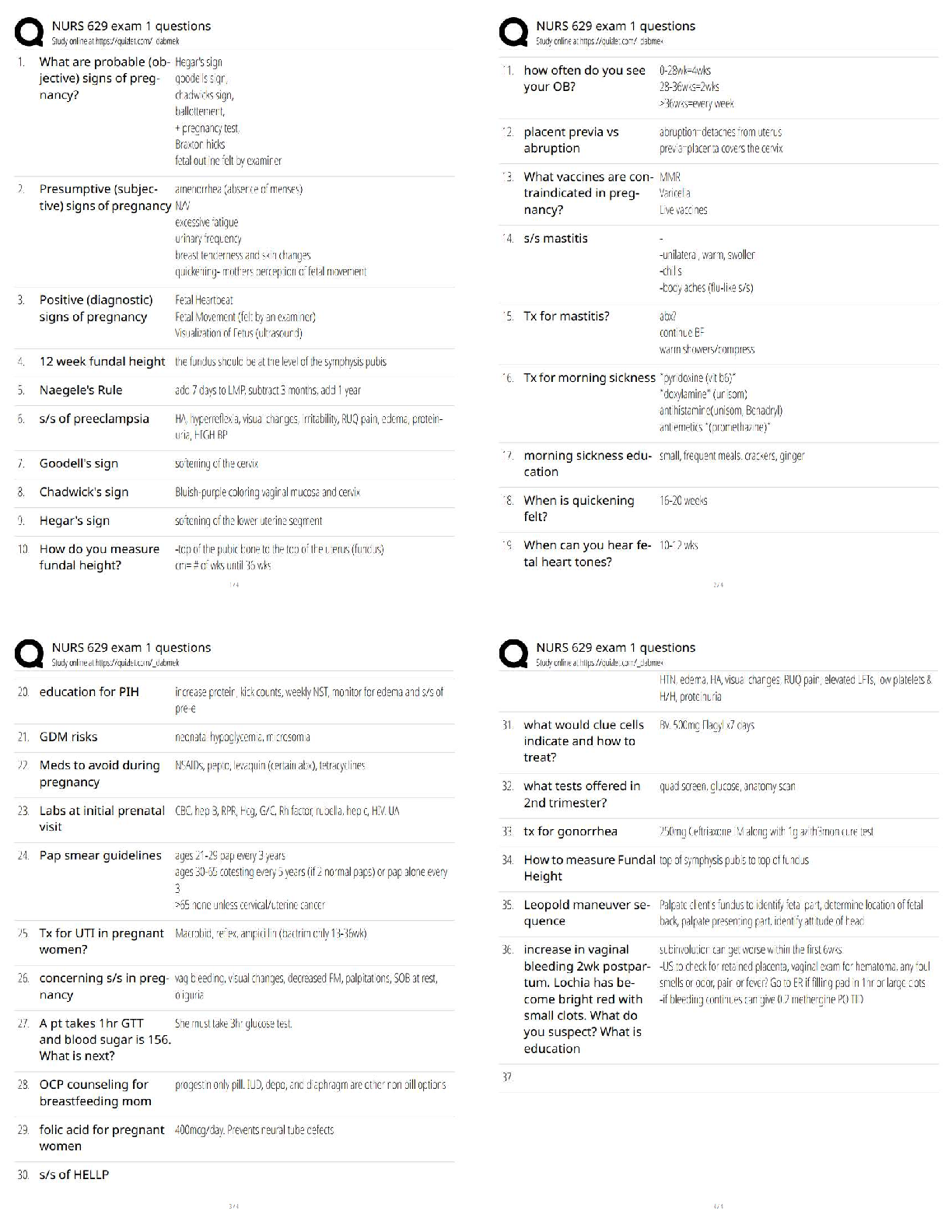
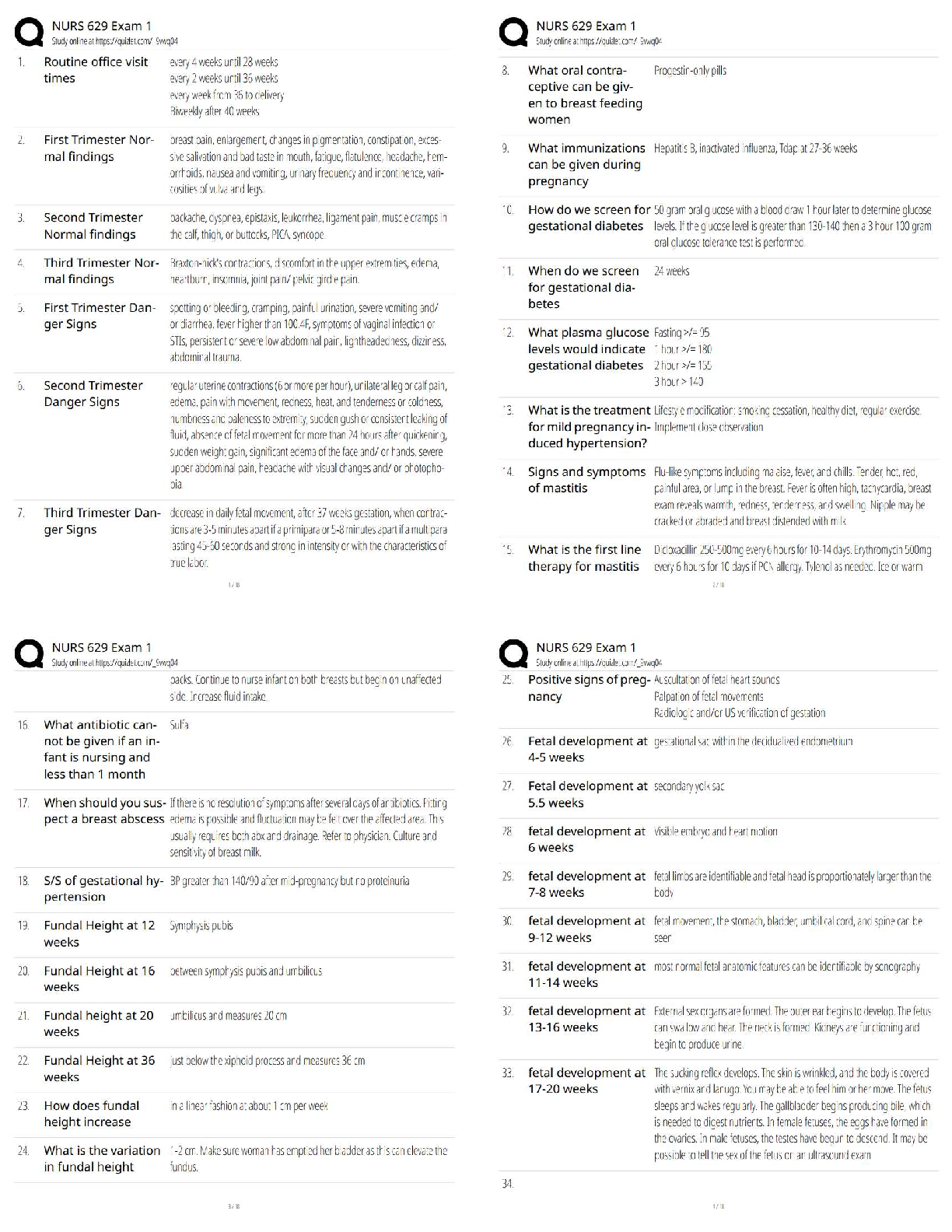
1. Assuming that data mining techniques are to be used in the following cases, identify whether the task required is supervised or unsupervised learning.
(a)Deciding whet
...
MSMIT CSC550Week1_hw
Chapter 2_Problems
1. Assuming that data mining techniques are to be used in the following cases, identify whether the task required is supervised or unsupervised learning.
(a)Deciding whether to issue a loan to an applicant based on demographic and financial data (with reference to a database of similar data on prior customers).
(b)In an online bookstore, making recommendations to customers concerning additional items to buy based on the buying patterns in prior transactions.
This is unsupervised learning, because there is no obvious outcome whether the recommendation has been followed or not.
(c) Identifying a network data packet as dangerous (virus, hacker attack) based on comparisons to other packets whose threat status is known.
This is supervised learning, because the result of identification is known.
(d) Identifying segments of similar customers.
This is unsupervised learning because there is no known possible outcome.
(e) Predicting whether a company will go bankrupt based on comparing its financial data
to those of similar bankrupt and nonbankrupt firms.
This is supervised learning, because financial data has been used to find the
result.
(f ) Estimating the repair time required for an aircraft based on a trouble ticket.
This is supervised learning, because the value of outcome of repair time is
known.
(g) Automatic sorting of mail by zip code scanning.
This is supervised learning, because there is a outcome of sorting.
(h) Printing of customer discount coupons at the conclusion of a grogery store checkout
based on what you just bought and what others have bought recently.
This is unsupervised learning, because no obvious outcome, it is hard to guess
about other customers.
2. Describe the difference in roles assumed by the validation partition and the test partition.
3. Consider the sample from a database of credit applications shown in Figure 2.13. Comment on the likelihood that it was sampled randomly, and whether it is likely to be a useful sample.
5. Using the concept of overfitting, explain why when a model is fit to training data, zero error with those data is not necessarily good.
8. Normalize the data in Table 2.3.
Normalization of a measurement is obtained by subtracting the average from
each measurement and dividing the difference by the standard deviation.
10. Two models are applied to a dataset that has been partitioned. Model A is
considerably more accurate than model B on the training data, but slightly less accurate
than model B on the validation data. Which one are you more likely to consider for final
deployment.
[Show More]
.png)