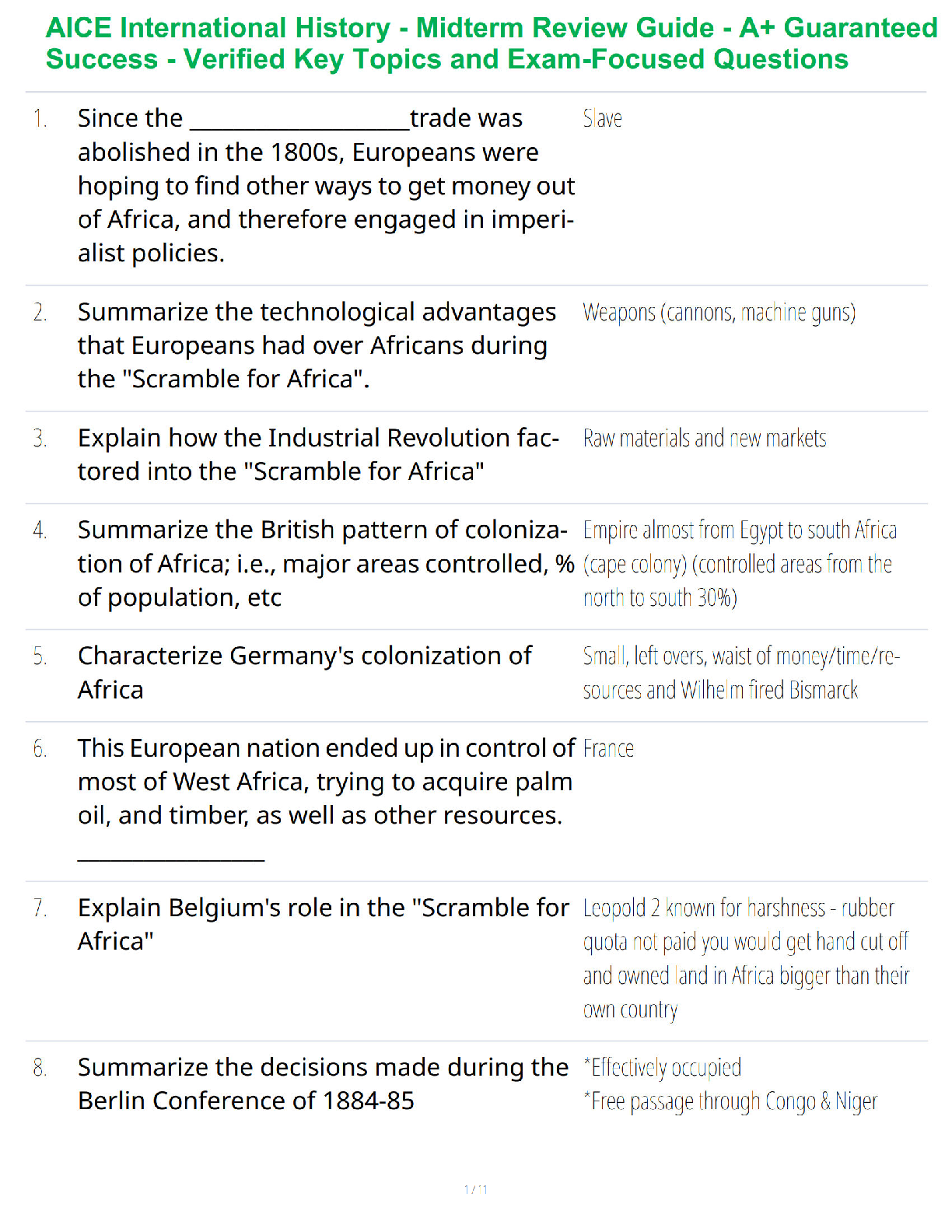
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
TERMINOLOGY
Absorb- take in or soak up
Ccute- has relatively severe manifestations but runs short course measured in hours, days, or a
few weeks.
Advers
...
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
TERMINOLOGY
Absorb- take in or soak up
Ccute- has relatively severe manifestations but runs short course measured in hours, days, or a
few weeks.
Adverse- preventing successes or development; harmful
Chronic- lasts for months to years.
Clinical- relating to the observation and treatment of actual patients rather than theoretical or
laboratory studies
Manifestations- are observed as signs of diseases, both objective and subjective
Compensate-to give something in recognition of loss/injury
cyanosis- a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from poor circulation or inadequate oxygen
to the blood.
Cytology- the branch of biology surrounding the structure of plant and animal cells
Detrimental- tending to cause harm
Disseminate- spread widely
Diagnosis- the identification of the nature of an illness by examination of symptoms
Endemic- a disease or condition regularly found among a particular people in a certain area
Epidemic- a disease is disseminated to many individuals at the same time
Epidemiology- the study and analysis of the distribution and patterns of health and disease
conditions in defined populations
Etiology- the study of causes or reasons for a phenomena
Exacerbate- to make worse
Excrete- to separate and expel as waste
Histology- the study of microscopic structure of tissues
Hypoxemia- poor oxygenation of blood
Hypoxia- a condition in which the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply
Iatrogenic- the cause is a result of an unintended or unwanted medical intervention
Idiopathic- the cause is unknown
Incidence- the occurrence, rate, or frequency of a crime
incubation period- the interval between exposure of a tissue to an injurious agent and the first
appearance of symptoms in the case of infectious diseases.
Infarction- death tissue due to inadequate blood supply to the affected area
Inhibit- to hold in/hold back, restrain
Insidious- proceeding a gradual, subtle way, but with harmful effects
Intermittent- occurring at irregular cycles
Ischemia- inadequate delivery of blood to cells
Latent period- the interval between exposure to a tissue to an injurious agent and the first
appearance of symptoms
Maladaptive- dysfunctional
Morbidity- the condition of being diseased
Mortality- the state of being subject to death
Multifactorial- involving or dependent on a number of factors or causes
Occlusion- the blockage or closing of a blood vessel or hollow organ
Occurrence- an event/incident
Pallor- an unhealthy appearance
Pandemic- are epidemics that affect large regions and perhaps spreading worldwide
Pathogenesis- refers to the development or evolution of a disease
Pathology- the study and diagnosis of disease through examination of organs, tissues, cells, and
bodily fluids
Pathophysiology- the disordered physiological processes associated with disease/injury
Perfusion- the passage of blood through the blood vessels or other natural channels
Physiology- the branch of biology that deals with live organisms and their parts
Prevalence- commonness
Prodromal period- the appearance of the first signs and symptoms indicating the onset of disease
Prognosis- the forecast of what is likely to come of the disease
Prolonged- extend the duration of
Remission- a temporary recovery
Risk factor- when the link between an etiologic
[Show More]