TIMS Exam Study Questions
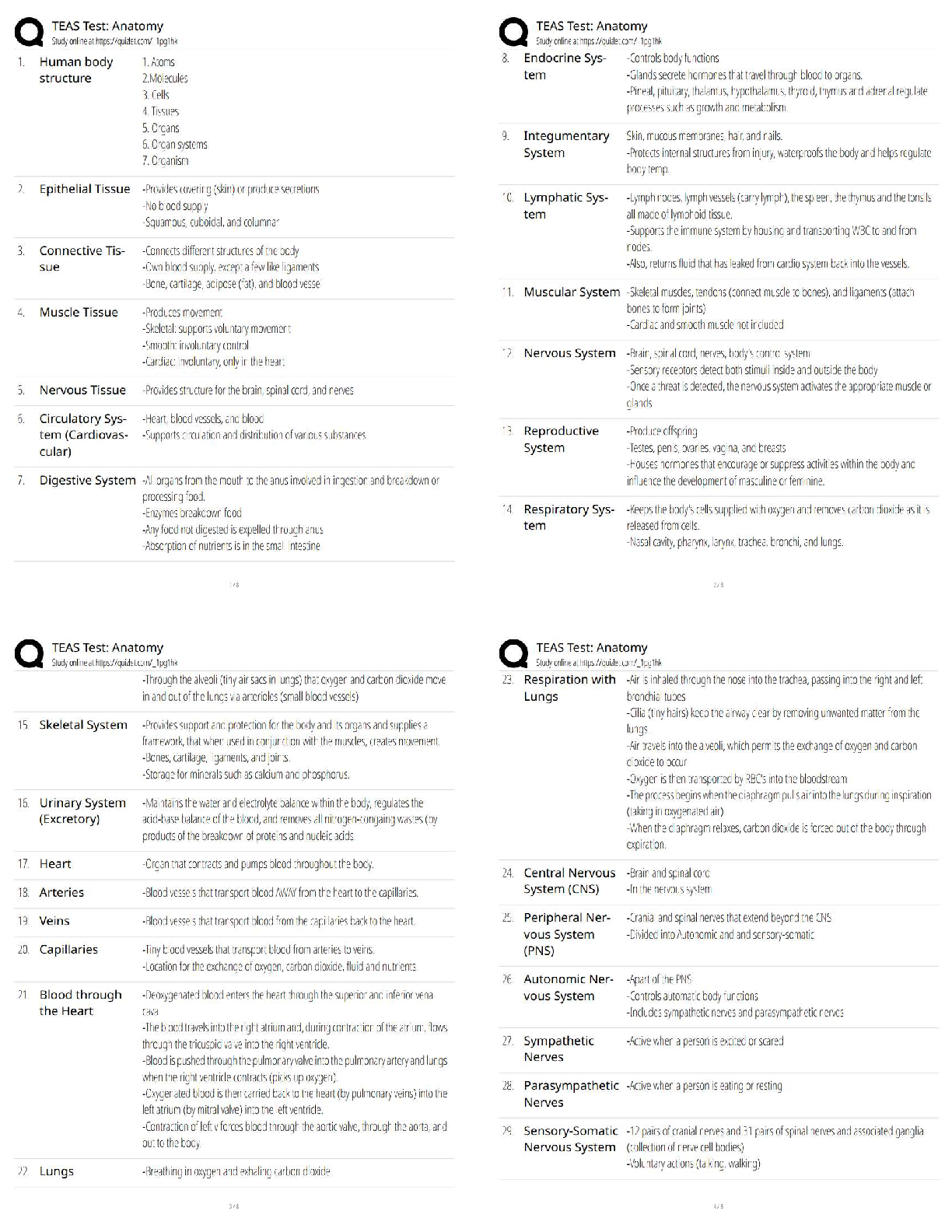
What does SHRP2 stand for? - ✔✔Strategic Highway Research Program 2
How many areas of focus does SHRP 2 have? what are they? - ✔✔4 areas of focus: 1. Safety 2.
Renewal 3. Reliability 4. Capac
...
TIMS Exam Study Questions
What does SHRP2 stand for? - ✔✔Strategic Highway Research Program 2
How many areas of focus does SHRP 2 have? what are they? - ✔✔4 areas of focus: 1. Safety 2.
Renewal 3. Reliability 4. Capacity National Unified
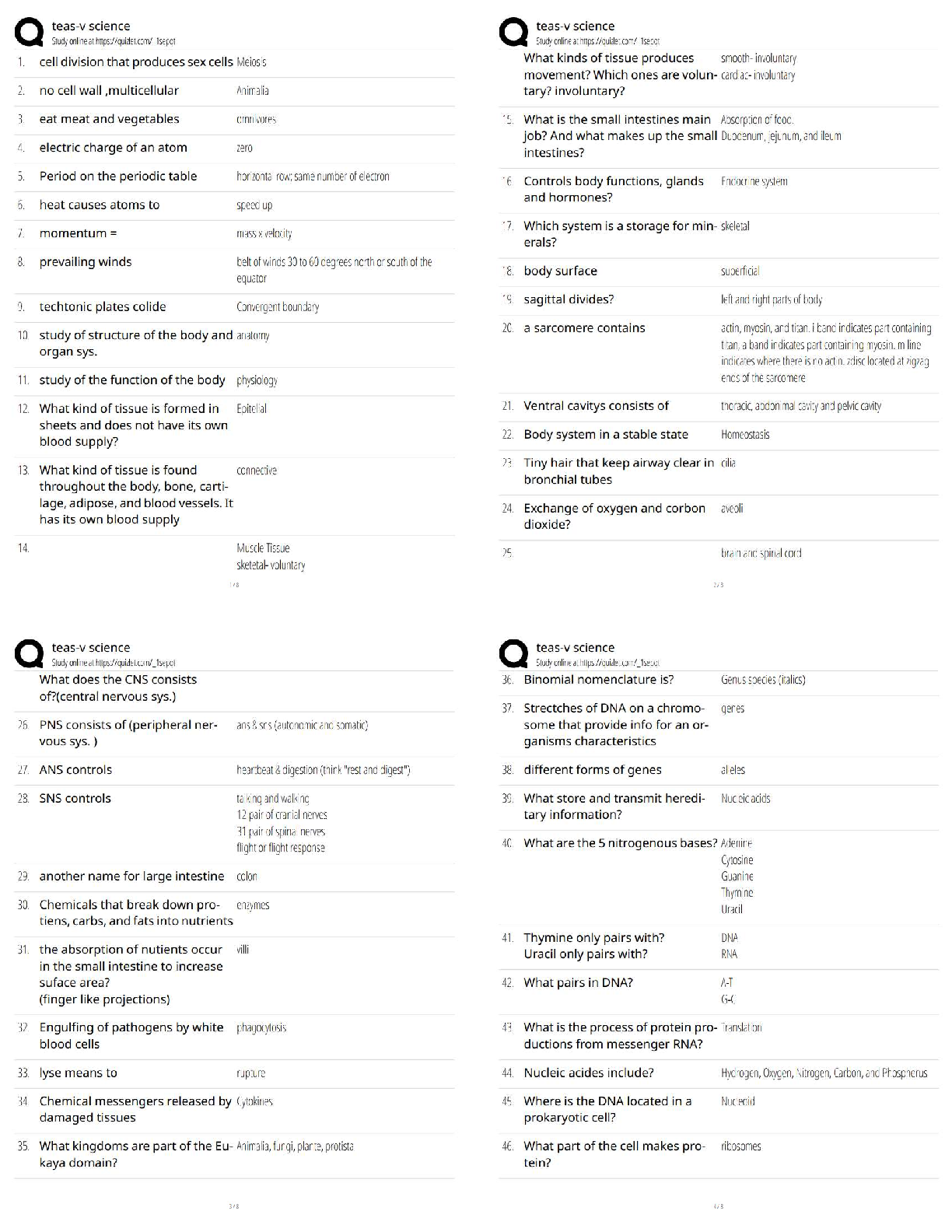
The TIM training program was designed to? - ✔✔Establish the foundation for and to promote
consistent training of all responders to achieve the three objectives of the TIM goal
What are the three objectives of the TIM National Unified Goal (NUG)? - ✔✔1. Responder
Safety 2. Safe, Quick Clearance 3. Prompt, Reliable, Interoperable Communications
What are D Drivers? - ✔✔Drunk Drugged Drowsy Distracted Dumb
Who suffers the most deaths by being struck each year? - ✔✔Tow truck drivers (Average 60)
On average, how many police officers die by being struck by traffic each year? - ✔✔Average of
12 per year over 24 years
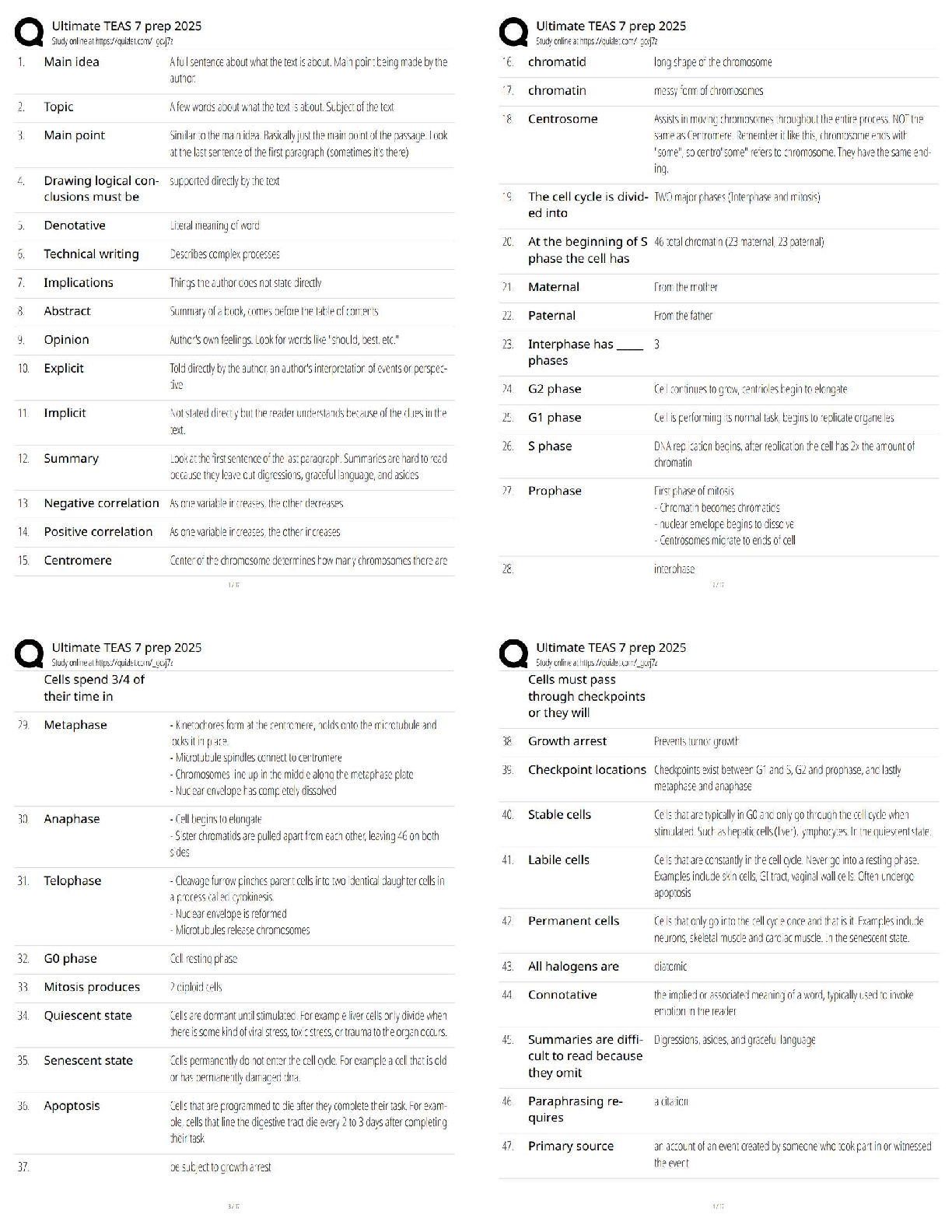
Crashes that occur within the incident scene or within the queue or backup, including the
opposite direction, resulting from an original incident. - ✔✔Secondary crashes
Effective TIM reduces and does what? - ✔✔Reduces the duration and impacts of traffic
incidents -Improves the safety of motorists, crash victims, and emergency responders.
Goods that have been imported or exported illegally into the dormitory, and are not allowed? (i.e.
testosterone supplements) - ✔✔Contraband
Goal of TIM is to? - ✔✔Shorten the time duration between when the incident occurs, and when
traffic resumes as normal.
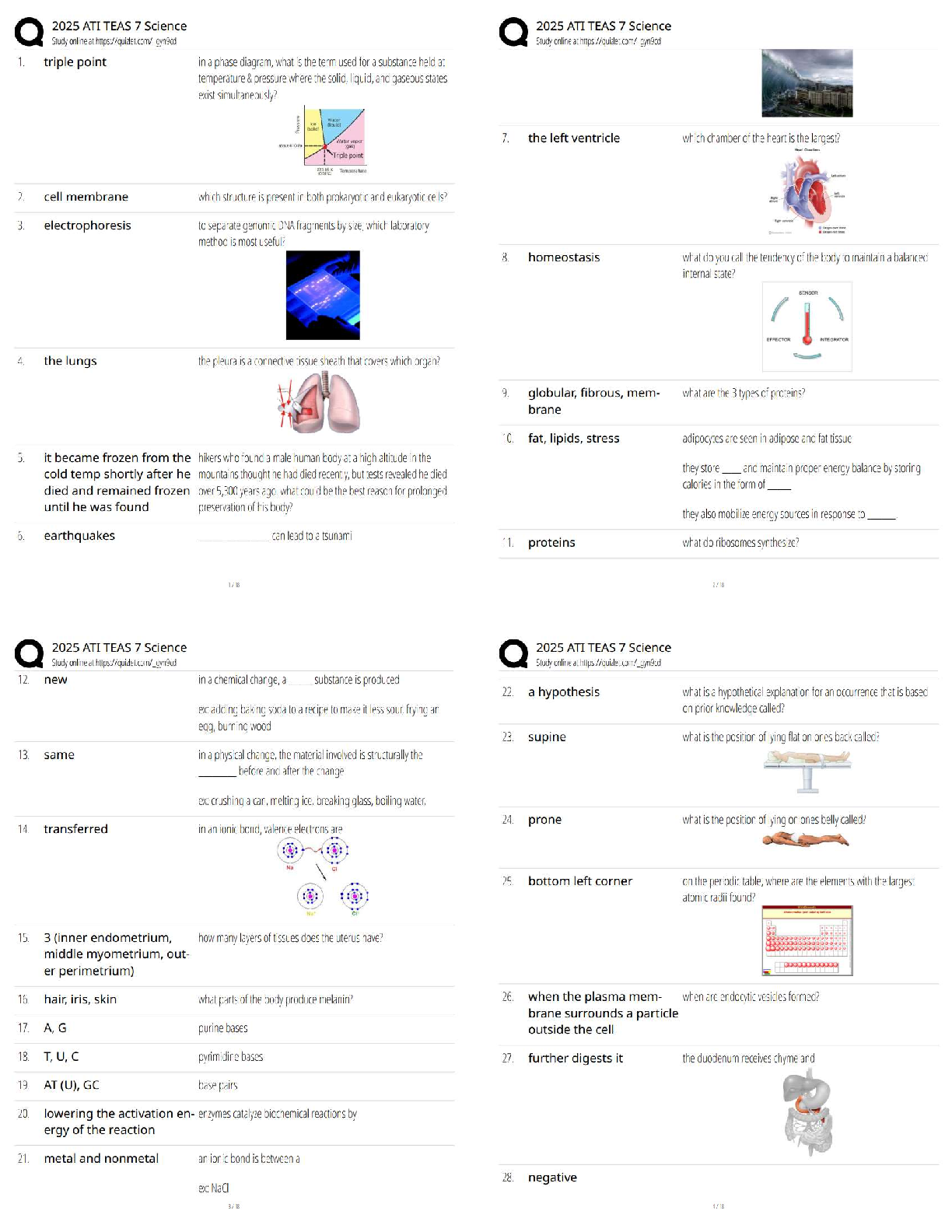
Three standards that TIM performance measures? - ✔✔1. Roadway clearance time 2. Incident
clearance time 3. Number of secondary crashes
The practice of rapidly, safely, and aggressively removing temporary obstructions from the
roadway? - ✔✔Safe, quick clearance
What does safe, quick clearance help to do? - ✔✔1. Minimizing exposure to adjacent passing
traffic 2. Reduce the probability of secondary crashes 3. Relieve overall congestion and delay.
Nationally, there are three types of laws that facilitate TIM, what are they? - ✔✔1. Move Over
Laws 2. Driver Removal Laws 3. Authority Removal Laws
Law that provides authority (and immunity from liability in general) for designated public
agencies to remove vehicles and/or spilled cargo from the roadway to restore traffic flow. -
✔✔Authority Removal Laws
Law that require motorists involved in minor crashes (where there are no serious injuries and the
vehicle can be driven) to move their vehicles out of the travel lanes to the shoulder or other safe
area? - ✔✔Driver Removal Laws
Law that requires drivers approaching a scene where emergency responders are present to either
change lanes when possible and/or reduce vehicle speed? - ✔✔Move Over Laws
National standard that was first published in 1935, and it has been maintained by FHWA since
1971? - ✔✔MUTCD - Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices
Purpose of MUTCD - ✔✔Promotes the uniformity of traffic control signs, signals, and markings
from state to state.
Lane Designation Terminology? - ✔✔Plain English
When describing highway lanes... - ✔✔left is analogous with inside and right with outside, from
the perspective of the flow of traffic.
A numbering system that assigns numbers 1, 2, 3, etc. from the left to right lane, again from the
perspective of the flow of traffic, can be used. - ✔✔Lane Numbering (terminology)
True or False: special or unique use lane(s), such as a high-occupancy vehicle (HOV) lane is not
a numbered lane. - ✔✔True
True or False: TIM terminology is not just applicable to urban roads and freeways, the
techniques apply to local streets and rural roadways too. - ✔✔True
Traffic that is entering or approaching the incident scene is considered? - ✔✔Upstream traffic
Traffic that is departing or past the incident is considered? - ✔✔Down stream traffic
Departing traffic is? - ✔✔Downstream
Approaching traffic is? - ✔✔Upstream
The backup of traffic that results from an incident or blocked lanes? - ✔✔A traffic queue
True or False: A queue may form in either direction of travel because of rubberneckers. -
✔✔True
Who is typically the first to receive notification of an incident? - ✔✔Dispatcher
Dispatchers are responsible for? - ✔✔-Providing a basic assessment of the situation -Dispatching
an appropriate response based on their knowledge of available resources
Steps to the notification and verification process? - ✔✔1. Detection 2. Verification 3.
Notification
The discovery of an incident and the first step in the TIM process. - ✔✔Detection
Involves collecting as much information as possible from the individual(s) reporting the incident
including the exact location, the make, model, and color of the involved vehicles, and a call back
number in case more information is needed - ✔✔Verification
When the communications center will dispatch the appropriate response? - ✔✔Notification
Whats a TMC? - ✔✔Transportation Management Center
Whats a TOC? - ✔✔Traffic Operations Centers
Serves as the hub for the collection and dissemination of incident information? - ✔✔Traffic
Operations Centers
Monitoring traffic conditions using? - ✔✔-(CCTV) cameras -Roadway detectors and congestion
maps -Public safety contacts via phone and/or computer-aided dispatch (CAD) links
TMCs are usually responsible for? (5) - ✔✔-Monitoring traffic conditions -Providing real-time
traveler information -Providing traffic and incident info notification to other traffic
management/communication centers, public safety partners and the news media -Monitoring
traffic management devices to ensure they are functioning properly -Controlling traffic
management devices, including ramp meters, traffic signal systems, etc.
Providing real-time traveler information using? - ✔✔-511 - phone systems, websites and social
media -Dynamic message signs (DMS) -Portable changeable message signs (PCMS) -Highway
advisory radio (HAR)
Initial arrival/windshield size-up report should include? - ✔✔-Unit identification -Exact location
of incident -Number and type of vehicles involved -Degree of damage -Number of lanes closed -
Hazards or problems -Establishment of command
Detailed and accurate size-up should be provided after the responder has? - ✔✔More fully
assessed the scene.
How should reporting go? (timeline) - ✔✔1. Initial/ Windshield Size-Up Report 2. 15-Minute
Detailed Size-Up Report 3. Regular Progress Reports
The following information should be provided during the detailed size-up report and/or during
subsequent progress reports? - ✔✔-Location -Vehicles - number/type -Injured Persons -Incident
Duration Classification (Minor, Intermediate, or Major) -On-Scene Conditions -Hazardous
Materials -Traffic Conditions -Towing and Recovery -Additional Resources Needed
MUTCD Chapter 6I divides traffic incidents into three general incident classes based on the
anticipated duration. What are they, and what are the time limits? - ✔✔-Minor: < 30 minutes -
Intermediate: 30 minutes to 2 hours -Major: > 2 hours
Refers to moving vehicles involved in an incident to a secondary location before being worked -
✔✔"Move It"
Describes a situation where the vehicles involved cannot be moved to a secondary location
before being worked. - ✔✔"Work It"
Safe-positioned, as defined by the MUTCD, is the positioning of emergency vehicles at an
incident in a manner that attempts to? - ✔✔1. Protect the responders performing their duties 2.
Protect road users traveling through the incident scene 3. Minimize, to the extent practical,
disruption of the adjacent traffic flow
True or False: The shoulder of a highway is considered a lane when establishing a block? -
✔✔True
A responder vehicle positioned to block a single lane or the shoulder is referred to as? -
✔✔Linear Block
When the responder vehicle is positioned to block multiple involved lanes it is called? -
✔✔Multi-lane Block
2 ways a blocking vehicle can be positioned on the roadway? - ✔✔1. Angled 2. Parallel
Meaning the vehicle is positioned at an angle with respect to the travel lanes? - ✔✔Angled Block
Meaning the vehicle is positioned parallel to the travel lanes or the shoulder? - ✔✔Parallel Block
True or False: Turning a blocking vehicle's wheels so that they are not facing the incident space
is a recommended practice referred to as critical wheel angle? - ✔✔True
During initial incident response, it is typical for law enforcement, fire, and DOT or Safety
Service Patrol vehicles to position? - ✔✔Upstream
During initial incident response, it is typical for ambulances, tow trucks, and other support units
to position - ✔✔Downstream
To ensure responder and motorist safety, it may be necessary to close additional lanes for a short
time, a practice referred to as? - ✔✔Lane +1 Blocking
Every block creates an area of danger between the blocking vehicle and moving traffic,
commonly referred to as the? - ✔✔Zero buffer
The use of a what during a traffic stop can reduce law enforcement exposure to the hazard of
being in the zero buffer? - ✔✔Non-traffic side approach
The ability of a vehicle to draw attention to its presence, even when other road users are not
actively looking for it? - ✔✔Conspicuity
Markings on responder vehicles are passive treatments that complement emergency lighting by
using? - ✔✔-Contrasting colors that make the vehicle stand out -Fluorescent colors to increase
daytime visibility -Retroreflective materials to maximize nighttime visibility
True or False: While an important tool for warning drivers, most emergency lighting does little
to augment traffic control or guide drivers, therefore more is not always better where emergency
lighting is concerned? - ✔✔True
True or False: The use of too many lights at an incident scene can be distracting and can create
confusion for approaching road users (and other responders), especially at night. - ✔✔True
When multiple responder vehicles are present, only the rear-most (upstream) vehicles and
blocking vehicles should continue the use of? - ✔✔emergency (warning) lights after appropriate
traffic control is in place.
All workers, including emergency responders, within the right-of-way of a roadway who are
exposed either to traffic (vehicles using the highway for purposes of travel) or to work vehicles
and construction equipment SHALL wear? - ✔✔high-visibility safety apparel
True or False: Law enforcement personnel are exempt from MUTCD high-visibility safety
apparel requirements when engaged in potentially confrontational law enforcement activities
such as traffic stops and searches? - ✔✔True
True or false: Police are required to wear high-visibility apparel any other time they are afoot
near a roadway including directing traffic, investigating crashes, or assisting other officers. -
✔✔True
What does ICS stand for? - ✔✔Incident Command System
Goals of ICS? - ✔✔1. Safety of responders and others 2. Achievement of tactical objectives 3.
Efficient use of resources
When one individual is designated as Incident Commander and has complete responsibility for
incident management. - ✔✔Single Command
A joint management and authority structure in which two or more individuals share the role of
Command. - ✔✔Unified Command
Unified Command is most appropriate for major incidents involving? - ✔✔Multiple agencies
Unified Command works together to develop and implement what? - ✔✔An Incident Action
Plan (IAP)
An IAP identifies: - ✔✔1. How the objectives will be accomplished 2. The resources needed to
achieve those objectives
For large-scale incidents, physical organization of a scene involves the establishment of what 4
things? - ✔✔1. Traffic Incident Management Area 2. Incident Command Post 3. Staging Area(s)
4. Diversion routes if necessary
A location where resources can be placed while awaiting tactical assignment, allow for the
organization of personnel and equipment for immediate use at the incident scene as soon as they
are needed? - ✔✔Staging Area
The 4 main components of a Traffic Incident Management Area are? - ✔✔1. Advance Warning
Area 2. Transition Area 3. Activity Area 4. Termination Area
Area that is established upstream of the incident to alert drivers of the upcoming incident scene.
All advance warning devices should be placed so that they will provide enough warning for
vehicles to slow before reaching the incident and any traffic queue that might form. -
✔✔Advance Warning Area
Section of roadway where drivers are redirected out of their normal path. Usually involve the
strategic use of tapers, which can be set up using cones or flares. - ✔✔Transition Area
Section of the roadway where incident response activities take place and is comprised of the
buffer space and incident space. - ✔✔Activity Area
Area used to notify drivers that the Traffic Incident Management Area is ending and they may
resume normal driving. Includes the downstream buffer space and taper, which is in place to
protect emergency responders working at the end of the Incident Space. - ✔✔Termination Area
Separates the Transition Area from the Incident Space and provides a recovery area for errant
vehicles. No vehicles should be positioned within this area. - ✔✔Buffer Space (Upstream)
Location where the incident has occurred and emergency responders are working. A blocking
vehicle should be positioned at the upstream end of this area to protect workers from impacts by
errant vehicles. - ✔✔Incident Space
True or False: Additional or extended advance warning may be necessary during adverse
weather conditions, such as rain, fog, and/or snow. - ✔✔True
Channelizing devices used to establish a taper are typically placed? - ✔✔No further apart in feet
than the speed limit (i.e., in a 35 mph zone the cones would be placed 35 feet apart).
How far is the distance between striped traffic lines? - ✔✔10 feet
Traffic Cone Deployment Technique? - ✔✔1. The responder retrieves available cones from the
trunk placing one at the rear of the responder vehicle on the edge line 2. Walking along the
shoulder, facing traffic, a cone is subsequently placed on the edge line at each skip line
(alternatively, they can be placed every 10 paces) 3. When the last cone has been placed on the
edge line, the responder begins walking backwards until the next cone is reached 4. The
responder takes one lateral step into the travel lane and places the cone, immediately returning to
the shoulder - facing traffic 5. The responder again walks backwards until the next cone is
reached and then takes two lateral steps into the travel lane to place the cone, immediately
returning to the shoulder 6. The steps are repeated until all cones are deployed
Never turn your back....? - ✔✔On traffic
The two types of buffers that may be established as part of the Traffic Incident Management
Area are? - ✔✔-Longitudinal buffer spaces -Lateral buffer spaces.
This buffer space covers the distance between the transition area and the incident Space,
basically the space up to the blocking vehicle. By definition, it is a recovery area for errant
vehicles, so no responder vehicles should be parked in the buffer space. - ✔✔longitudinal buffer
space
This buffer space is the area between the incident space and the adjacent travel lanes, and can be
beneficial because it allows more room for responders to work. It can be increased through the
use of Lane +1 blocking when necessary. It is recommended that the entire lane be closed and
that partial lane closures be avoided. - ✔✔Lateral Buffer Space
This presents a danger zone that specifically includes the area directly in front of and behind the
vehicle where projectiles, like gas-charged struts and pistons, may launch from the vehicle -
✔✔Vehicle Fire
Where should you avoid, and remain during a vehicle fire incident? - ✔✔Avoid all sides.
Remain uphill and upwind of the incident.
Hazardous materials (hazmat) can be identified through? - ✔✔labels, markings, or placards.
Where should placards be placed on transport vehicles? - ✔✔Each side and each end of the
transport vehicle
Placards are based on? - ✔✔Color-code based on the class of hazardous material being
transported and contain a 4 digit number that can help to identify the material being transported
Steps to do once a HAZMAT spill has been identified as a vehicle fluid that does not meet
reportable quantity thresholds: (5) - ✔✔1. Stop leaking material at the source 2. Contain and
limit the spill from spreading 3. Apply available absorbents 4. Remove material from travel lanes
5. Gradually restore traffic flow
The foundation of traffic crash investigations involves? - ✔✔1. the collection of info that
ultimately helps understand when, where, and why crashes occur. 2. Investigations also help to
identify who is at fault, enabling vehicle repairs and other compensation.
Remember, all debris should be considered evidence until? - ✔✔law enforcement personnel
indicates otherwise.
Evidence which will most likely be lost, destroyed, or compromised once the scene has been
cleared. Can disappear when walked on by responders, flushed away with water, or
unintentionally swept away with a broom. - ✔✔Short-lived Evidence
Tow operator responsibilities include? - ✔✔1. Loading vehicles and departing the scene as
quickly as possible. 2. Transporting occupants from towed vehicles to a safe location away from
the incident. 3. Handling financial negotiations off-site.
Final stage of incident response? - ✔✔Termination
Termination includes? - ✔✔Demobilizing and removing all equipment, personnel and response
vehicles, and restoring traffic flow to normal.
Major activities during termination include: - ✔✔1. Recovering the roadway from any damage
caused by the incident 2. Removing temporary traffic control devices from the incident scene 3.
Lifting the alternate route or detour restrictions 4. Informing drivers of the return to normal
traffic flow conditions 5. Departure of the responders from the incident scene
Termination Checklist: - ✔✔1. Let other responders know when you're leaving 2. Protect towers
while they finish up 3. Check with Incident Commander prior to leaving 4. Make sure all
personnel are accounted for 5. Let the TMC know that lanes are open
[Show More]