● Lots of family members in the room - family centered care
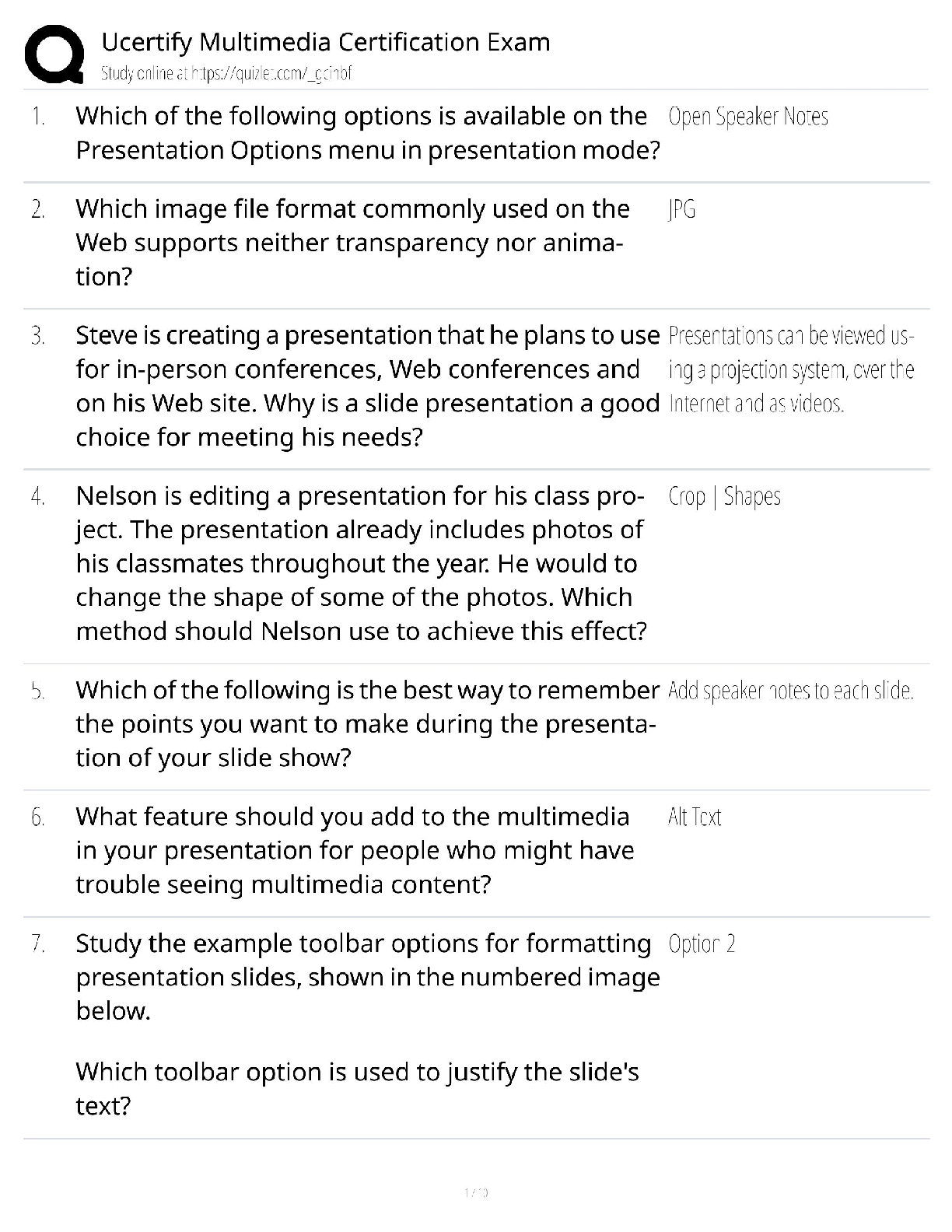
○ Some situations deal with separation anxiety
● Child and the families or their primary care taker - main focus - extended patient
● The younger the child t
...
● Lots of family members in the room - family centered care
○ Some situations deal with separation anxiety
● Child and the families or their primary care taker - main focus - extended patient
● The younger the child the worse the mortality rate - still have extremely high mortality
rate compared to other first world countries - health disparity
● Main goal as pediatric nurse
○ Keep kids healthy - primary intervention
■ Screening, immunizations
○ Going to see 1-3% of things that can go wrong at any given time - 97% of kids are
healthy
● Peds nurse is a family nurse
● Wide range of settings
○ Hospitals
○ Offices and clinics
○ Home of the child
○ Rehabilitation centers
○ Schools, childcare centers, camps
○ Community
● Many school systems cannot afford in house nurses mon-friday
○ Nurses at schools tend to be on rotating basis
○ In miami dade - school nurses cannot give an epipen because not there every day
● Pediatric healthcare
○ Role of the nurse
■ Interact effectively with children and family.
■ Modify physical assessment techniques to age.
■ Identify strategies to reduce pain and stress.
■ Calculate accurate medication dosages. - very few standardized doses
● Weight per kilo - important to look up meds
● Overdoses can cause worse side effects or be lethal
■ Provide safety for child’s developmental status.
■ Adapt procedures to child’s age and development.
■ Education
● May be challenging because of range of understanding
● Goals in helping child and parents/guardians.
● Make informed choices.
● Adapt to healthcare settings.
● Prepare for procedures.
■ Advocacy
● Enable child and family to adjust to changes in child’s health.
● In their own way and time
● Needs of both children and adults
● Awareness of resources
● Psychosocial needs
■ Case management
● Importance of coordinated interprofessional team
● Nurse is often aware of family’s desires
● Continuity of care
● Utilizing evidence based practice
○ Ask and clearly describe specific clinical question.
○ Collect most relevant and best evidence from well-designed studies.
○ Review, synthesize, analyze evidence using critical thinking.
○ Integrate evidence with clinical experience.
○ Develop practice guideline.
○ Evaluate change in practice for effect on quality care.
○ Examples include infection control practices to prevent infections, antibiotic
stewardship, IV catheter size for blood administration and noninvasive
measurement of BP in children.
○ “Babies should start solid foods at 6 months” - new evidence shows parents can
start feeding them whatever they want
■ Give what they are allergic to
● Bindler-Ball Continuum of Pediatric Health Care for Children and Their Families
○
● Standards of pediatric nursing
○ The Society of Pediatric Nurses (SPN) developed the scope and standards of
pediatric nursing practice
○ National Association of Pediatric Nurse Practitioners (NAPNAP)
○ Clinical practice guidelines-evidence based statements about care used to make
decisions about care for a child with a certain diagnosis.
● Responsibilities of pediatric nurses
○
● Nurses may work in many different areas of pedatric care
○ Direct patient care
■ Many sub–specialization areas (i.e. intensive care, trauma, neonatal,
cardiac, med-surg)
○ Education
○ Advocacy
○ Case management
○ Research
● Advanced practice nurses
○ Master’s-level education:
■ Master’s Degree in nursing (MSN)
■ Clinical nurse specialist (CNS)
■ Pediatric nurse practitioner (NP, PNP, APRN)
○ More responsibility for care of client and client outcomes
○ Doctoral-level education:
■ Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP)
■ Doctor of Philosophy in Nursing (PhD)
○ More research related responsibilities
● Supervising unlicensed persons
○ Medical assistants (MA)
○ Certified nursing assistants (CNA)
○ Licensed practical nurse (LPN)/Licensed vocational nurse (LVN)
● History of child health care
[Show More]