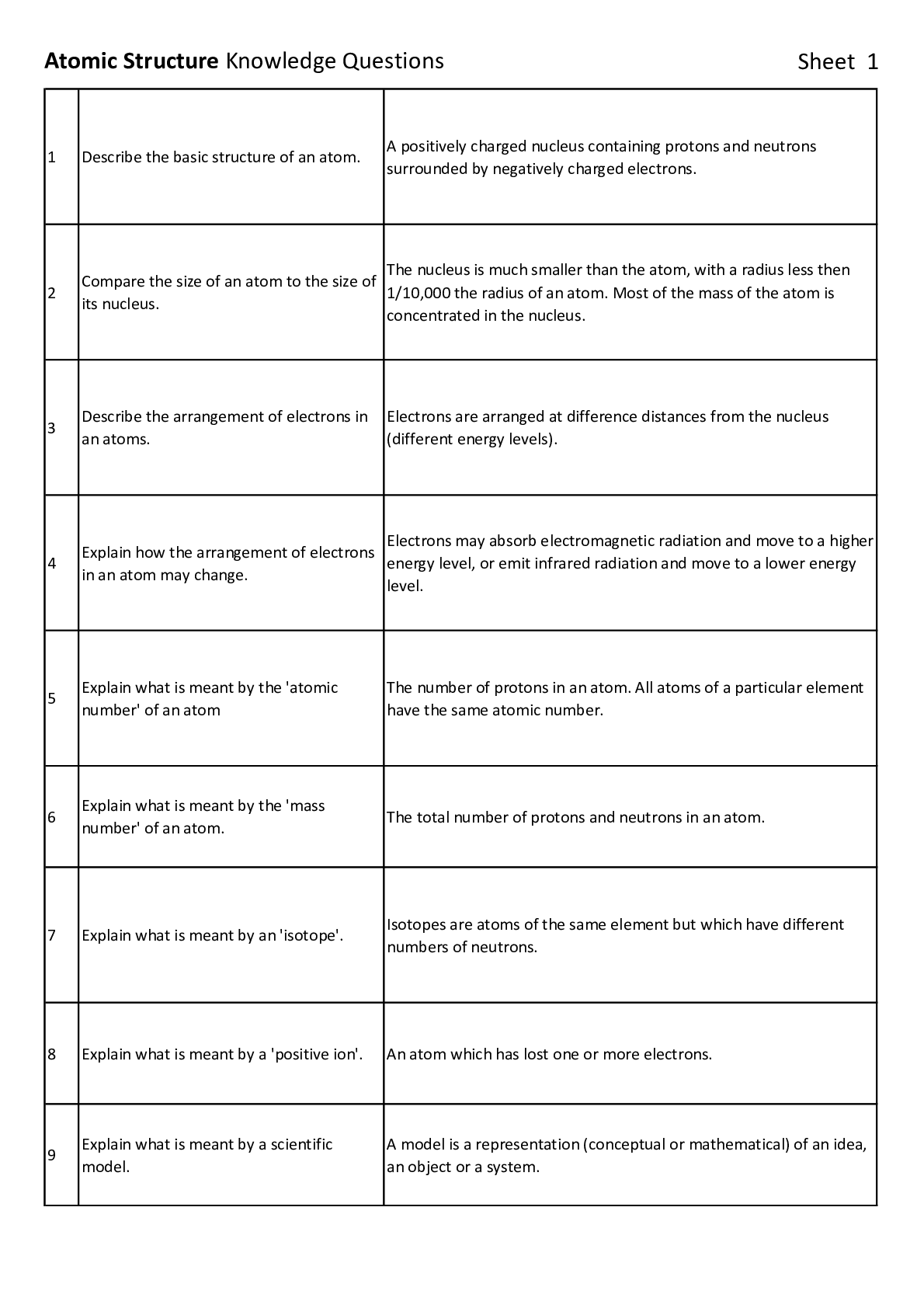
Describe the basic structure of an atom. A positively charged nucleus containing protons and neutrons
surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
2
Compare the size of an atom to the size of
its nucleus.
The nucleus
...
Describe the basic structure of an atom. A positively charged nucleus containing protons and neutrons
surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
2
Compare the size of an atom to the size of
its nucleus.
The nucleus is much smaller than the atom, with a radius less then
1/10,000 the radius of an atom. Most of the mass of the atom is
concentrated in the nucleus.
3
Describe the arrangement of electrons in
an atoms.
Electrons are arranged at difference distances from the nucleus
(different energy levels).
4
Explain how the arrangement of electrons
in an atom may change.
Electrons may absorb electromagnetic radiation and move to a higher
energy level, or emit infrared radiation and move to a lower energy
level.
5
Explain what is meant by the 'atomic
number' of an atom
The number of protons in an atom. All atoms of a particular element
have the same atomic number.
6
Explain what is meant by the 'mass
number' of an atom. The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
7 Explain what is meant by an 'isotope'. Isotopes are atoms of the same element but which have different
numbers of neutrons.
8 Explain what is meant by a 'positive ion'. An atom which has lost one or more electrons.
9
Explain what is meant by a scientific
model.
A model is a representation (conceptual or mathematical) of an idea,
an object or a system.Atomic Structure Knowledge Questions Sheet 2
10
Explain why a scientific model may
changed or replaced. New experimental evidence proves the old model to be incorrect.
11
Describe the 'plum pudding' model of the
atom.
The atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons
embedded inside.
12
Explain what happens to an unstable
nucleus.
An unstable nucleus gives out radation as it changes to become more
stable. This is a random process called radioactive decay.
13
Explain what is meant by the 'activity' of a
radioactive source.
The rate at which a source decays. Activity is measured in becquerel
(Bq)
[Show More]


.png)
.png)








.png)




