7th Edition SERVSAFE Exam
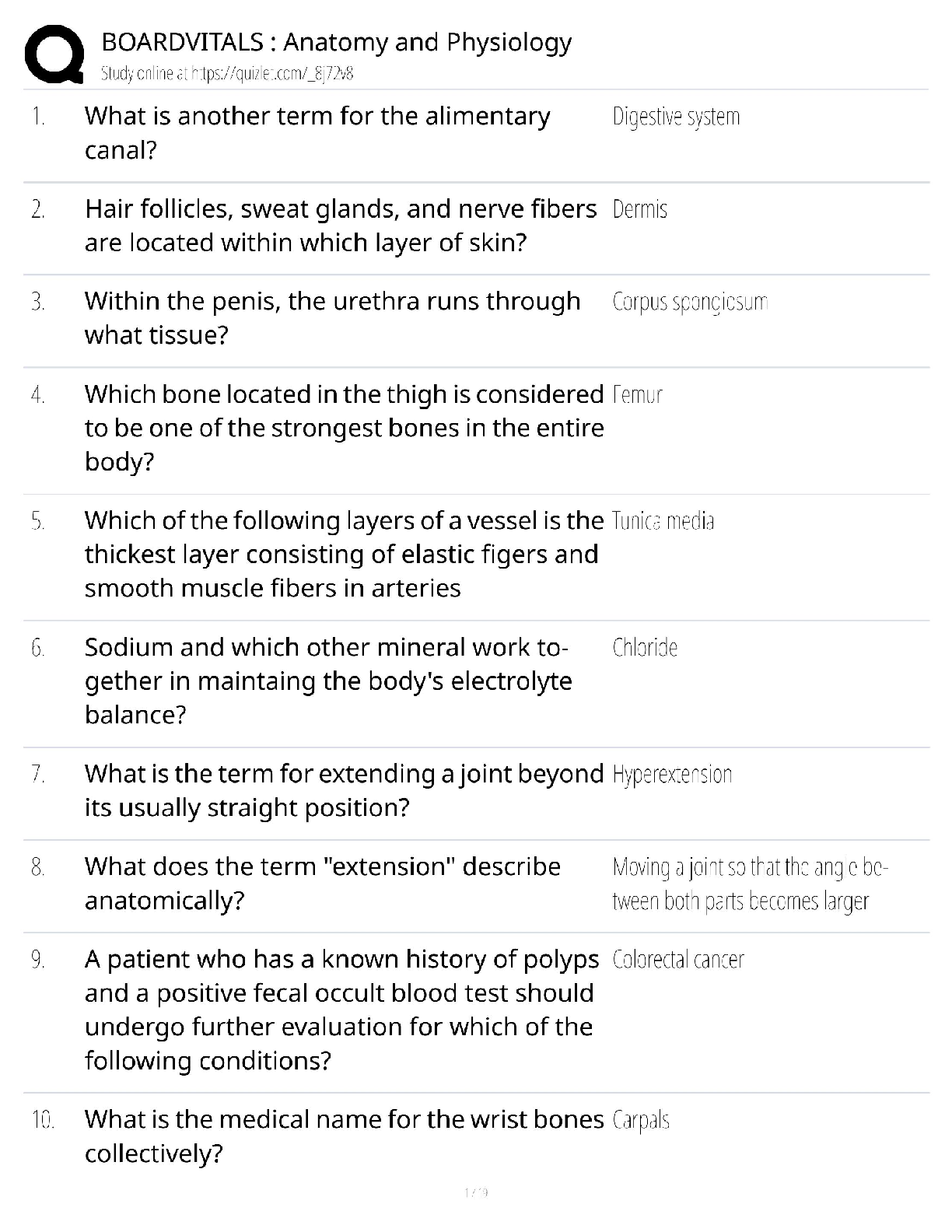
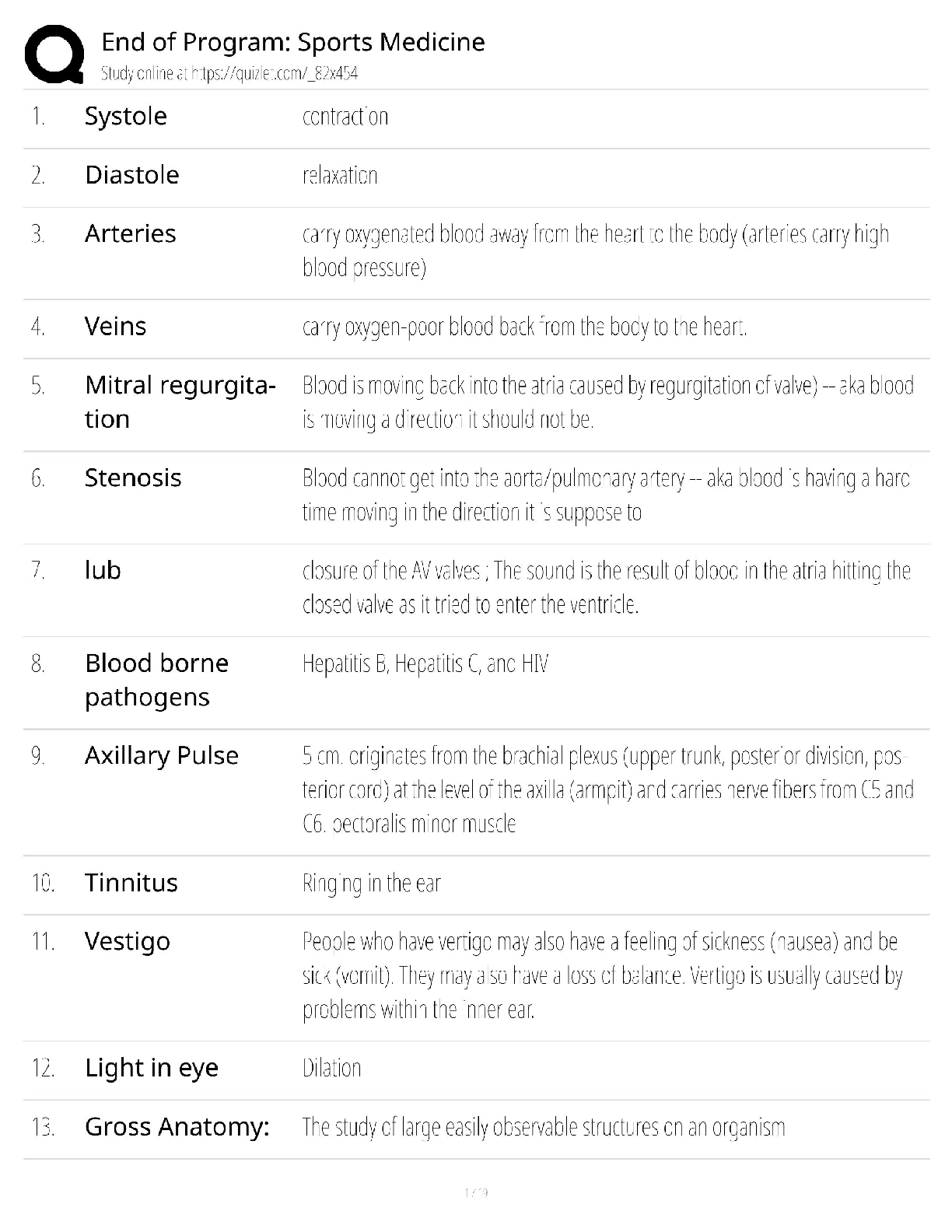
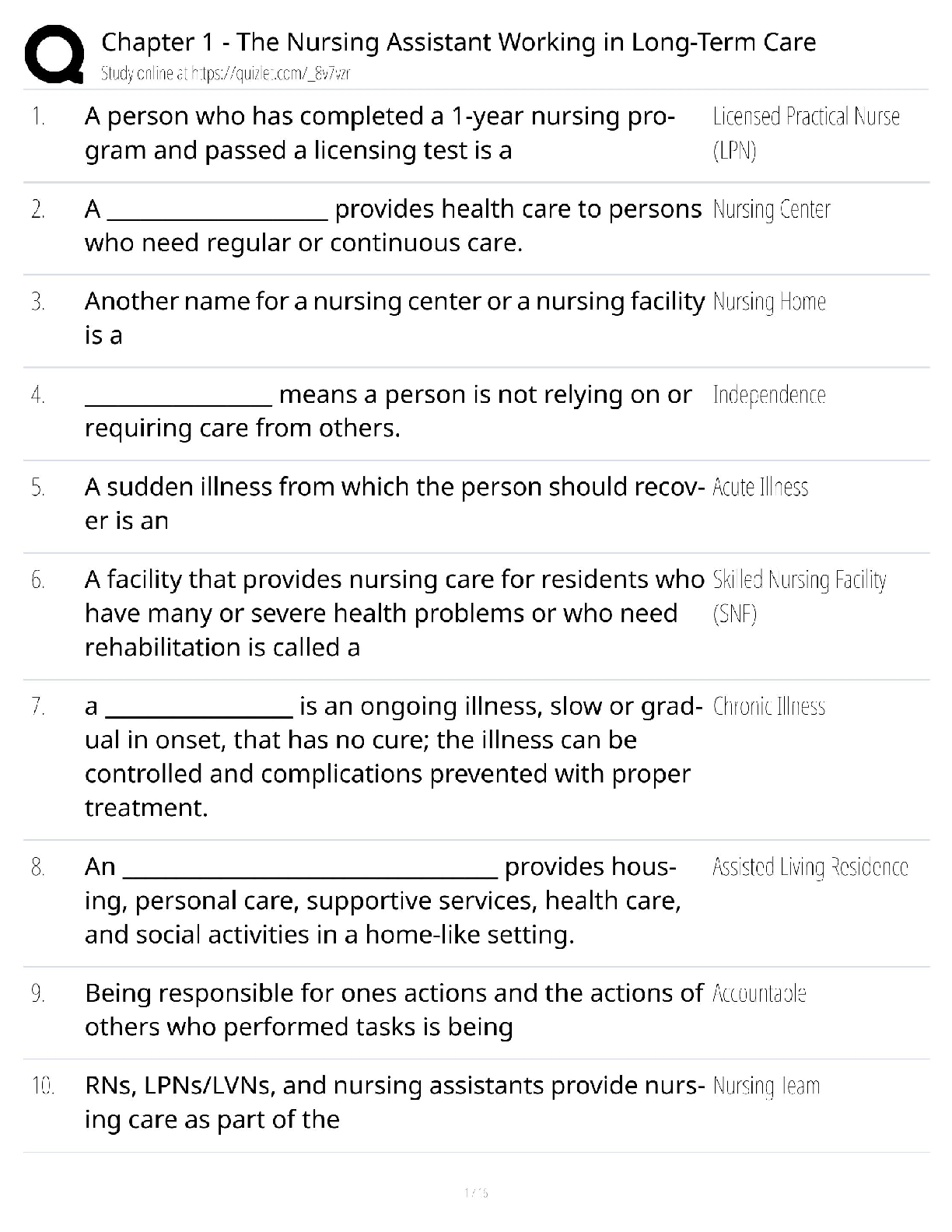
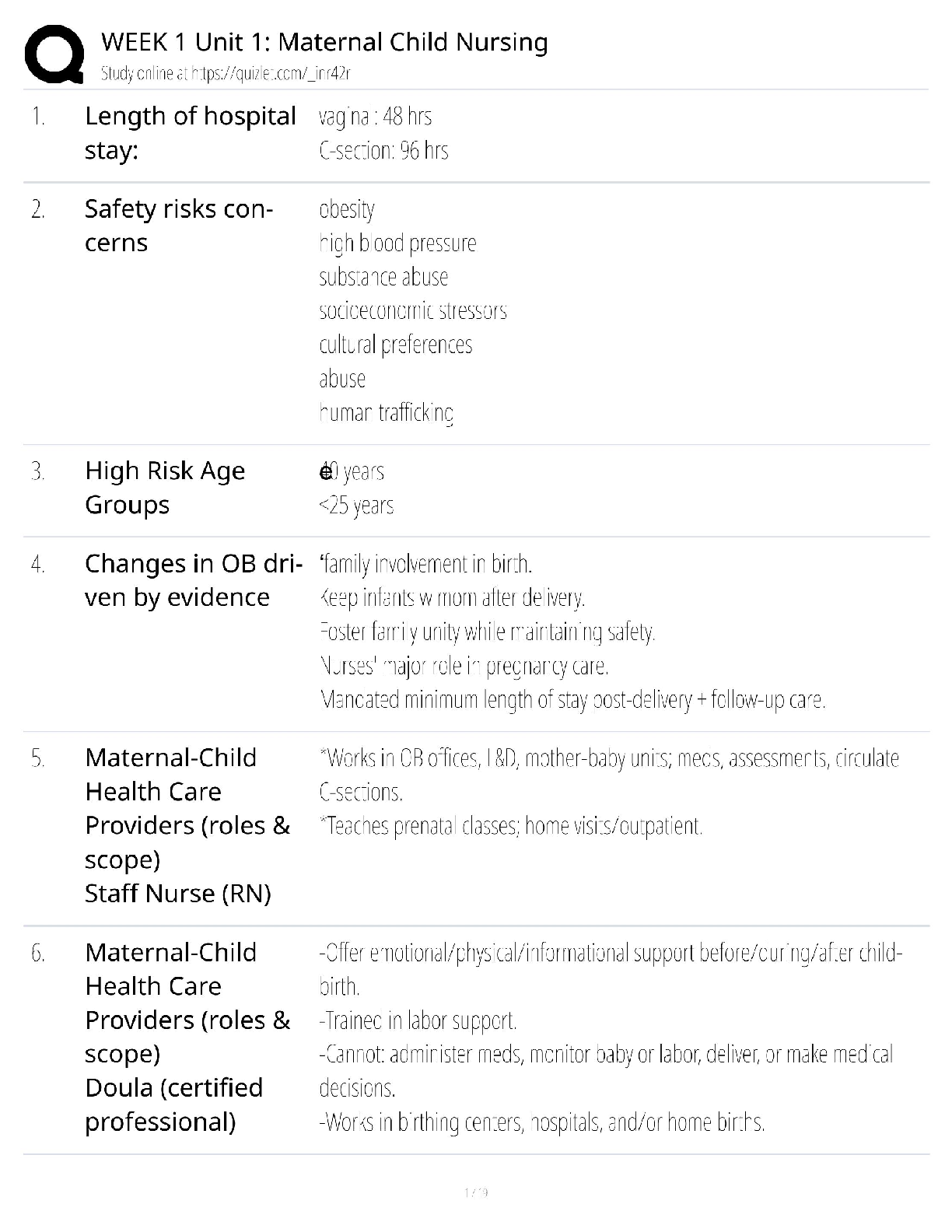
Define foodborne illness. - ✔✔a disease transmitted to people by food
When is a foodborne illness considered an outbreak? - ✔✔when 2 or more people have the same
symptoms after eating the sam
...
7th Edition SERVSAFE Exam
Define foodborne illness. - ✔✔a disease transmitted to people by food
When is a foodborne illness considered an outbreak? - ✔✔when 2 or more people have the same
symptoms after eating the same food
What food saftey challenges do operations face? - ✔✔time pressure, potentially unsafe supplies,
high risk populations, and staff related challenges
What does a foodborne illness cost? - ✔✔guests and operations
After a foodborne illness, what may an operation experience? - ✔✔negative publicity, decreased
business, lawsuits, legal fees, increased insurance premiums, and personnel issues
What are the types of contaminants that threaten food safety? - ✔✔biological, chemical, and
physical
Which type of contaminant poses the greatest danger? - ✔✔biological contaminants
What can happen if a food handler does not follow the correct procedures? - ✔✔they can
threaten the safety of food
How can a food handler threaten the safety of food? - ✔✔by failing to cook the food enough,
holding food at incorrect temperatures, contaminating equipment, and practicing poor personal
hygiene
When has food been time temperature abused? - ✔✔when it has stayed too long at temperatures
that are good for the growth of pathogens
How can pathogens be spread to food? - ✔✔if equipment has not been cleaned and sanitized
correctly between uses
Define cross contamination. - ✔✔when pathogens are transferred from one surface or food to
another
What find of food do pathogens grow well in? - ✔✔TCS food
How can the growth of pathogens be prevented in food? - ✔✔by giving the food time and
temperature control
What groups of people are considered high risk? - ✔✔young children, the elderly, people with
cancer or on chemotherapy, people with HIV/AIDS, transplant recipients, and people on certain
medications
What are important prevention measures to keep food safe? - ✔✔controlling time and
temperature, preventing cross contamination, practicing good personal hygiene, purchasing from
approved, reputable suppliers, and cleaning and sanitizing items correctly
What conditions do bacteria need to grow? - ✔✔FAT TOM- food, acidity, temperature, time,
oxygen, and moisture
What temperatures are in the temperature danger zone? - ✔✔41 F to 135 F
What can some bacteria change into? - ✔✔spores
Why do some bacteria change into spores? - ✔✔to preserve themselves when lacking nutrients
What can bacteria produce in food? - ✔✔toxins that can make people sick
What is the leading cause of foodborne illnesses? - ✔✔viruses
What cannot grow in food? - ✔✔viruses
What can viruses survive? - ✔✔refrigeration and freezing temperatures
What can help prevent the spread of viruses? - ✔✔good personal hygiene
What do parasites need to survive? - ✔✔to be in another animal
What can parasites contaminate? - ✔✔food and water
What kind of water is often contaminated by parasites? - ✔✔water used to irrigate produce
How can foodborne illnesses caused by parasites be prevented? - ✔✔by purchasing products
from approved, reputable suppliers
What are example of fungi? - ✔✔mold and yeast
What does fungi do? - ✔✔spoil food
What can some molds produce? - ✔✔harmful toxins
What should be done with food that has mold? - ✔✔it should be discarded unless the mold is a
natural part of the product
What can spoil food quickly? - ✔✔yeast
What should be done with food spoiled by yeast? - ✔✔it should be thrown out
What can be a natural part of a fish? - ✔✔fish toxins
How can fish become toxic? - ✔✔when fish eat smaller fish containing the toxin
How can shellfish, such as oysters, become contaminated? - ✔✔when they eat marine algae that
have a toxin
What is the most important prevention measure for seafood toxins? - ✔✔purchasing products
from approved, reputable suppliers
How are foodborne illnesses linked with mushrooms caused? - ✔✔by eating toxic wild
mushrooms collected by amateur hunters
What can naturally occuring plant toxins cause? - ✔✔foodborne illnesses
When can physical contamination occur? - ✔✔when foreign objects get into the food and when
natural objects are left in food
How can physical contamination be prevented? - ✔✔closely inspect the food you receive and
take steps to make sure food will not become physically contaminated during its flow through
your operation
How can chemical contamination be prevented? - ✔✔use only utensils and equipment that are
made for food handling, store chemicals away from food, utensils, and equipment used for food,
and follow chemical manufacturers' directions for use
How can deliberate contamination be prevented? - ✔✔make food very difficult to tamper with
What does a food defense program address? - ✔✔where food can be at risk
Who should be aware of the most common food allergens? - ✔✔managers and staff
What are the most common food allergens? - ✔✔milk, eggs, fish, crustacean shellfish, wheat,
soy, peanuts, and tree nuts
What should service staff be able to tell guests about? - ✔✔menu items that contain potential
allergens
What does kitchen staff need to make sure of? - ✔✔that allergens are not transferred from food
containing an allergen to good being served to a guest
When do food handlers pose a greater threat for contaminating food? - ✔✔when they have a
foodborne illness, wounds or boils that contain a pathogen, contact with someone who is ill, go
to the bathroom and do not was their hands, touch themselves, wearing or touching a dirty
uniform, coughing or sneezing into their hands, spitting in the operation, and has symptoms of a
foodborne illness
What symptoms make a food handler unable to work around food? - ✔✔sneezing, coughing,
vomiting, diarrhea, or jaundice
What parts of their body could a food handler touch that they should not when working with
food? - ✔✔their scalp, hair, nose, ear,s pimple, or wound
What kind of sink must hands be washed at? - ✔✔a sink designated for hand washing
[Show More]