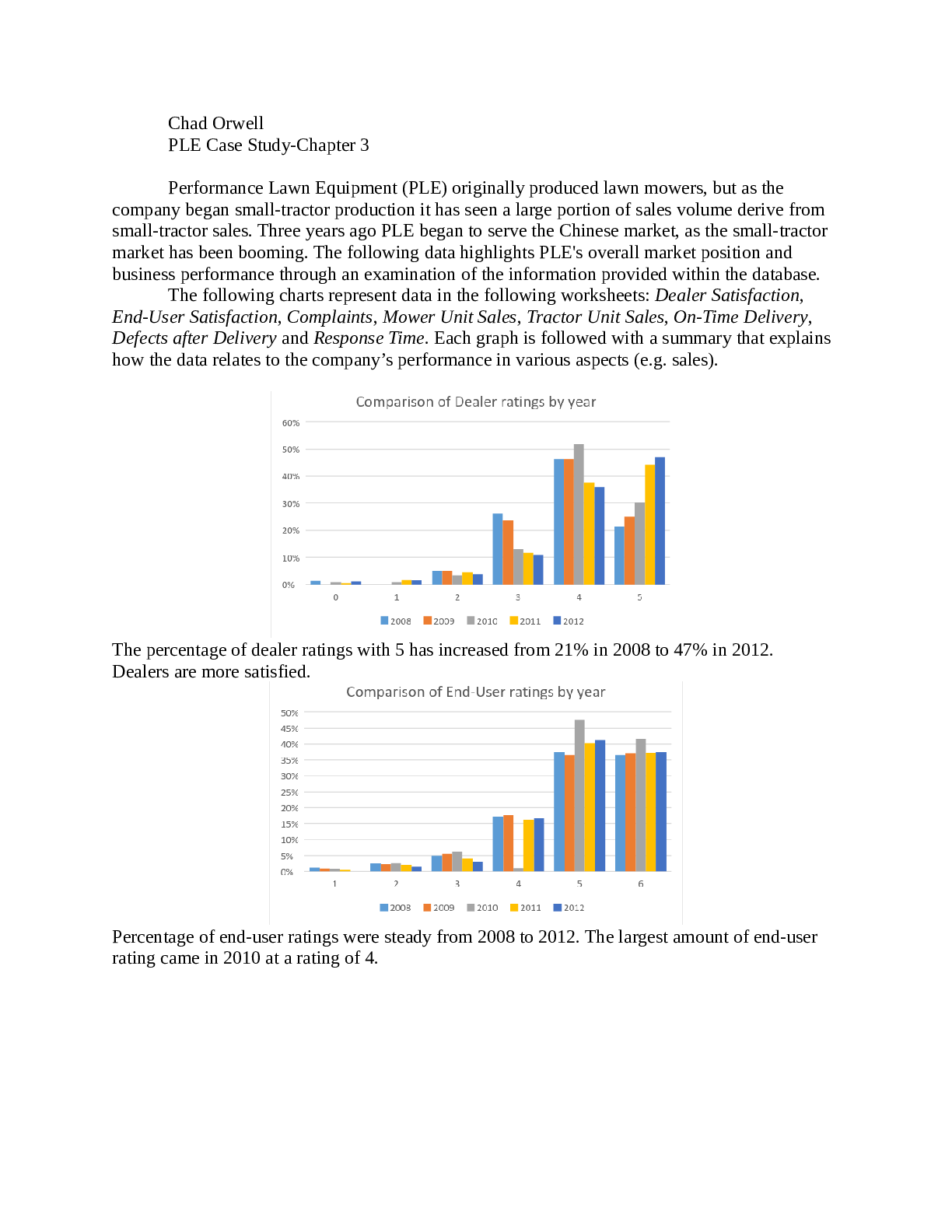
The Haier Case Study Potential Controlling issue | Address the potential controlling issue facing the Haier Group, as it may be a vital component in the company’s future successes.
1. Introduction and Problem Identific
...
The Haier Case Study Potential Controlling issue | Address the potential controlling issue facing the Haier Group, as it may be a vital component in the company’s future successes.
1. Introduction and Problem Identification
The purpose of this report is to address the potential controlling issue facing the Haier
Group, as it may be a vital component in the company’s future successes. The Haier
Group is a household appliance and electronics company and is one of the most valued
brands in China (Lin, 2014). Amongst a companies many achievements and successes,
they are still susceptible to potential problems. According to Ilias, Abdulatiff and
Mohamed (2016), for companies to succeed and excel in performance, it is essential to
incorporate management control systems within a business. These systems are used to
measure and assess performance allowing corrective action to take place; ensuring
desired goals are achieved (Illias et al., 2016). In this particular case the Haier Group
implemented the OEC management control system, which required employees to
complete the mandatory work with a 1% increase over what was done the previous day
(Lin, 2014). This implementation was designed to monitor the work performance of
individuals as a means of feedback control. This may however cause more harm than
originally thought, as the extent to which control may hinder performance should be
considered in regards to this case study (Wijethilake, Munir, & Appuhami, 2016).
With the unsustainable goal of increasing productivity everyday and as well as penalties
for incompliance, synergy is problematic. When employees fear their own failure they
are more likely to work individually rather than as a cohesive team. Levecque, Roose,
Vanroelen, & Rossem (2014) states that employees with a negative perception of the
affective climate of their team may experience higher levels of psychological stress in
the workplace. Therefore, in Haier’s case creating this highly competitive atmosphere
with unobtainable goals, may amplify stress in employees. This could inturn lead to
higher turnover or devious and unethical behaviour if not resolved (Chovwen,
Olowokere & Balogun, 2014). This report will firstly discuss contemporary literature
on management controls such as feedback and bureaucratic control. They will then be
contrasted and examined in light of the Haier case. Finally, this report will provide a
solution utilising bureaucratic control.
1. Introduction and Problem Identification 2
2. Discussion 3
2.1 Feedback Control 3
2.2 Bureaucratic Control 4
3. Conclusion 6
4. Recommendations 7
5. References:
Firstly levels of authority must be established consisting of a few high-ranking
managers who must determine organisational goals that are clear, realistic, challenging
and obtainable. They are then assigned responsibility to control and monitor employees
and their performance. This can be achieved by defining rules that set guidelines for
behaviour as well as methods for executing work tasks through clear policies and
procedures that are enforced strongly through authority. Employees will also be
recognised and rewarded relative to organisational goals and standards, not favouritism
or luck. Authority figures are then required to patrol and supervise daily activities
providing guidance and support for employees. This implementation will allow
employees access to strict instructions to ensure production follows managerial
procedures, decreasing chances of devious behaviour and induced stress due to inability
to complete tasks correctly.xxxxxxx sxxxxxxx xxxxxxx
8
5. References:
Ahmad, Z., & Norhashim, M. (2008). The control environment, employee fraud and
counterproductive workplace behaviour: An empirical analysis.
Communications of the IBIMA, 3, 145-155.
Chovwen, C. O., Olowokere, B. O., & Balogun, S. K. (2014). Determinants of job
hopping experience among private and public sector employees' turnover
intention. IFE Psychologia: An International Journal, 22(2), 114-124.
Ebrahimi, M., & Sadeghi, M. (2013). Quality management and performance: An
annotated review. International Journal of Production Research, 51(18),
5625-5643. doi:10.1080/00207543.2013.793426
Grabner, I., & Speckbacher, G. (2016). The cost of creativity: A control perspective.
Accounting, Organizations and Society, 48, 31-42.
Hoggett, P. (1996). New modes of control in the public service. Public
Administration, 74(1), 9-32. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9299.1996.tb00855.x
Ilias, N., Abdulatiff, N. K., & Mohamed, N. (2016). Management control system and
performance: Accountability attributes in local authorities. International
Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 6(4), 26-35.
Kreitner, R. (1982). The feedforward and feedback control of job performance
through organizational behavior management (OBM). Journal of
Organizational Behavior Management, 3(3), 3-20.
doi:10.1300/J075v03n03_02
Lechler, T. G., & Cohen, M. (2009). Exploring the role of steering committees in
realizing value from project management. Project management journal,
40(1), 42-54.
Levecque, K., Roose, H., Vanroelen, C., & Rossem, R. V. (2014). Affective team
climate: A multi-level analysis of psychosocial working conditions and
psychological distress in team workers. Acta Sociologica, 57(2), 153-166.
doi:10.1177/0001699313498262
Lin, T. W. (2005). OEC management-control system helps china haier group achieve
competitive advantage. Management Accounting Quarterly, 6(3).
Shiraz, N., Rashid, M., & Riaz, A. (2011). The impact of reward and recognition
programs on employee's motivation and satisfaction. Interdisciplinary
Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, 3(3), 1428.
Tat Wai Yu, B., & Wai Ming, T. (2008). Effects of control mechanisms on positive
organizational change. Journal of Organizational Change Management,
21(3), 385-404.xxxxxxx sxxxxxxx xxxxxxx
9
Wijethilake, C., Munir, R., & Appuhami, R. (2016). Environmental innovation
strategy and organizational performance: Enabling and controlling uses of
management control systems. Journal of Business Ethics, 1-22.
doi:10.1007/s10551-016-3259-7
Wynder, M. (2007). The interaction between domain-relevant knowledge and control
system design on creativity. Australian Journal of Management, 32(1), 135-
152.
[Show More]






.png)