Mathematics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Fundamentals of Mathematics for Nursing (All)
Fundamentals of Mathematics for Nursing
Document Content and Description Below
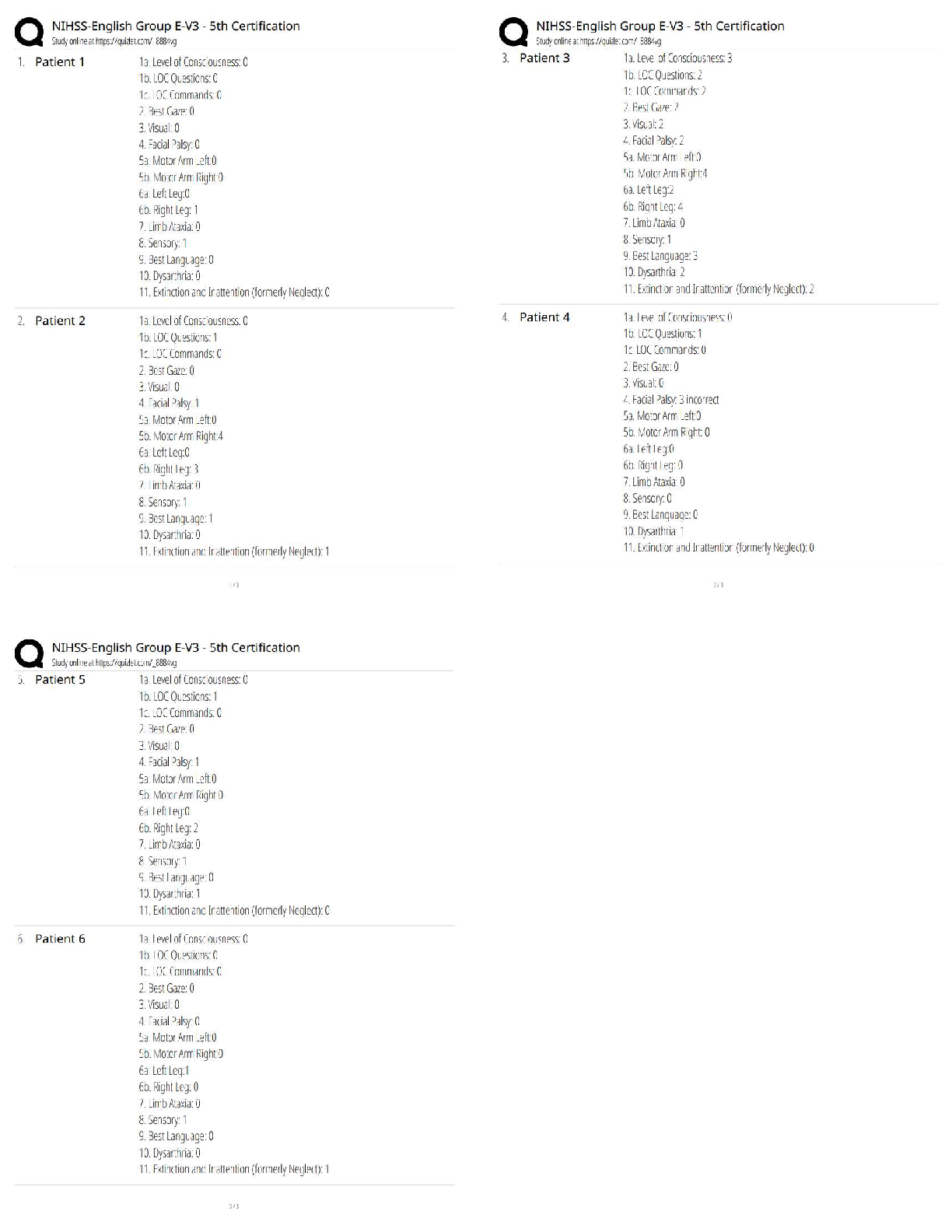
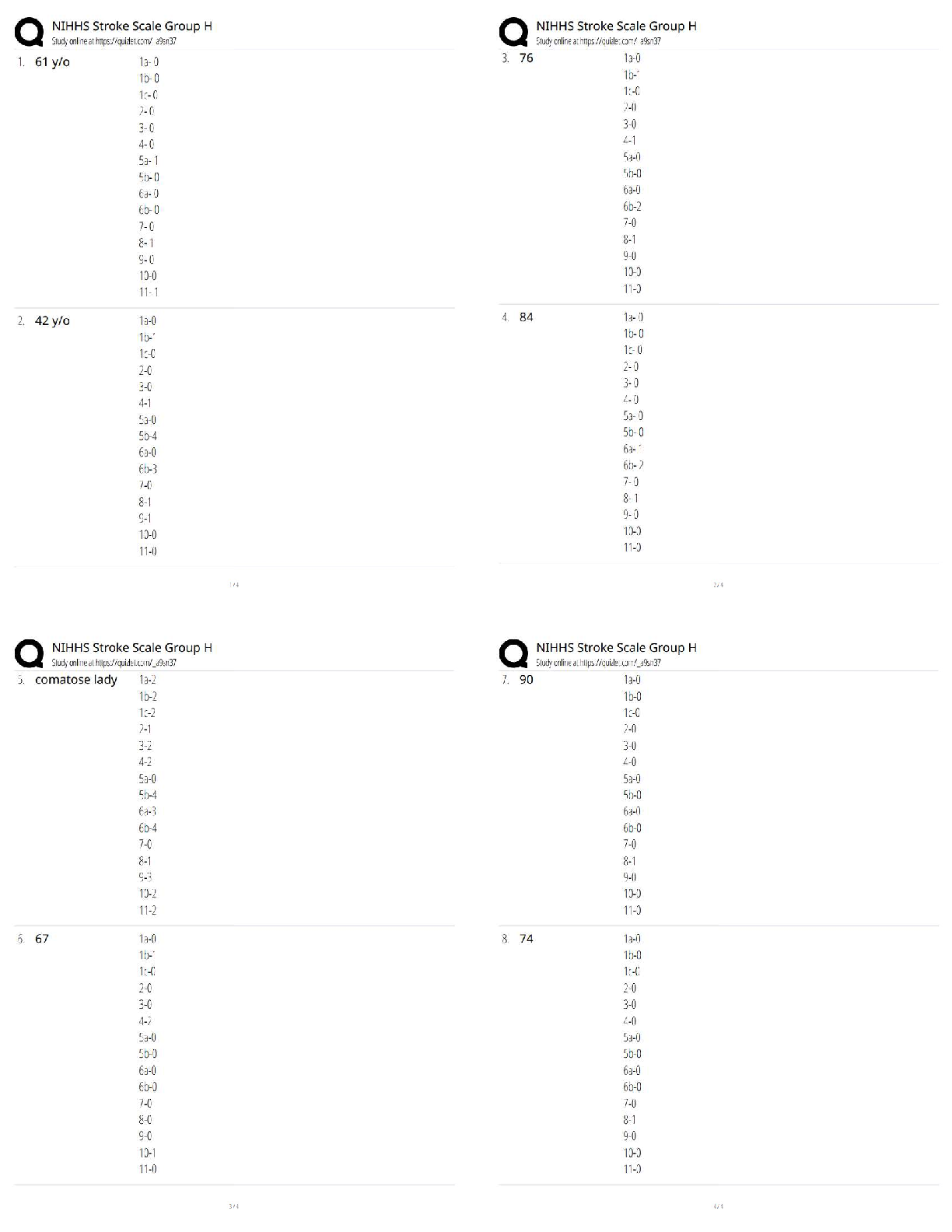
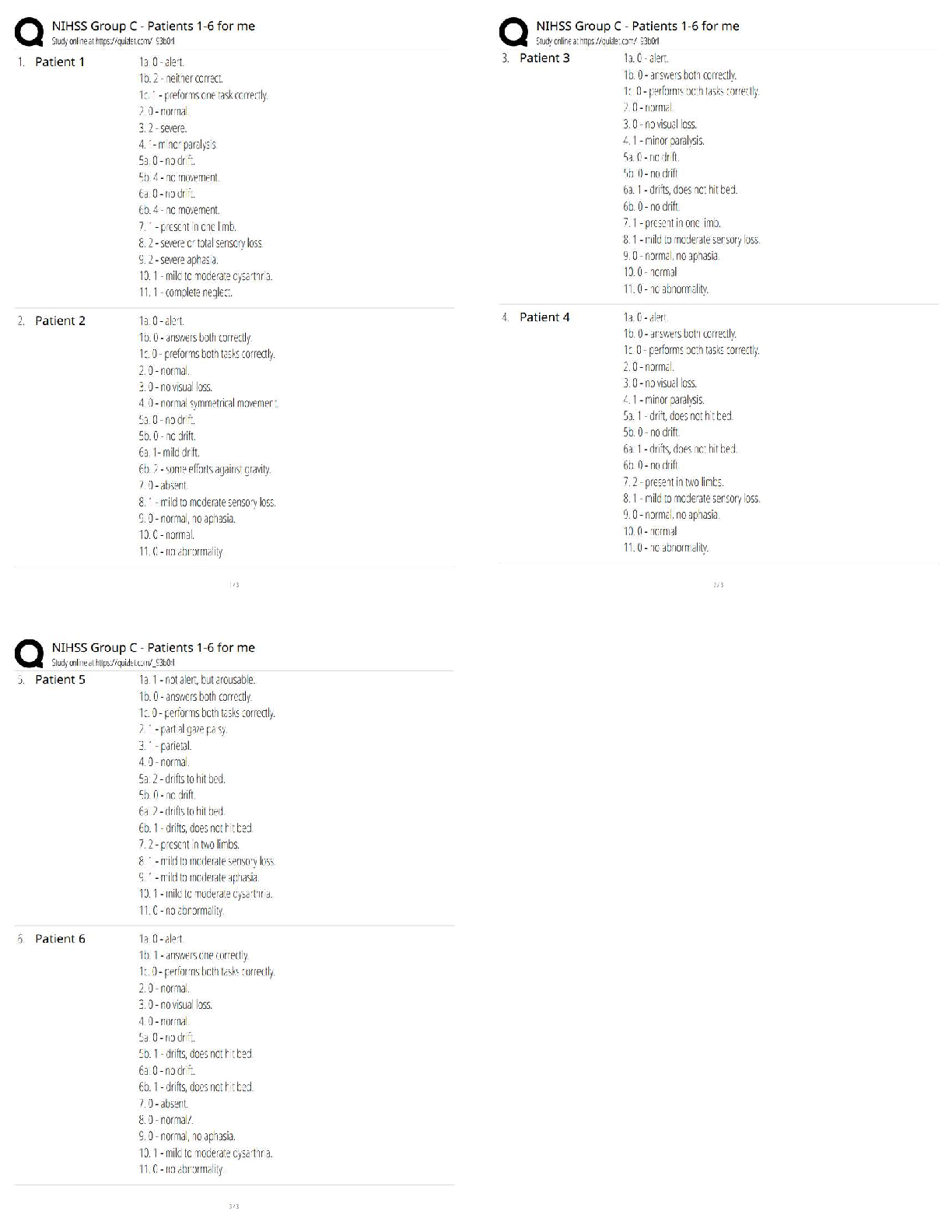
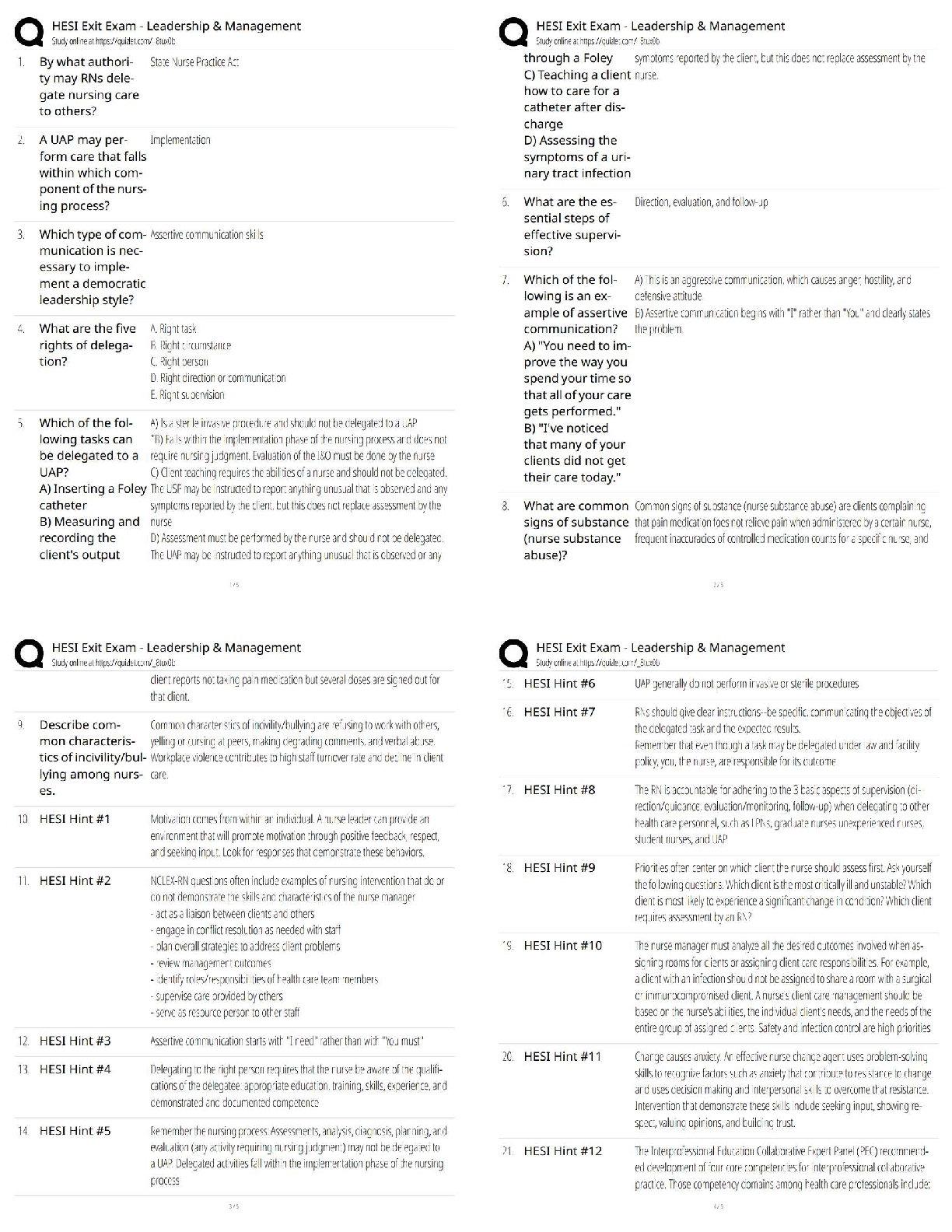
PART A BASIC MATH REVIEW The following section serves as a review of basic math principles and allows students to identify any areas that will require further study. Students who find they need fur ... ther development in basic math should refer to the table of math resources on page 5. Answers for practice problems are located in Part G, beginning on page 48. I = 1 V = 5 X = 10 L = 50 C = 100 D = 500 M = 1000 The basic form is to place the larger numerals to the left and add other numerals. XXXIII = 33 (30 + 3 = 33) There is an exception to the basic form. If smaller numeral precedes a larger numeral, the smaller should be subtracted from the larger. IX = 9 (1 - 10 = 9) If there seems to be several ways of writing a number - use the shorter form. XVVI - incorrect XXI - correct (10 + 10 + 1 = 21) Only one smaller numeral is allowed to precede a larger numeral. XCV = 95 - correct IXCV - incorrect (10 - 100 = 90 + 5 = 95) Numerals may be written as lower case letters and the number one may have a line and/or a dot over it. . .. iv = 4 1 = 1 xv11 = 17 1 - 5 = 4 10 + 5 + 2 = 17 Numerator Denominator 2 = Proper fraction = numerator is smaller than denominator. 3 3 = Improper faction = numerator is larger than denominator. 2 1 1 = Mixed fraction = whole number and a fraction. 2 To change an improper fraction to a mixed number: a. Divide the numerator by the denominator. 13 = 2 3 b. Place remainder over denominator. 5 5 To change a mixed number to an improper fraction: a. Multiply denominator by the whole number. 3 1 = 7 b. Add numerator. 2 2 c. Place sum over the denominator. To reduce a fraction to its lowest denominator: a. Divide numerator and denominator by the greatest common divisor. b. The value of the fraction does not change. EXAMPLE: Reduce 12 60 12 divides evenly into both numerator and denominator 12 ) 12 = 1 12 = 1 60 ) 12 = 5 60 5 EXAMPLE: Reduce 9 12 3 divides evenly into both 9 ) 3 = 3 12 )3 = 4 9 = 3 12 4 EXAMPLE: Reduce 30 45 15 divides evenly into both 30 ) 15 = 2 45 ) 15 = 3 30 = 2 45 3 You can multiply or divide when denominators are NOT alike. You CANNOT add or subtract unless the fractions have the same denominator. Addition of fractions: a. Must have common denominator. b. Add numerators. 1+ 2 = (change 2 to 1 ) = 1 + 1 = 2 = 1 4 8 8 4 4 4 4 2 Subtraction of fractions: a. Must have common denominator. b. Subtract numerators. 6 - 3 = (change 6 to 3 ) = 3 - 3 = 0 8 4 8 4 4 4 Multiplication of fractions: a. To multiply a fraction by a whole number, multiply numerator by the whole number and place product over denominator. 4 x 3 = 12 = 1 4 = 1 1 8 8 8 2 b. To multiply a fraction by another fraction, multiply numerators and denominators. 4 x 3 = 15 = 5 5 4 24 8 Division of fractions: a. Invert terms of divisor. b. Then multiply. EXAMPLE 1: 2 ) 4 3 5 [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 75 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 08, 2021
Number of pages
75
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
82