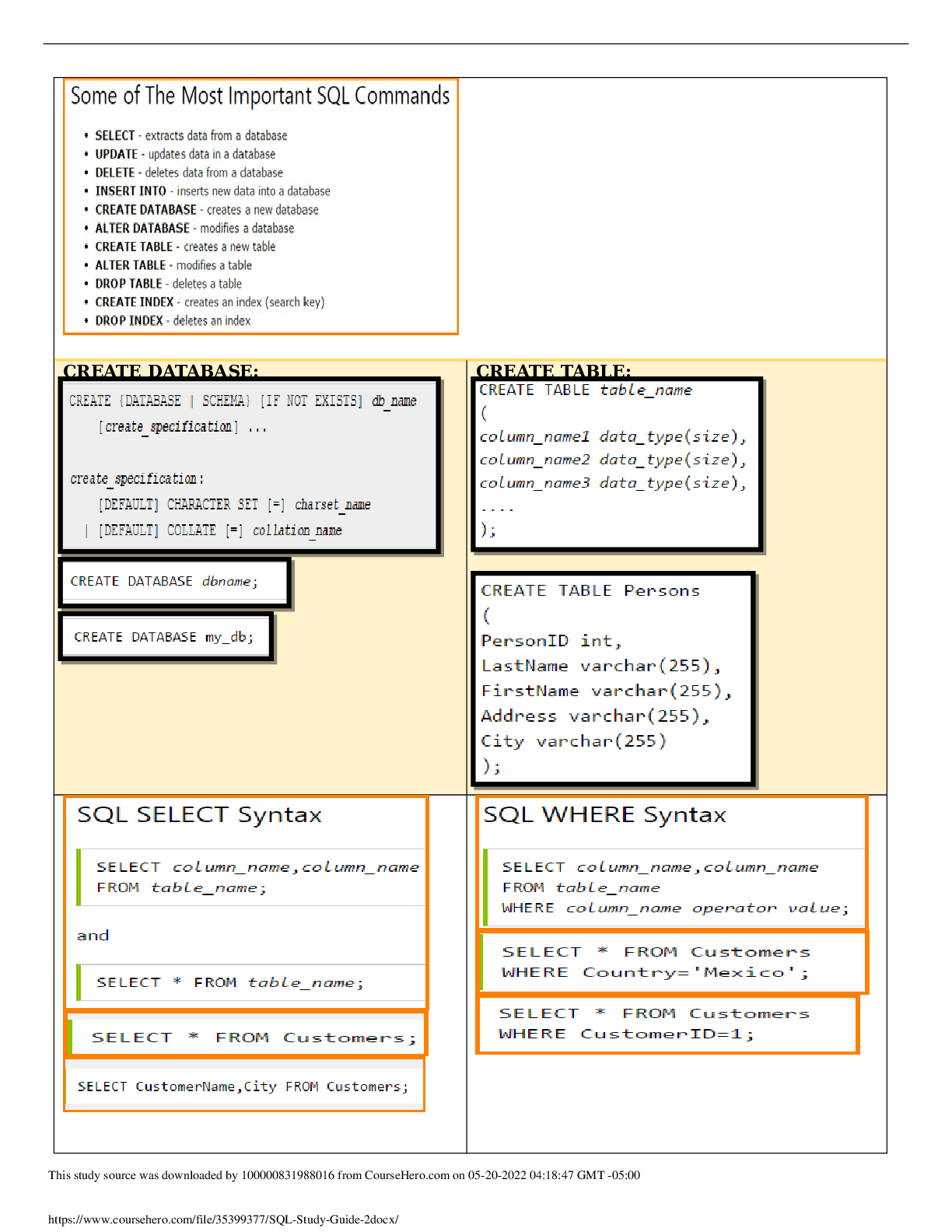
CREATE DATABASE: CREATE TABLE:
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-12-2022 13:25:00 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/35399377/SQL-Study-Guide-2docx/
ALTER TABLE:
DR
...
CREATE DATABASE: CREATE TABLE:
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-12-2022 13:25:00 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/35399377/SQL-Study-Guide-2docx/
ALTER TABLE:
DROP TABLE DROP INDEX DROP DATABASE
CREATE VIEW:
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-12-2022 13:25:00 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/35399377/SQL-Study-Guide-2docx/
ALTER TABLE & VIEW: DISTINCT:
DROP VIEW: The IF EXISTS clause prevents an error from occurring
for views that don't exist. When this clause is given,
a NOTE is generated for each nonexistent view.
CREATE INDEX:
DROP INDEX: AND / OR OPERATOR
GRANT PRIVILEGES:
GRANT privilege_name ON object_name
TO {user_name |PUBLIC |role_name} [WITH
GRANT OPTION];
REVOKE PRIVILEGES:
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-12-2022 13:25:00 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/35399377/SQL-Study-Guide-2docx/
GROUP BY: ORDER BY:
Select all customers from the "Customers" table, sorted
DESCENDING by the "Country" column:
HAVING: ORDER BY SEVERAL COLUMNS:
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-12-2022 13:25:00 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/35399377/SQL-Study-Guide-2docx/
INSERT INTO: EXAMPLE:
DELETE FROM: DELETE ALL DATA:
This means that the table structure, attributes, and
indexes will be intact:
DELETE FROM table_name;
or
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-12-2022 13:25:00 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/35399377/SQL-Study-Guide-2docx/
DELETE * FROM table_name;
UPDATE TABLE:
Update Warning! Be careful when updating records.
If we had omitted the WHERE clause, in the example
above, like this:
CONSTRAINTS:
The constraints available in SQL are Foreign
Key, Not Null, Unique, Check.
Constraints can be defined in two ways
1) The constraints can be specified immediately
after the column definition. This is called
column-level definition.
2) The constraints can be specified after all the
columns are defined. This is called table-level
definition.
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-12-2022 13:25:00 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/35399377/SQL-Study-Guide-2docx/
GROUP FUNCTIONS: These functions
are: COUNT, MAX, MIN, AVG, SUM,
DISTINCT.
COMPLEX JOINS-USING WHERE SUBQUERIES:
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-12-2022 13:25:00 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/35399377/SQL-Study-Guide-2docx/
Multiple-Table Retrievals with Joins
MySQL provides 2 statements for creating new tables from other tables or from query results:
CREATE TABLE ... LIKE
Advantages
creates a new table as an empty copy of the
original one.
copies the original table structure exactly,
each column is preserved with all of its
attributes.
Disadvantages
Statement is needed (such as INSERT
INTO ... SELECT).
cannot create a new table from a subset
of the original table's columns.
Cannot use columns from any other
table but the original one.
[Show More]