Solutions Manual for Automation, Production Systems, and Computer Integrated Manufacturing Third Edition Mikell P. Groover
$ 19

NR 511 Week 3 Practice Questions And Answers( Top Solution)
$ 14.5

eBook PDF {EPUB} Conversational Artificial Intelligence 1st Edition By Romiri Srividya, Krishnan Sakthidasan
$ 20

Student Solutions Manual, Single Variable for Calculus Roger Lipsett,William L. Briggs,Mark Woodard,Lyle. Cochran,Bill L. Briggs,
$ 15

(WGU D472) BUS 4900 21st Century Operations & Supply Chain Objective Assessment Guide Q & A 2024
$ 13

BSN 1004 Evolve / Test bank (Combined Questions And Answers).
$ 16.5
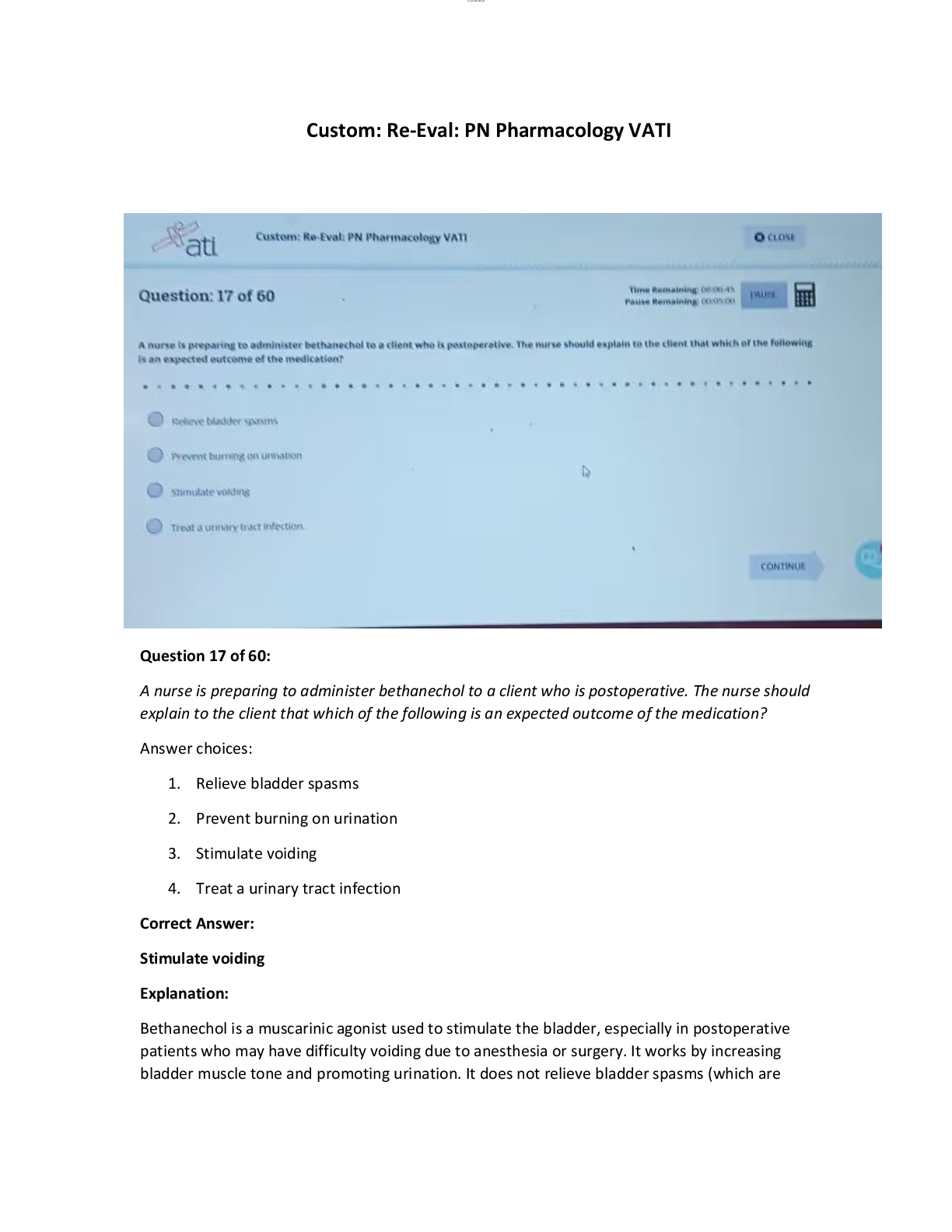
Custom PN Pharmacology VATI Comprehensive Exam Guide
$ 30

The Flirting Playbook The World’s First Step-By-Step System On Engaging Women In Fun, Natural And Sexy Conversations…And Get Them Fall In Love With You! by Derek Rake
$ 9

Musyoka Marketing Planning ( Market Analysis, Goals And Marketing Strategies
$ 10.5
.png)
WGU C777 Web Development Applications Pre-Assessment Latest 2022
$ 6

Lippincott nclex pn 9th












 BMAL 590- QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH TECHNIQUES AND STATISTICS TEST WITH SUMMARIZED STUDY GUIDE.png)