WGU C170 Data Management – Applications domain Answer- In data modeling, the construct used to organize and describe an attribute's set of possible values
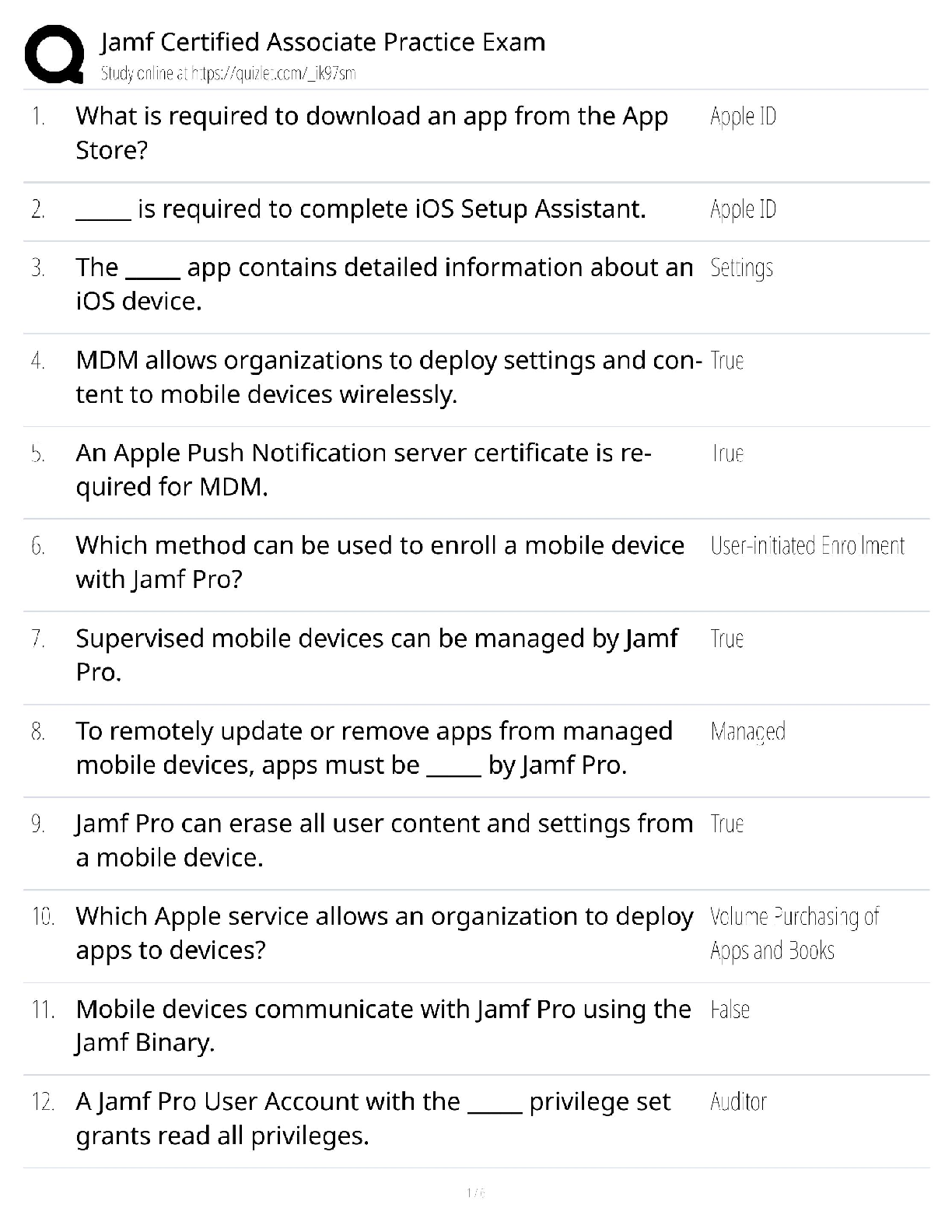
superkey Answer- An attribute or attributes that uniquely identi
...
WGU C170 Data Management – Applications domain Answer- In data modeling, the construct used to organize and describe an attribute's set of possible values
superkey Answer- An attribute or attributes that uniquely identify each entity in a table. Any composite key with this is also this.
candidate key Answer- A minimal superkey; that is, a key that does not contain a subset of attributes that is itself a superkey
entity integrity Answer- The property of a relational table that guarantees each entity has a unique value in a primary key and that the key has no null values
referential integrity Answer- A condition by which a dependent table's foreign key must have either a null entry or a matching entry in the related table
data dictionary Answer- A DBMS component that stores metadata. It contains the data definition & their characteristics and relationships; may also include data external to the DBMS
system catalog Answer- A detailed system data dictionary that describes all objects in a database
homonym Answer- The use of the same name to label different attributes, much like similar-sounding words with different meanings
synonym Answer- The use of different names to identify the same object, such as an entity, an attribute, or a relationship. These should generally be avoided.
not null and unique Answer- Any candidate key must have these two constraints enforced
cardinality Answer- Term for how many instances of one object are related to instances of another object (maximum)
modality Answer- Term for whether an instance of a specific entity is optional or mandatory in a relationship (minimum)
connectivity Answer- Term for the classification of the relationship between entities. Classifications include 1:1, 1:M, and M:N
CREATE SCHEMA AUTHORIZATION Answer- SQL command to create a database schema
DEFAULT Answer- SQL option to define a default value for a column (when no value is given)
CHECK Answer- SQL command to validate data in an attribute, used during table column creation
CREATE TABLE AS Answer- SQL command to create a new table based on a query in the user's database schema
HAVING Answer- SQL option that restricts a selection of grouped rows based on a condition
EXISTS Answer- SQL option that checks whether a subquery returns any rows
DECIMAL Answer- SQL data type like the NUMBER specification, but the storage length is a minimum specification
True Answer- True or false: if an INSERT or SELECT command is embedded inside a program for later use, the attribute list should always be used, as the table may change over time
inner join Answer- A join operation in which only rows that meet a given criterion are selected. The most common type of join
outer join Answer- A join operation that produces a table in which all unmatched pairs are retained; unmatched values in the related table are left null
cross join Answer- A join operation that returns the Cartesian product of two sets or tables
natural join Answer- Join type that returns only the rows with matching values in the matching columns; the matching columns must have the same names and similar data types
left, right, full Answer- Name the three types of outer joins
ALL Answer- This operator can be used to compare something to every returned row of a subquery
ANY Answer- This operator can be used to compare something to a list of values and return any rows that satisfy the criteria
correlated subquery Answer- A subquery that executes once for each row in the outer query
UNION Answer- SQL statement that combines rows from two or more queries without including duplicate rows, as long as the queries return the same # of attributes and similar data types
UNION ALL Answer- SQL statement similar to UNION but retaining duplicate rows
INTERSECT Answer- SQL statement used to combine rows from two queries, returning only the rows that appear in both sets
EXCEPT (MINUS) Answer- SQL statement that combines rows from two queries and returns only the rows that appear in the first set but not in the second
view Answer- A virtual table based on a SELECT query that is saved as an object in the database
base table Answer- The table on which a view is based
batch update routine Answer- A routine that pools transactions into a single group to update a master table in a single operation
updatable view Answer- A view that can update attributes in
[Show More]