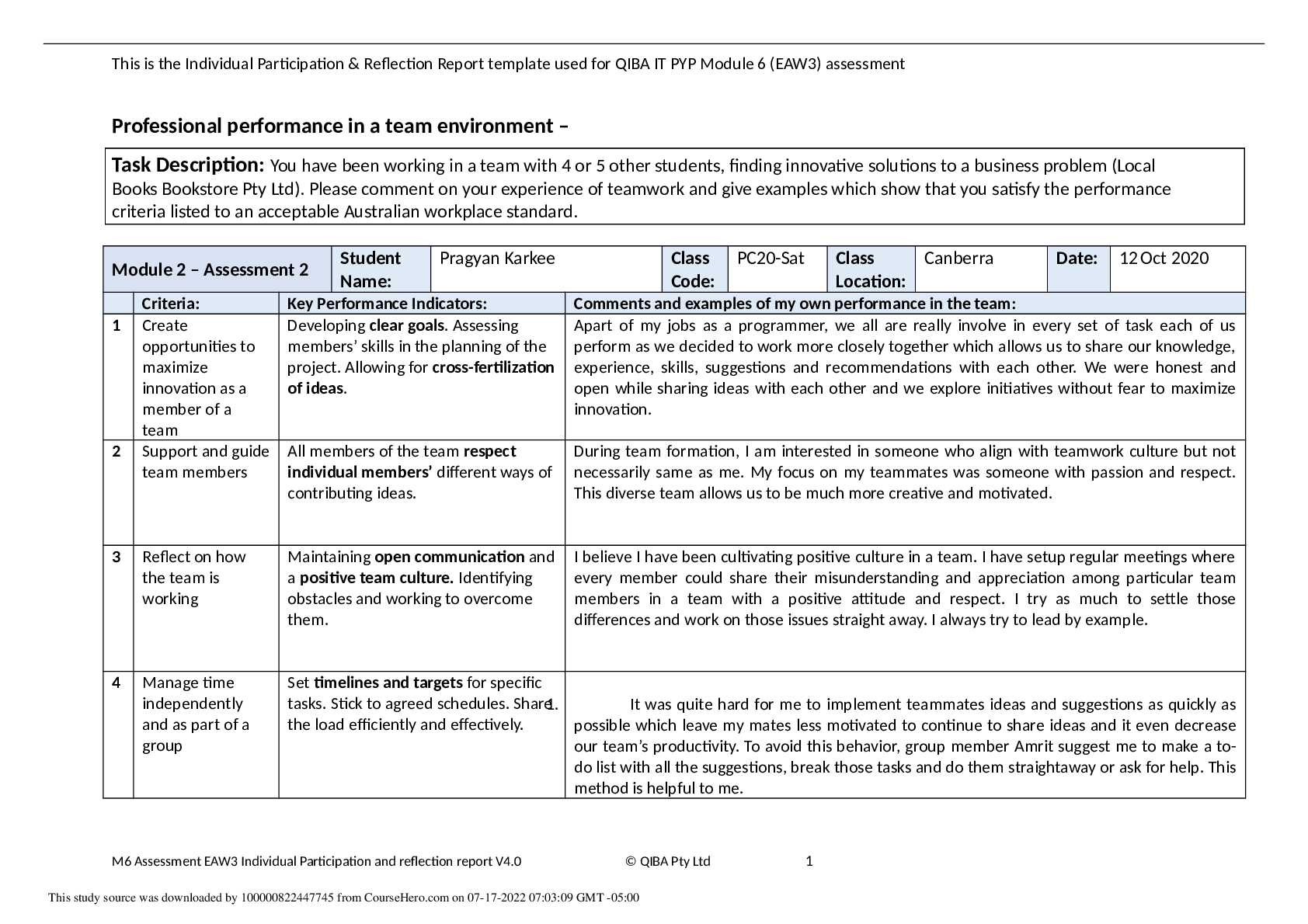
Laker Company report
Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product.
Date
Jan. 1 Beginning inventory $840
Jan. 10 Sales 100 units @ $15.00 = $1,500
Jan. 20 Purchase 300
J
...
Laker Company report
Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product.
Date
Jan. 1 Beginning inventory $840
Jan. 10 Sales 100 units @ $15.00 = $1,500
Jan. 20 Purchase 300
Jan. 25 Sales 80 units @ $15.00 = $1,200
Jan. 30 Purchase 810
380 units $1,950 180 units $2,700
60 units @ $5.00 =
180 units @ $4.50 =
Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units sold at Retail
140 units @ $6.00 =
Laker uses a perpetual inventory system. Complete comparative income statements for the month of January for Laker
Company for the four inventory methods. Assume expenses are $1,250, and that the applicable income tax rate is 40%.
For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 200 units, where 180 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from
the January 20 purchase, and 15 are from beginning inventory.
Exercise
5-‐4
5-2
Date
Jan. 1 Beginning inventory $840
Jan. 10 Sales 100 units @ $15.00 = $1,500
Jan. 20 Purchase 300
Jan. 25 Sales 80 units @ $15.00 = $1,200
Jan. 30 Purchase 810
380 units $1,950 180 units $2,700
60 units @ $5.00 =
180 units @ $4.50 =
For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 200 units, where 180 are from the January 30 purchase,
5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 15 are from beginning inventory.
Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units sold at Retail
140 units @ $6.00 =
Date Activity Units Unit
Cost
Units
Sold
Unit
Cost
COGS Ending
Inventory
Units
Cost per
Unit
Ending
Inventory
Cost
Jan. 1 Beg. Inv. 140 $6.00 125 $6.00 $750 15 $6.00 $90
Jan. 20 Purchase 60 $5.00 55 $5.00 275 5 $5.00 25
Jan. 30 Purchase 180 $4.50 0 $4.50 0 180 $4.50 810
$1,025 $925
Specific identification.
Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory
Specific Weighted
Identification Average FIFO LIFO
Sales $2,700
Cost of goods sold 1,025
Gross profit 1,675
Operating expenses 1,250
Income before tax 425
Income tax expense (40%) 170
Net income $255
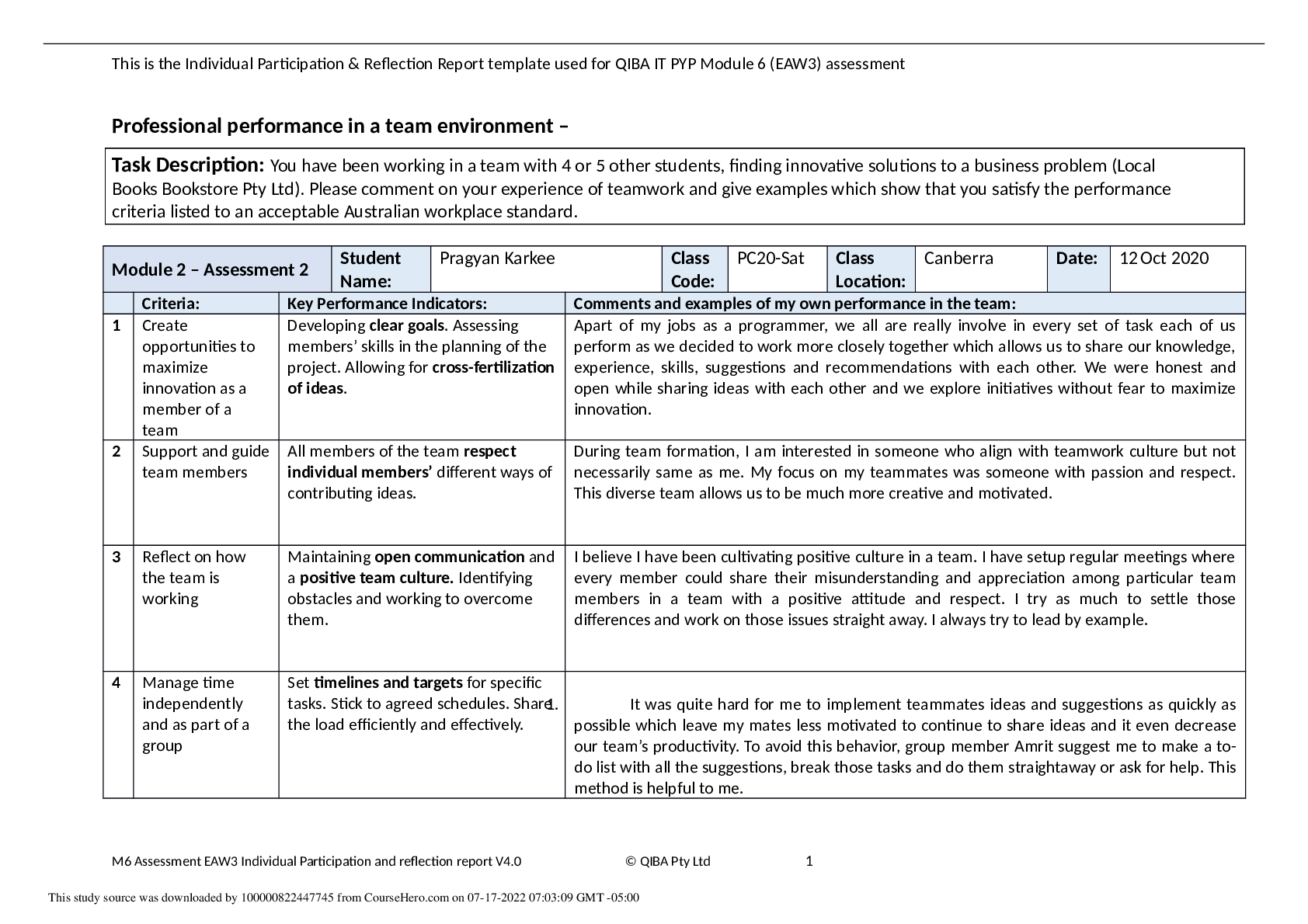
Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product.
Date
Jan. 1 Beginning inventory $840
Jan. 10 Sales 100 units @ $15.00 = $1,500
Jan. 20 Purchase 300
Jan. 25 Sales 80 units @ $15.00 = $1,200
Jan. 30 Purchase 810
380 units $1,950 180 units $2,700
60 units @ $5.00 =
180 units @ $4.50 =
Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units sold at Retail
140 units @ $6.00 =
Laker uses a perpetual inventory system. Complete comparative income statements for the month of January for Laker
Company for the four inventory methods. Assume expenses are $1,250, and that the applicable income tax rate is 40%.
For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 200 units, where 180 are from the January 30 purchase, 5 are from
the January 20 purchase, and 15 are from beginning inventory.
Exercise
5-‐4
5-2
Date
Jan. 1 Beginning inventory $840
Jan. 10 Sales 100 units @ $15.00 = $1,500
Jan. 20 Purchase 300
Jan. 25 Sales 80 units @ $15.00 = $1,200
Jan. 30 Purchase 810
380 units $1,950 180 units $2,700
60 units @ $5.00 =
180 units @ $4.50 =
For specific identification, ending inventory consists of 200 units, where 180 are from the January 30 purchase,
5 are from the January 20 purchase, and 15 are from beginning inventory.
Activities Units Acquired at Cost Units sold at Retail
140 units @ $6.00 =
Date Activity Units Unit
Cost
Units
Sold
Unit
Cost
COGS Ending
Inventory
Units
Cost per
Unit
Ending
Inventory
Cost
Jan. 1 Beg. Inv. 140 $6.00 125 $6.00 $750 15 $6.00 $90
Jan. 20 Purchase 60 $5.00 55 $5.00 275 5 $5.00 25
Jan. 30 Purchase 180 $4.50 0 $4.50 0 180 $4.50 810
$1,025 $925
Specific identification.
Available for Sale Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory
Specific Weighted
Identification Average FIFO LIFO
Sales $2,700
Cost of goods sold 1,025
Gross profit 1,675
Operating expenses 1,250
Income before tax 425
Income tax expense (40%) 170
Net income $255
[Show More]











.png)





