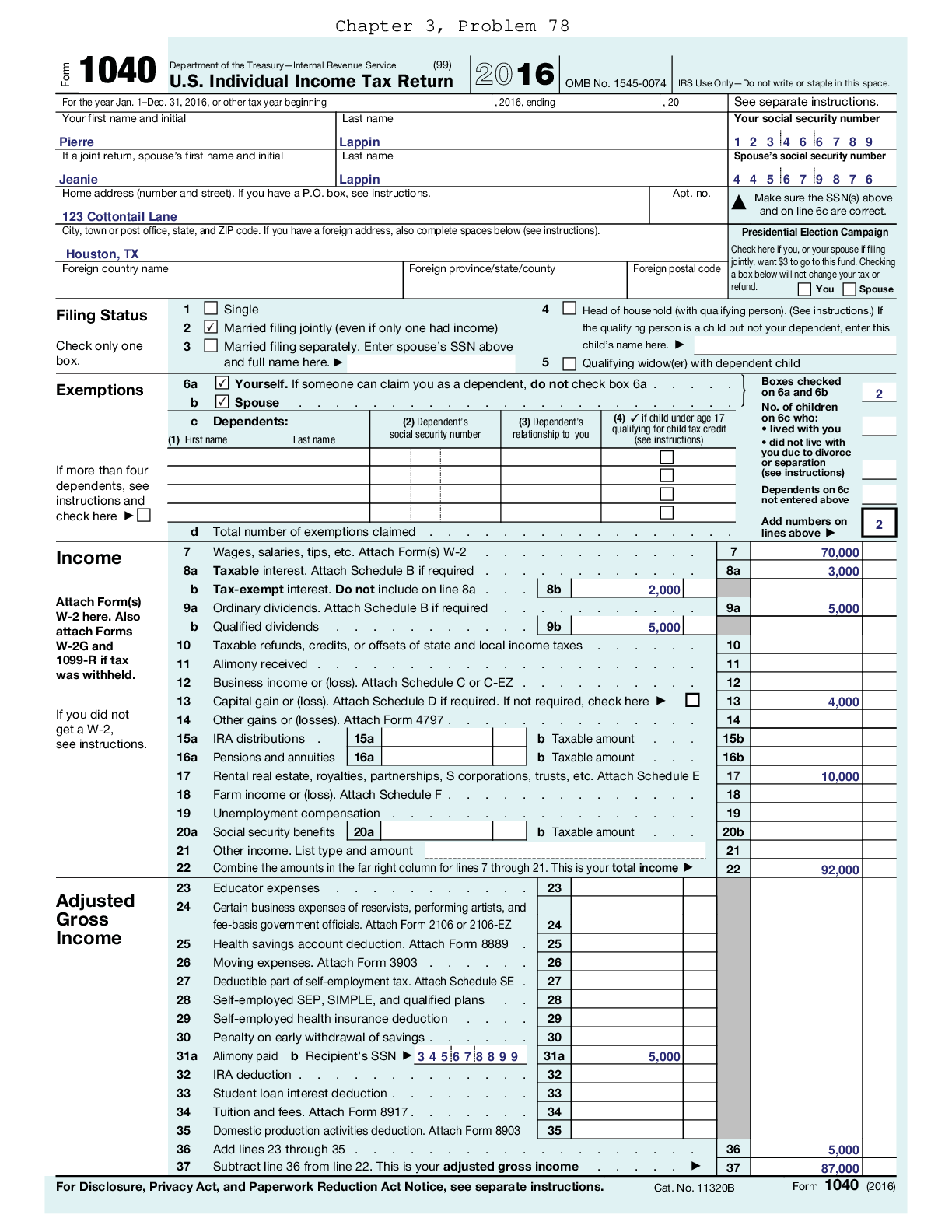
Linear Programming
Linear Programming
Solutions of Homework 2
Problem 1 (0.4 points): Linear programming models are used by many Wall Street firms to select
a desirable bond portfolio. The following is a simplified v
...
Linear Programming
Linear Programming
Solutions of Homework 2
Problem 1 (0.4 points): Linear programming models are used by many Wall Street firms to select
a desirable bond portfolio. The following is a simplified version of such a model. Solodrex is
considering investing in four bonds; $1,000,000 is available for investment. The expected annual
return, the worst case annual return, and the \duration" of each bond are given in Table 1.
Table 1: Return and duration of bonds
Expected return Worst-case return Duration
Bond 1 13% 6% 3
Bond 2 8% 8% 4
Bond 3 12% 10% 7
Bond 4 14% 9% 9
The duration of a bond is a measure of the bond’s sensitivity to interest rates. Solodrex wants to
maximize the expected return from its bond investments, subject to three constraints.
(a) The worst-case return of the bond portfolio must be at least 8%.
(b) The average duration of the portfolio must be at least 6. For example, a portfolio that invested
$600,000 in bond 1 and $400,000 in bond 4 would have an average duration of
600; 000(3) + 400; 000(9)
1; 000; 000
= 5:4
(c) Because of diversification requirements, at most 40% of the total amount can be invested in a
single bond.
Formulate an LP that will enable Solodrex to maximize the expected return on its investments.
Solution: Let xi be the amount of money invested in Bond i, i = 1; 2; 3; 4. Then the LP problem can
be formulated as
maximize 0:13x1 + 0:08x2 + 0:12x3 + 0:14x4
subject to 0:06x1 + 0:08x2 + 0:1x3 + 0:09x4 ≥ 0:08(x1 + x2 + x3 + x4)
3x1 + 4x2 + 7x3 + 9x4 ≥ 6(x1 + x2 + x3 + x4)
0 ≤ xi ≤ 400; 000; i = 1; 2; 3; 4:Problem 2 (0.4 points, Exer. 14 (a) in Linear Programming Exercises):
An illumination problem. We consider an illumination system of m lamps, at positions l1; · · · ; lm 2
R2, illuminating n flat patches. The patches are line segments; the i-th patch is given by [vi; vi+1],
where v1; · · · ; vn+1 2 R2. The variables in the problem are the lamp powers p1; · · · ; pm, which can
vary between 0 and 1.
[Show More]












 V1-V2.png)