Stats 1430 Final Exam
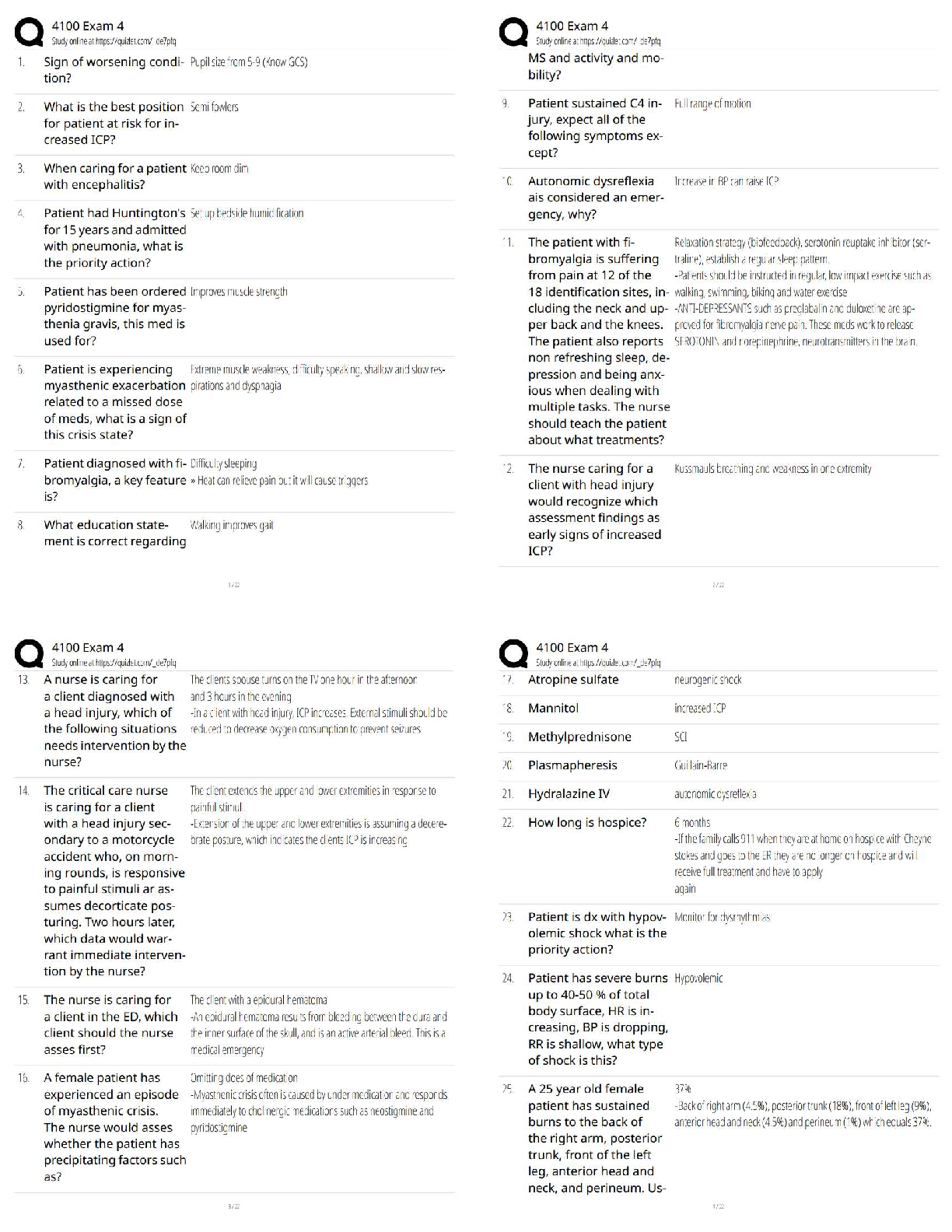
p-value characteristics (for HT population mean) - ✔✔depends on data, changes with each
sample, sig level alpha stays the same once its is chosen
can outliers affect the CI - ✔✔yes
if x is not n
...
Stats 1430 Final Exam
p-value characteristics (for HT population mean) - ✔✔depends on data, changes with each
sample, sig level alpha stays the same once its is chosen
can outliers affect the CI - ✔✔yes
if x is not normal for CI, what must be known - ✔✔population standard deviation
parameter - ✔✔what you are looking for (number describes pop)
sampling dist - ✔✔set of all values of a stat for all possible samples of size n from the population
the mean of all the sample means equals - ✔✔mean of the population (mu xbar= mux)
as population standard deviation increases, standard error... - ✔✔increases
if random variable X has a normal distilled, then x bar has a _________ shape - ✔✔normal
the mean of x bar equals the mean of ____ - ✔✔X (all the time)
as n increases, standard error..... - ✔✔decreases
the standard error of x bar is ______ than standard deviation of X - ✔✔less
if X has normal distilled, x bar has... - ✔✔exact normal diet for any n
3 items affect the margin of error of a CI: - ✔✔z-value, n, standard deviation of the population
as confidence level of CI increases, the z-value... - ✔✔increases
The object of a HT is to challenge a claimed value of a - ✔✔population parameter
alternative hypothesis - ✔✔the one we believe is correct, Ha
test statistic - ✔✔When doing a HT: collect data, find stat, change it to a z-score (name given to
z-score)
p-value - ✔✔the probability of being at or beyond your z-score in the direction of your
alternative hypothesis (HT def)
if you have enough evidence against Ho and are able to reject it, the p-value must have been -
✔✔small (less than .05)
the closer your test stat is to the middle of the z-dist, the ________ likely you are to reject Ho -
✔✔less
conditions for binomial dist - ✔✔np >=10, n(1-p)>=10
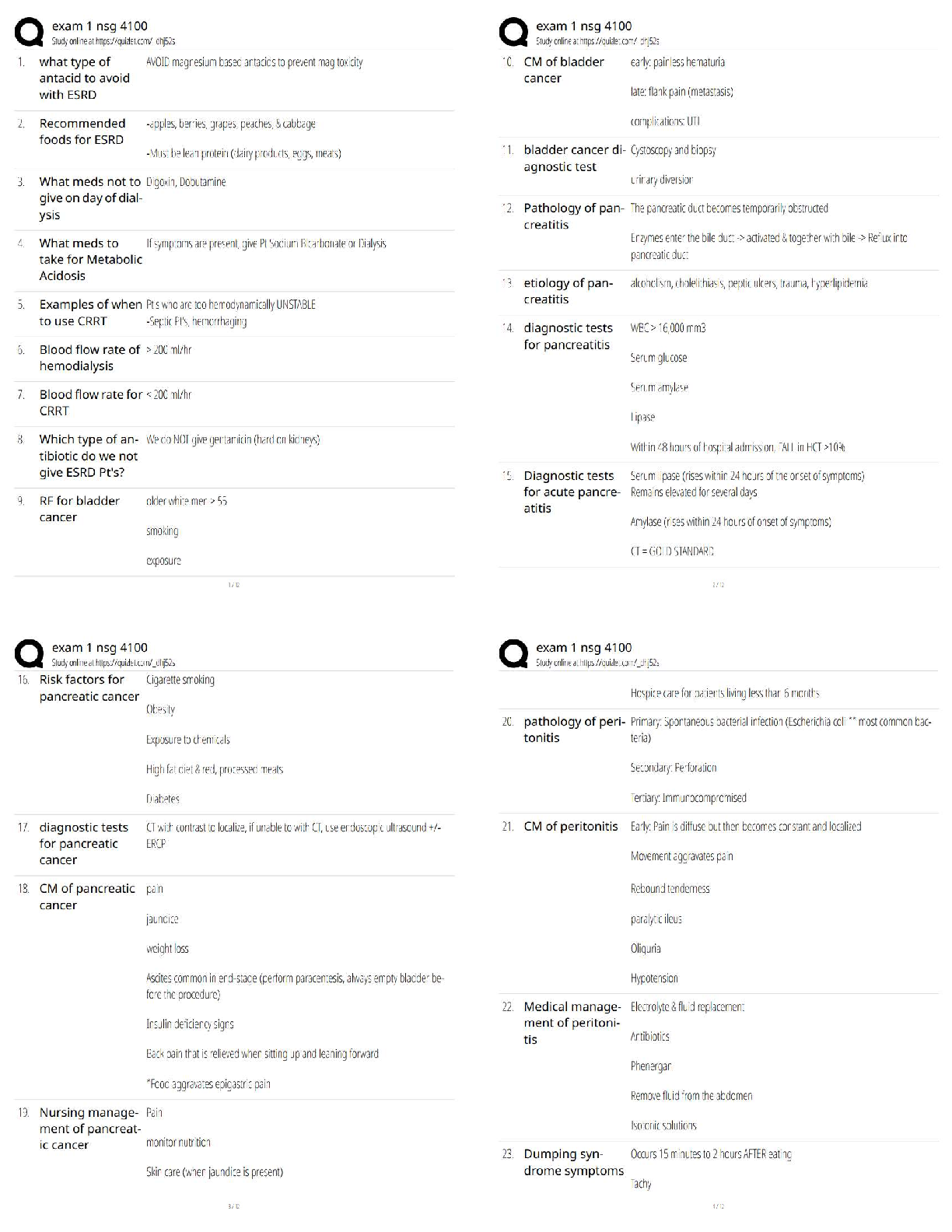
if X has an unknown dist, x bar has an approximately ________ dist if sample size is large
enough - ✔✔normal
we use stats to estimate: - ✔✔population parameters
as n increases, the mean of x bar... - ✔✔stays the same
as standard error increases, the sample size of x bar... - ✔✔decreases
increasing the CI and population standard deviation ( increases or decreases) the MOE -
✔✔increases
what does CLT apply to - ✔✔shape
There is a _____ chance that your sample mean lies within your 95% CI - ✔✔100%
if X has a normal dist, then the sampling distilled of x bar is __________ - ✔✔exactly normal
for any n
can p-values change if you take a new sample - ✔✔yes
large p-values mean you have ______ evidence against Ho - ✔✔little
p hat is the _______ proportion - ✔✔sample
why does the formula for a CI for p involve a z value - ✔✔because of the central limit theorem
a p value in HT testing means the same thing as the sample proportion (T/F) - ✔✔false
if you have a z value of .6, that means 60% of the data lie below you (T/F) - ✔✔false
a normal probability plot showing a straight line indicates what type of dist? - ✔✔normal
as n increases, what happens to mu x bar? - ✔✔stays the same
P(z<-2.72)= P(z>2.74) (T/F) - ✔✔true
if you want to estimate the pop mean, which technique do you use - ✔✔find a CI for u
if X is a random variable with a standard deviation of 10, then 3X has a standard deviation of -
✔✔30
the variance of X+Y= the variance of X + the variance of Y if X and Y are independent (T/F) -
✔✔true
when to use binomial distribution - ✔✔counting yes/ nos in a series of n trials or sample size of
n, only 2 categories
population - ✔✔entire group of interest
sample - ✔✔subject of entire group
what 3 things must be found out about the sampling distribution to make inferences about
population parameter - ✔✔mean, spread (standard deviation) and shape
Confidence Interval - ✔✔a range of likely values for the parameter
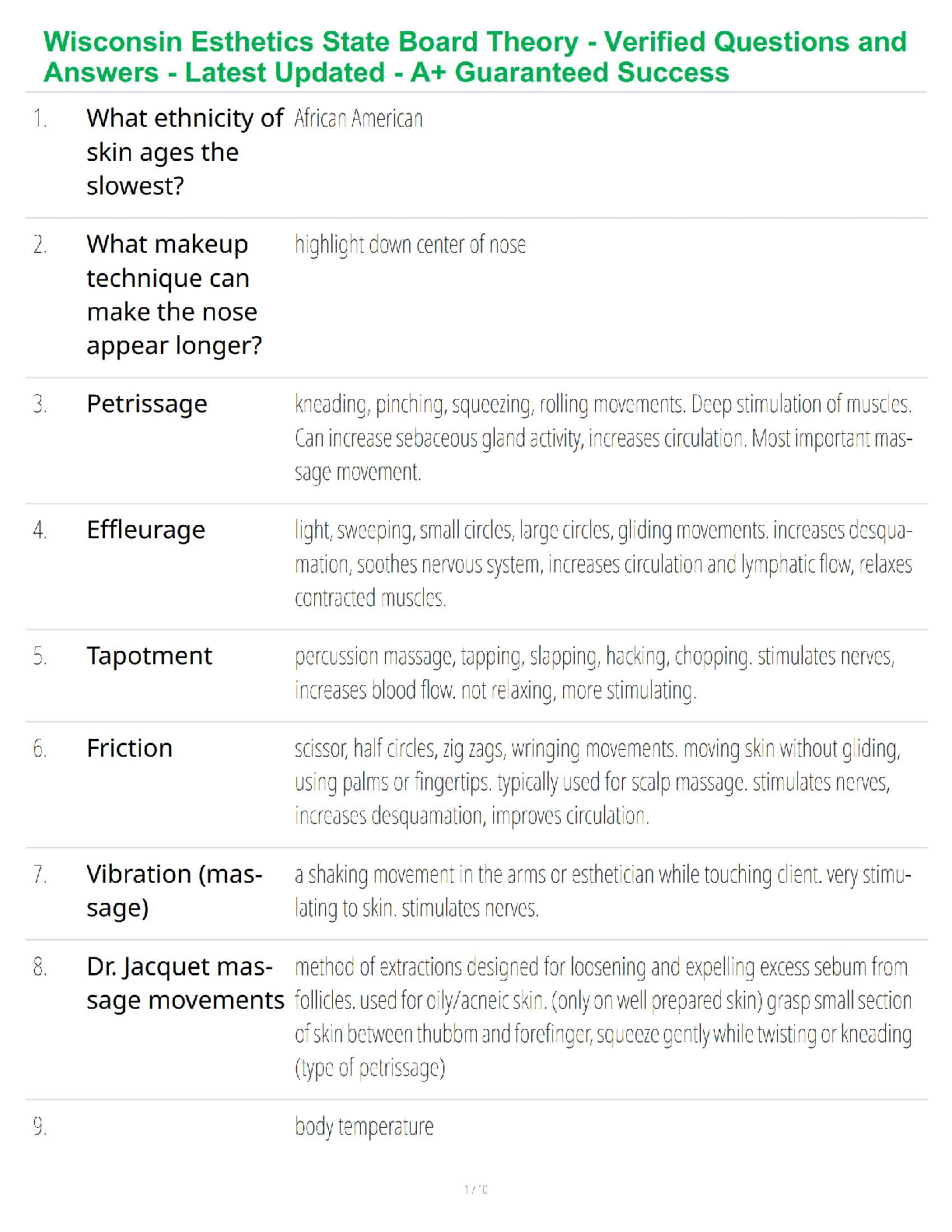
factors that affect moe - ✔✔confidence level (direct), n (inverse) , population standard deviation
(direct)
can you have a high level of confidence yet a small Moe? - ✔✔yes, use a large n
when looking at CI for population mean formulas must be... - ✔✔normal or use large n
significance level - ✔✔pre-set cutoff (.05)
p hat - ✔✔proportion of yeses in a sample, sample statistic
conditions for CI for pop proportions - ✔✔nphat>=10, n(1-phat)>=10
quick way to estimate MOE - ✔✔1/ square root of n
hypothesis tests give information about.. - ✔✔population parameters (p), not sample stays like
phat
if the sample mean increases, what happens to MOE - ✔✔nothing, stays the same
in a two-tailed hypothesis, any values within the confidence interval will result in the decision to
__________ the null hypothesis - ✔✔fail to reject
random variable - ✔✔characteristics that takes on random values, values unknown until data is
collected
discrete random variable - ✔✔finite, can be measured
continuous random variable - ✔✔cannot be measured
if X is a continuous random variable. then P(X=x)= - ✔✔0 for any value of X
examples of discrete random variables - ✔✔number of accidents on a busy highway, number of
red cares that go by out of a sample of 100
NOT EXAMPLE: time between accidents on a busy highway
we find a probability for a continuous random variable X by finding the _________ under the
________ - ✔✔area under the curve
normal distribution is/ shape - ✔✔continuous and symmetric
if X is above the mean, the Z score will be a ______ number - ✔✔positive
a z-value tells you how many _______ the X value is above or below its ______ - ✔✔standard
deviations, mean
the z-table always gives you the probability of being _____ than the number you are looking up -
✔✔less
[Show More]