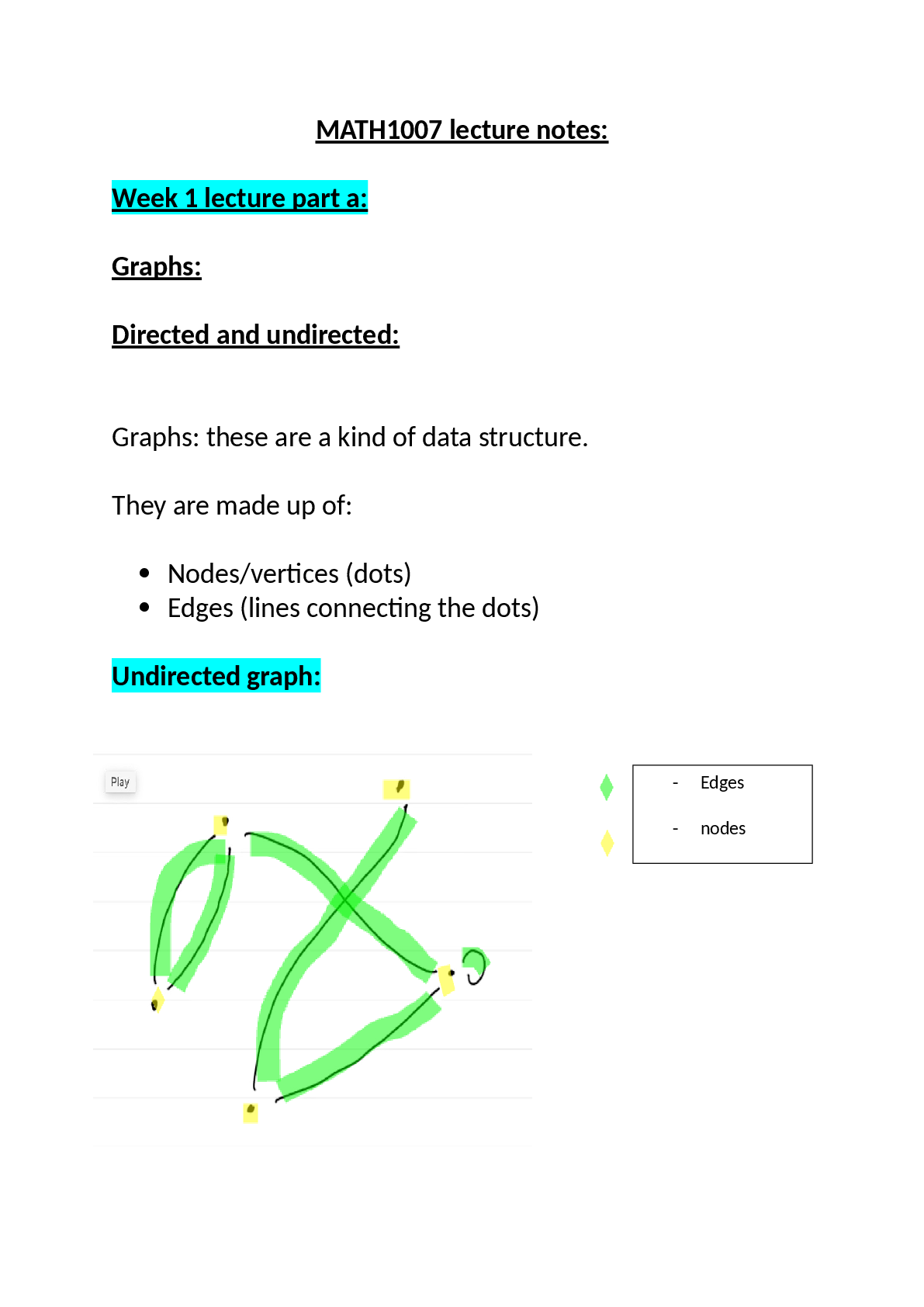
ANTH 160 A1EXAM 4 LECTURE 17
Lecture 17: Mediterranean Civilizations
What is one of the main differences in the development of complex societies in comparison to the other regions that we have looked at so far?
Al
...
ANTH 160 A1EXAM 4 LECTURE 17
Lecture 17: Mediterranean Civilizations
What is one of the main differences in the development of complex societies in comparison to the other regions that we have looked at so far?
All interconnected
Mobile Mediterranean
Hittites (1650-1200 BC)
Where was the Hittite kingdom?
Boghazköy capital (nowadays Turkey, near Black Sea)
-royal archives
Whose downfall did they cause? Who else were they fighting with?
- Brought down old Babylonian empire
- Egyptians vs. Hittites (Ramses’ II version)
- Treaty of Kadesh
Phoenicians (1100-800 BC)
Who were the Phoenicians?
Where did they originate?
Many theories: Lebanon and Egypt; Canaan?
- maritime traders
- Phoenician Alphabet (ca. 1100 BC)
- by 800BC colonies in the southern Mediterranean
Carthaginian Empire (Phoenicians) (814-146 BC)
Carthage capital
in Roman times three Punic Wars
(264-241BC; 218-201 BC; 149-146 BC)
Hannibal (2nd Punic War)
146 BC Carthage finally destroyed by Rome
Early Bronze Age (3200-2100 BC)
Crete:
Early Minoan/Pre-Palatial Period
copper
development of more hierarchical society
differential treatment of the dead
some have valuable grave goods è gold
mostly small villages, but increase in settlement size è earliest settlement at Knossos
Minoan Civilization: Palace Period (2100-1450 BC)
First Palace Period (Middle Minoan) 2100-1700 BC
Second Palace Period (Late Minoan) 1700-1450 BC
- Knossos, Frescoes, Second Palace Period
What was the layout of a Minoan palace? What was its function?
Large palaces
What was the political system?
Monarch: king, priests, scribes, officials
Writing System:
- Hieroglyphic c. 2000 BC, First Palace Period
- Linear A Second Palace Period
- Linear B Third Palace Period, Myceneans (c. 1450-1200 BC)
Which of these writing systems has been deciphered?
Hieroglyphics
- Craft Specialization
- Ideology? Ritual rooms and peak sanctuaries
seafaring wide influence in the Mediterranean, e.g., Minoan pottery in Lower Egypt
- by ca, 1450BC all major palaces and villas except Knossos destroyed and abandoned apparently taken over by the Mycenaeans
The Mycenaeans (1600-1050 BC)
Where were they located?
Greece
- start in Second Palace Period
- major centers, among others, Mycenae, Tiryns, Pylos
- heavily fortified citadels and lower towns e.g., Mycenae, in 1300BC cyclopean walls
- palaces How are they different from Minoan palaces?
- shaft graves (1500s BC)
- Linear B
- economic system: bipartite (a first group worked in the orbit of the palace, while another was self-employed)
- craft specialization: textiles, metallurgy, perfume
- technology: vases, chain of production in factories
What were their exterior relations? How were Mycenaean good distributed?
Egypt, Sicily. Nodules carrying an ideogram representing an ox
- Uluburun shipwreck What was in the cargo?
• Raw materials for trade, royal gifts
- around 1200 BC palaces destroyed
Postpalatial Period (1200-1050 BC)
political disintegration and decline
time period that is mentioned in later Greek legendary accounts è e.g. Homer’s Illiad
[Show More]

.png)