ATI Medical Surgical Nursing, Concepts of Emergency and Trauma Nursing, updated
$ 7

WGU C961 Ethics In Technology Acts
$ 8
.png)
Class 2 - Article Summaries and Case analysis
$ 15
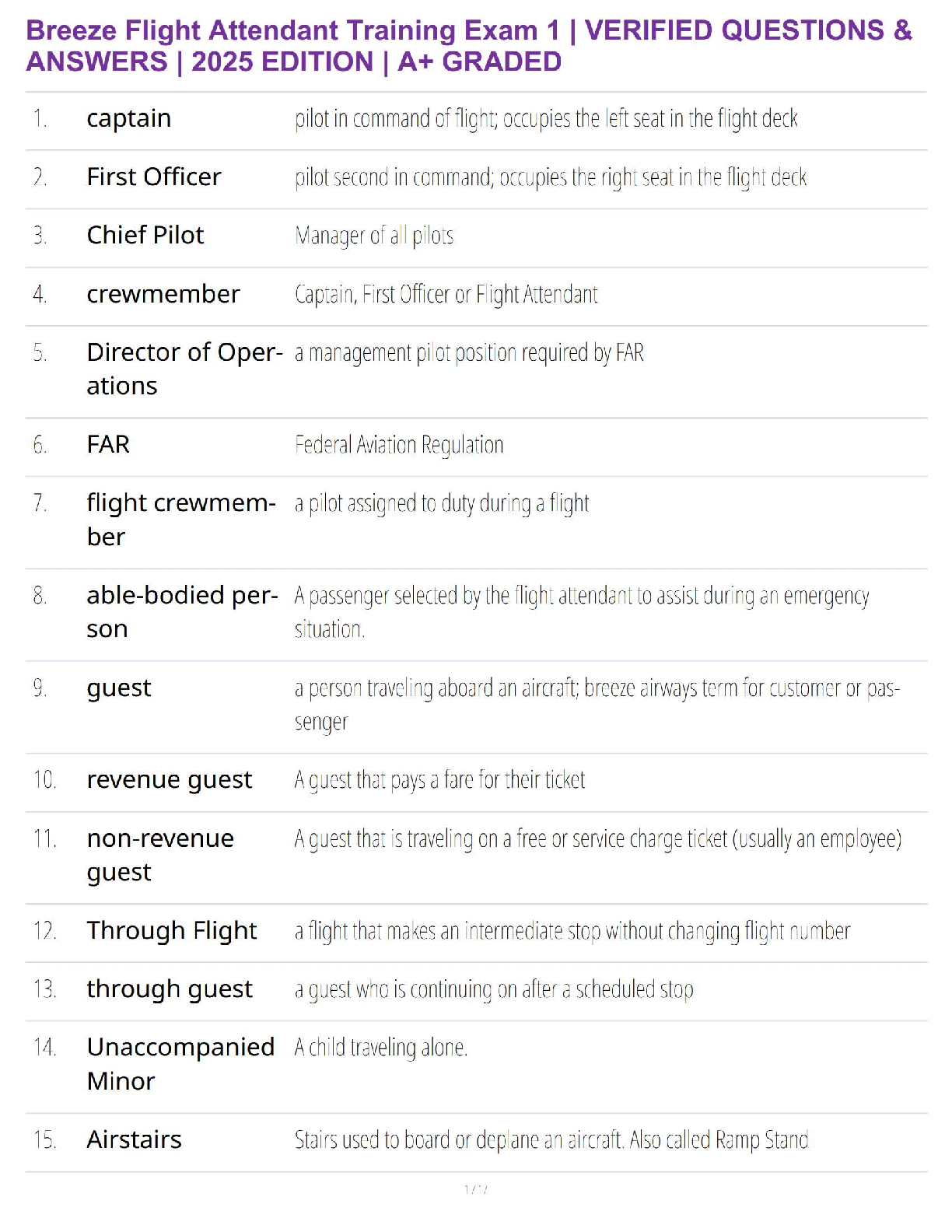
Breeze Flight Attendant Training Exam 1 | VERIFIED QUESTIONS & ANSWERS | 2025 EDITION | A+ GRADED
$ 14.5

NJ CALA Exam Questions and Answers 100% Correct Score
$ 8

Med Aide quizzes and tests from all units latest 2022 already passed
$ 9

TEST BANK WOMEN'S HEALTH CARE IN ADVANCED PRACTICE NURSING IVY M. ALEXANDER 2nd Edition
$ 27.5

OSHA 30 Final Exam Complete with Correct Answers 2023
$ 7

Pearson Edexcel Mark Scheme (Results) November 2021 Pearson Edexcel International GCSE In English Literature (4ET1) Paper 2: Modern Drama and Literary Heritage Texts
$ 6

eBook [PDF] Mighty Microeconomics A Guide to Thinking Like An Economist By Michihiro Kandori
$ 23

CBSPD TECH CERTIFICATION EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2023 SOLUTIONS.
$ 10

Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical MARK SCHEME - March 2022
$ 4.5

Test Bank to accompany Animal Behavior, Twelfth Edition John Alcock, Linda Green, Paul Nolan, Stefanie Siller, and Dustin Rubenstein A+ 2025
$ 9.5

AWS DevOps Engineer Professional Latest Final Exam Study Guide with complete solutions
$ 10

UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING CPEN 211 – Introduction to Microcomputers 2015 Review for the Exam
$ 6

CSE 205 GradebookReader.java (//Complete Code)
$ 8
.png)
MACRO FTC1 Unit 7 Study Guide The World Economy Introduction- Western Governors University.
$ 15

WGU D488 OA FINAL EXAM /WGU D488 CYBERSECURITY ARCHITECTURE & ENGINEERING EXAM 2026
$ 23

(LU) BUSI 411 Operations Strategy - Latest Finals Review Q & S 2024
$ 11

Case Notes & Answer for Martha McCaskey, By Bart J. Van Dissel, Joshua D. Margolis
$ 15

TEST BANK FOR SOCIOLOGY A GLOBAL PERSPECTIVE 8TH EDITION BY FERRANTE
$ 9

AQA A-level COMPUTER SCIENCE 7517/1 Paper 1 Mark scheme June 2020
$ 9.5

AQA A-level LAW Paper 2 QP Thursday 11 June 2020
$ 6

HRCI APHR CERTIFICATION EXAM SAMPLE QUESTIONS 2023 LATEST UPDATE
$ 12

Pearson Edexcel IASL In A Level Physics WPH15/01 Paper 01 Thermodynamics, Radiation, Oscillations and Cosmology. Mark Scheme (Results) January 2022
$ 4

NGN NCLEX PN ACTUAL EXAM 2025 WITH NGN /PN NCLEX ACTUAL EXAM (NEXT GENERATION) 2025-2026 COMPLETE 180 QUESTIONS AND CORRECT ANSWERS
$ 60.5

eBook [PDF] Applied Psychology for Social Work 2nd Edition By Ewan Ingleby
$ 20

Solution Manual For MicroEconomics 13th Edition By Michael Parkin
$ 25

Safe Scrum Master Exam Questions and Answers Already Graded A+
$ 14

ITSC 280 Data Storage Associate Certification Exam / Study Guide & Test Bank / 2025 SNIA Update / Score 100%
$ 21
.png)
NETW 583 Week 1 Case Study 1: Apple Case Analysis (GRADED A)
$ 12
2023 AQA GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY 8464/B/2F Biology Paper 2F Question Paper & Mark scheme (Merged) June 2023 [VERIFIED]
$ 7
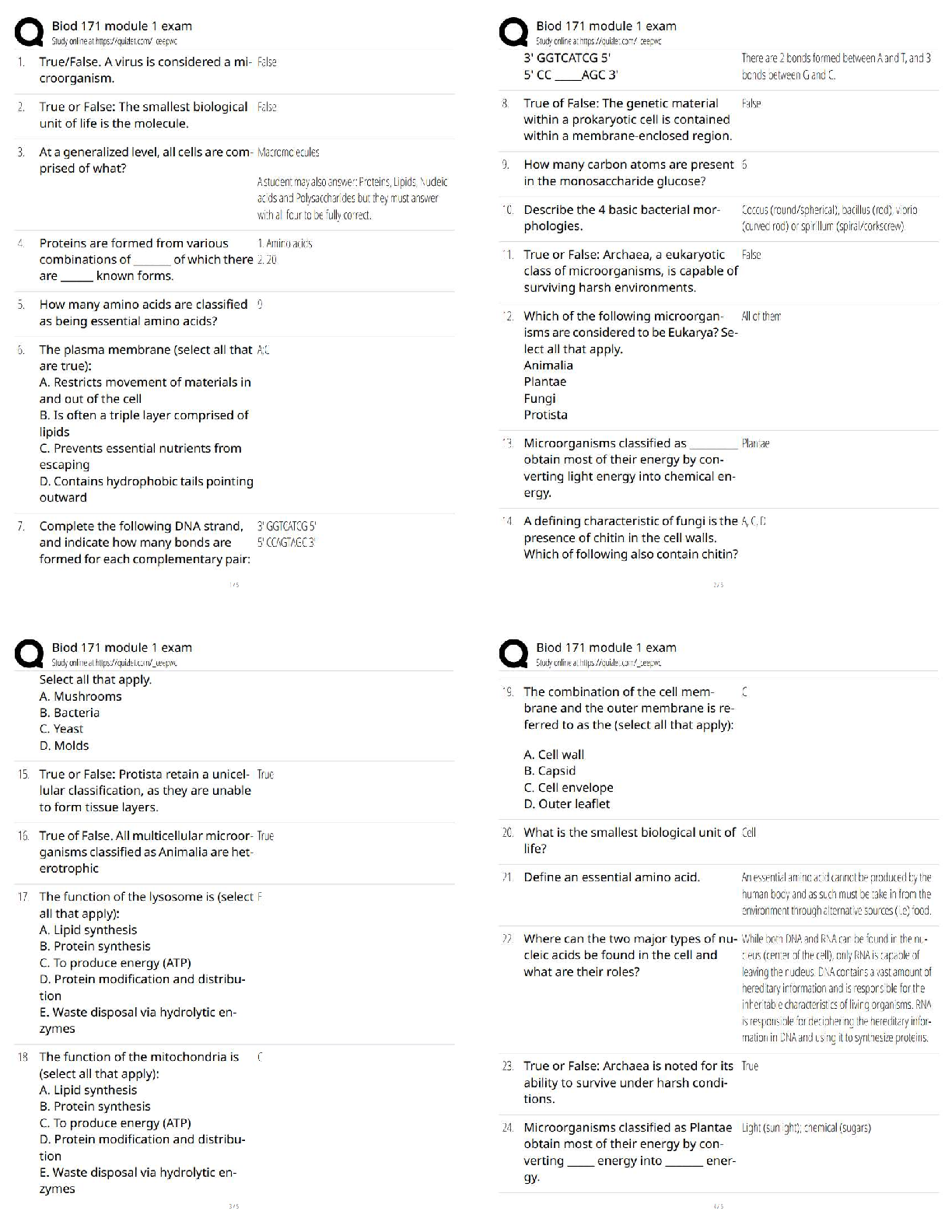
BIOD 171 Module 1 Exam / Score 100% / New Version / 2025 Update / Study Guide & Test Bank
$ 10.5

Microsoft MTA 98-366 Practice Exam 2022 with Questions and Answers
$ 8

Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9–1) 4CP0/02: Computer Science PAPER 2: Application of Computational Thinking MARK SCHEME - Summer 2021
$ 6

CHIA Certification Exam, CHIA Practice Exam, CHIA Exam Study Guide, CHIA Final Practice Actual Exam Newest Actual Exam With Complete 850+ Questions And Correct Detailed Answers (Verified Answers) |Already Graded A+
$ 17

Lab Report Whirling of shaft
$ 12
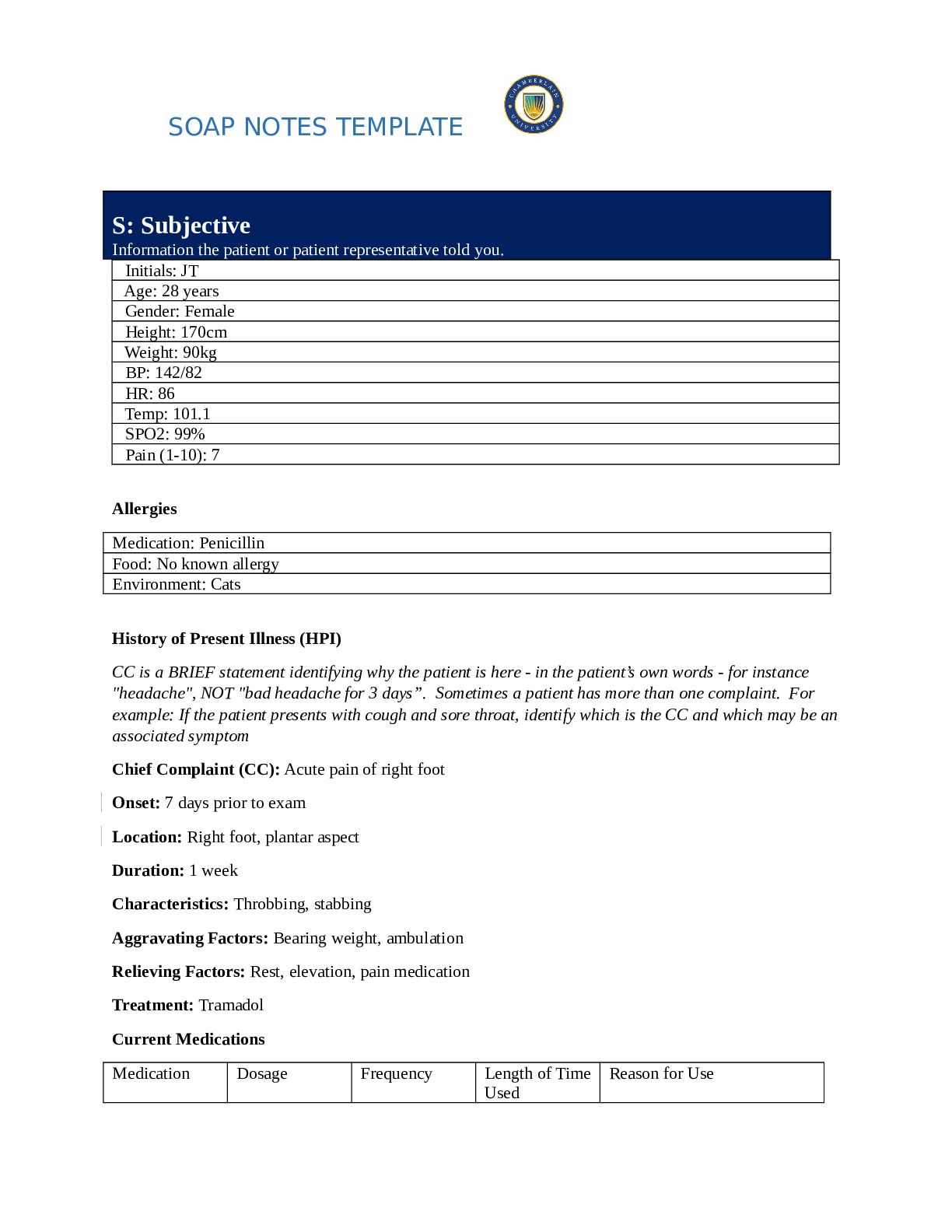
NR509 Week 1 SOAP Note
$ 15.5

SOCS-325 Week 2 Article Summary (Review, Discover, and Comment)
$ 7

NUR 2214 Module 7 Care map 2
$ 14

Test Bank for Database Systems, Edition 2.0 by Nenad Jukić
$ 49

[eBook][PDF] Madrasas in the Age of Islamophobia, 1st Edition By Ziya Us Salam, Mohammad Aslam Parvaiz