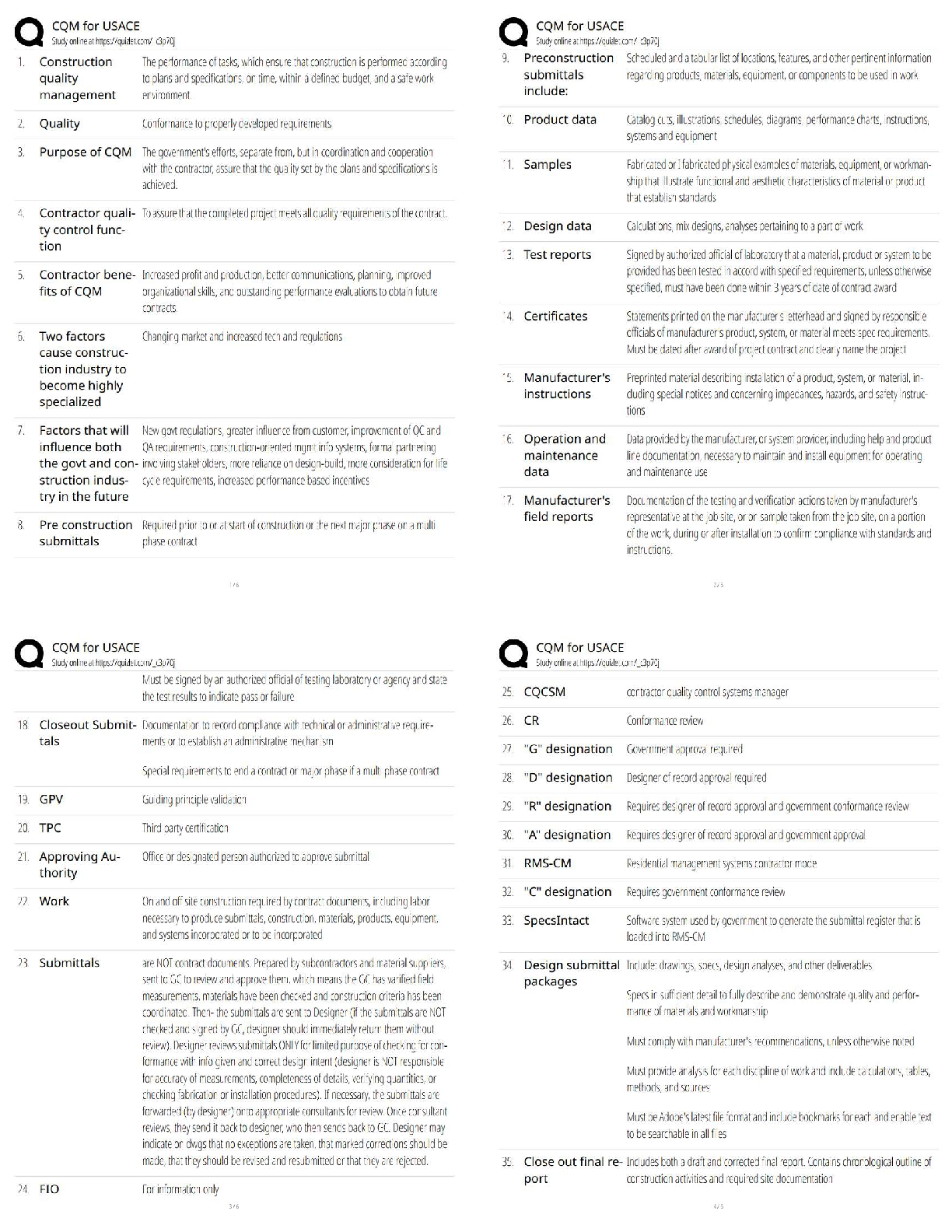
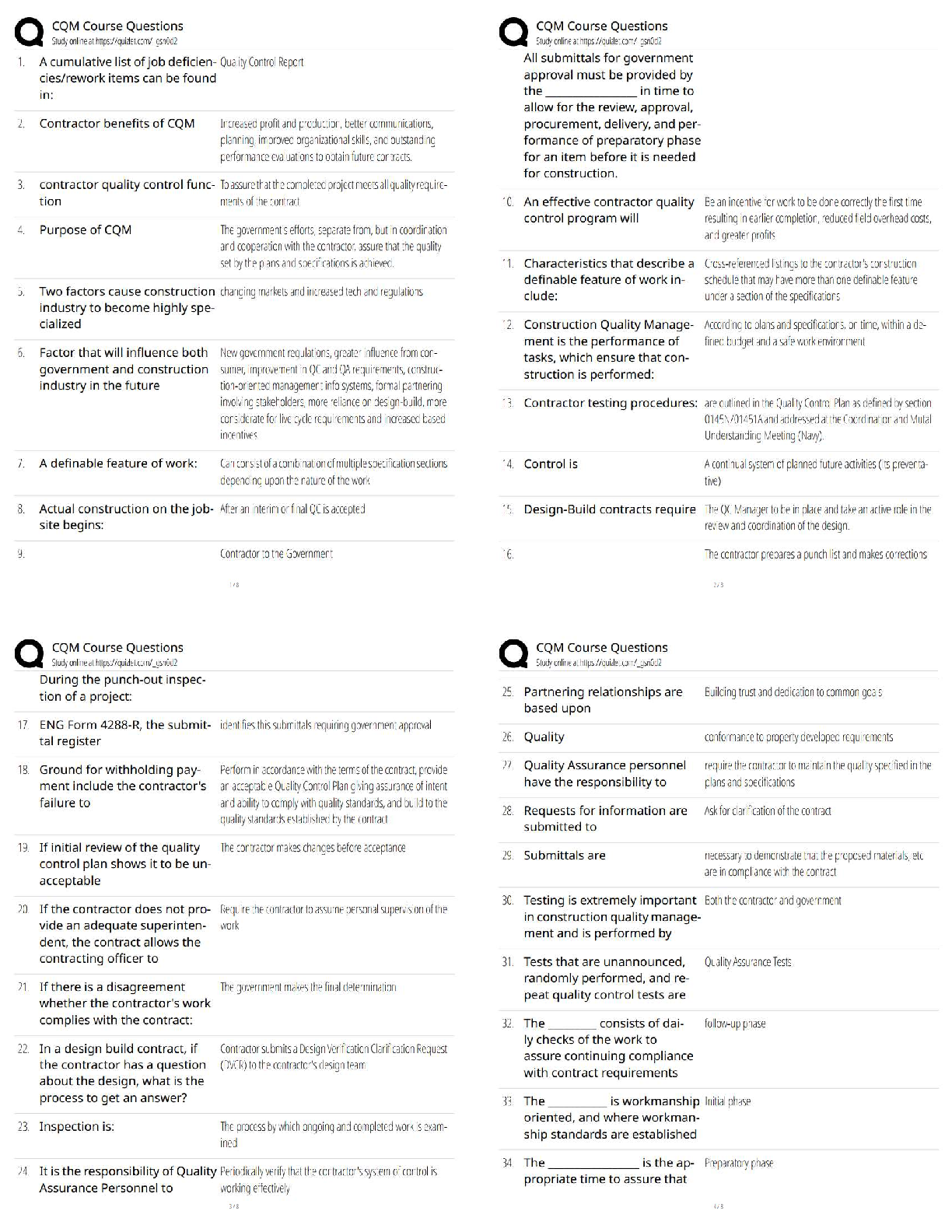
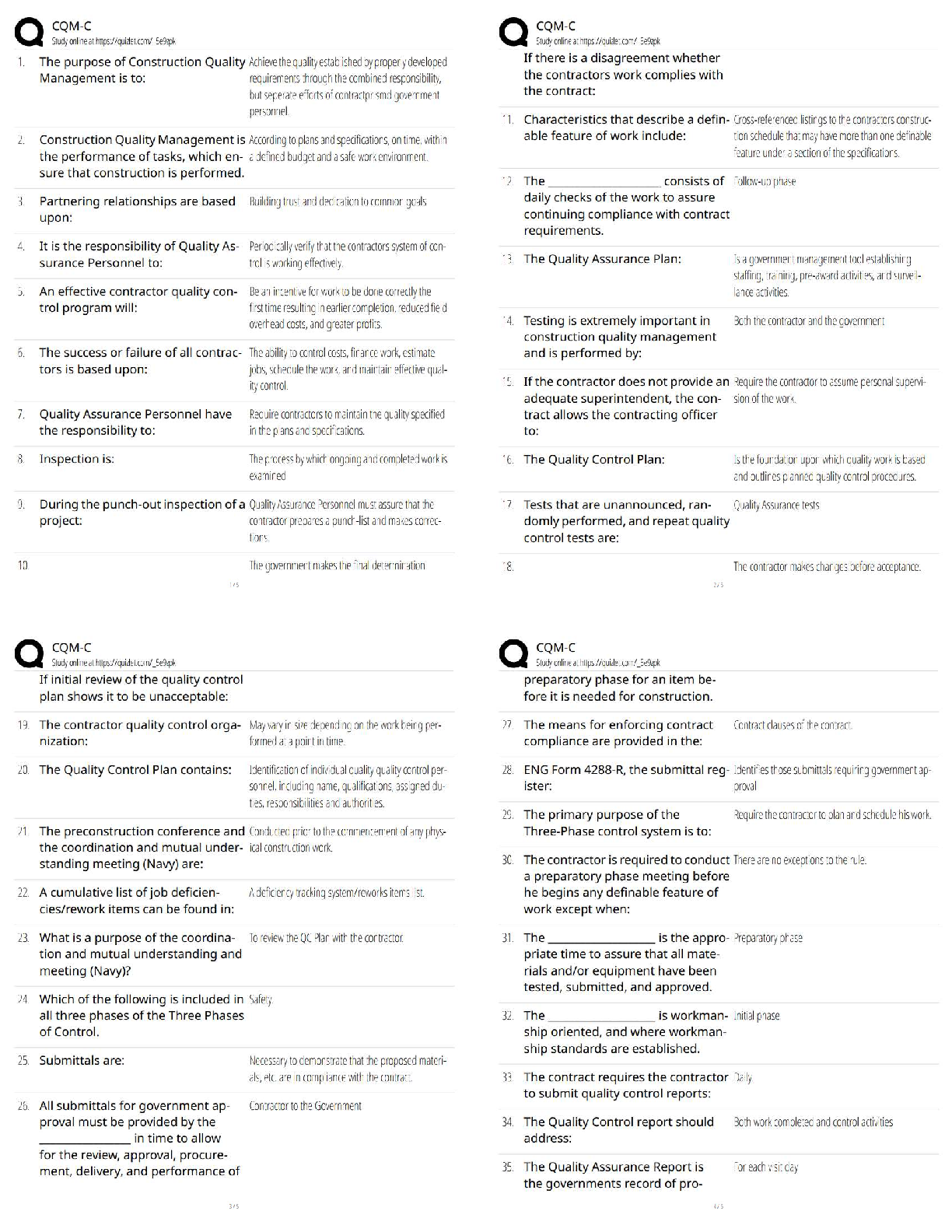
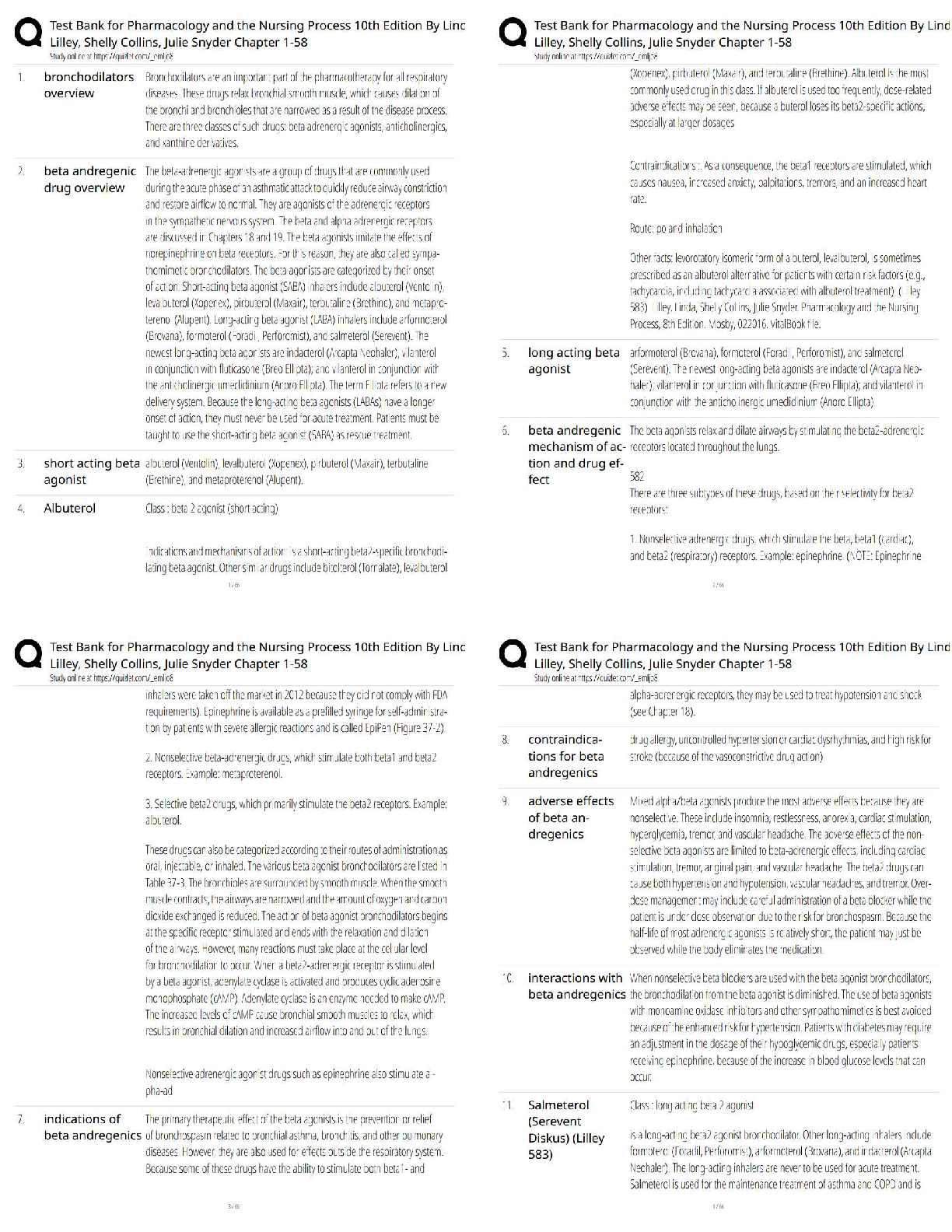
1. As an example of a price index, consider the A.C.D.P.I. (a fictitious price index). The
associated basket of goods is:
Good Quantity Price
Coffee 3 lb $8/lb
Bread 3 loaves $1/loaf
Tea 1 lb $15/lb
Aspirin 1 200-t
...
1. As an example of a price index, consider the A.C.D.P.I. (a fictitious price index). The
associated basket of goods is:
Good Quantity Price
Coffee 3 lb $8/lb
Bread 3 loaves $1/loaf
Tea 1 lb $15/lb
Aspirin 1 200-tablet bottle $2/bottle
Cola 1 case $6/case
A. If the price of coffee doubles, what is the resulting percentage change in
the price level? (2 points)
The resulting percentage change is 48%
B. If the price of bread doubles, what is the resulting percentage change in
the price level? (2 points)
The resultant percentage change is 6%
C. Why is the effect of a 100% increase in the price of coffee so much
greater than the effect of a similar change in the price of bread? (4 points)
Coffee costs a lot more, so it would increase by $8 bringing the total price of
coffee to $16 dollars, whereas bread would only increase by $1, bringing the
total price to $2.
D. Assume that the mix of goods in a basket is kept constant for long periods. If
the price of one good rises very rapidly over several years, what will happen
to the relative importance of the other goods in the basket? Is this a
problem? (6 points)
The other goods will not be affected much because they are all independent.
For example, if the price of gasoline went up significantly, the price level and
the total price would change for that year, but it would not affect the other
goods in the unless they were substitutes for the good that drastically
changed in price. This is not a problem since changing the price of one good
drastically would only affect the price total and price level, not the other
goods in that basket if they were not substitutes for the good.
E. If the price of coffee increases, we get a positive rate of inflation, even if
no other price rises. Is this really inflation? Explain. (6 points)
This is not really inflation, because only one price has increased, and inflation
is defined as a general increase in many, but not all prices. So the increase in
price of coffee could be caused by another factor such as a quality change or
substitute goods and may not be inflation. Coffee could also be a volatile
good.
2. In 1997, the price of a particular basket of goods was $2,900. In 1998, the price of the
same basket was $3,300. In 1996, the base year, the price of the basket was $2,500.
(Hint: price index is price indexed to a base year.)
A. Calculate price index for 1996, 1997, and 1998. (3 points)
The price index for 1996 = 2500/2500 *100 = 100
The price index for 1997 = 2900/2500 *100 = 116
The price index for 1998 = 3300/2500 *100 = 132
B. Calculate inflation rates for 1996-97 and 1997-98. Is inflation increasing
or decreasing (2 points)
The inflation rate from 1996-1997 is 16%.
The inflation rate from 1997-1998 is 14%
Inflation is decreasing because disinflation is happening.
You buy a certificate of deposit (CD) that pays a nominal rate of 12% annually. You have
a tax rate of 25%, so if the interest on this CD is taxable (which it may not be) your
after-tax nominal rate is (1 – 25%) 12% = 9%. Since 10% equals .1, we can rewrite the
equation as: (1 – .25) .12 = .09. For parts (A-C), the nominal rate if 12%, annually and
the after-tax nominal rate is 9%.
A. If the inflation rate is 6% and interest on this CD is not taxable, what is the
real interest rate on the CD? Hint: What is the relationship between the real rate of
interest and the nominal rate of interest? (2 points)
The real rate is (12-6) 6%.
B. If the inflation rate is 6% and the interest on this CD is taxable, what is
the real interest rate on the CD? (2 points)
[Show More]