Alpha2-adrenergic receptor stimulators (agonists)/clonidine
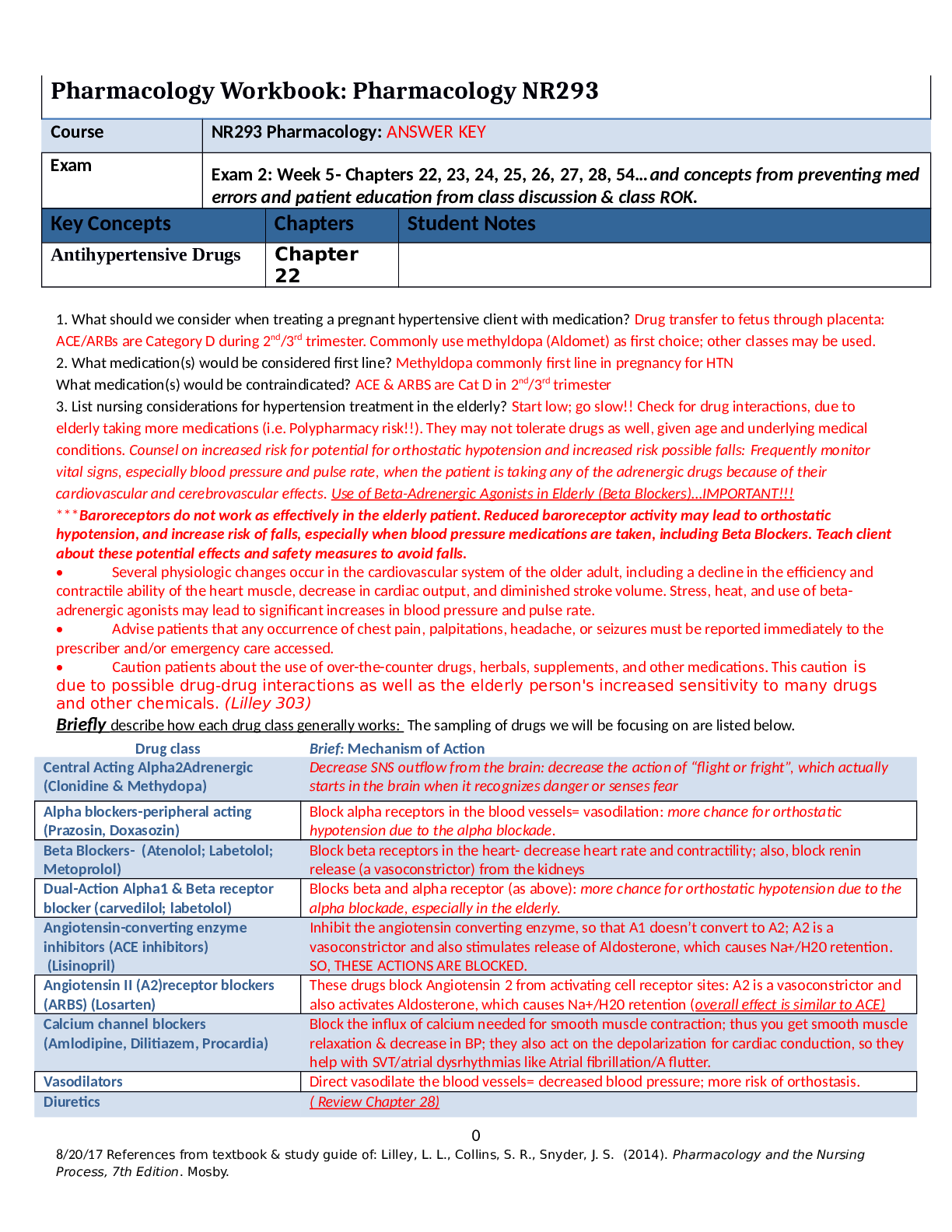
o Stimulate alpha2-adrenergic receptors in the brain
o Decrease sympathetic outflow from the CNS, decrease norepinephrine
production
o Stimulates alpha2-adr
...
Alpha2-adrenergic receptor stimulators (agonists)/clonidine
o Stimulate alpha2-adrenergic receptors in the brain
o Decrease sympathetic outflow from the CNS, decrease norepinephrine
production
o Stimulates alpha2-adrenergi receptors, thus reducing renin
o Examples: Clonidine (Catapres), Methyldopa (aldomet): used for pregnant
women w/htn
Alpha1-blockers/”azosin,”
o Block alpha1-adrenergic receptors
o Management of severe heart failure (HF) when used with cardiac
glycosides and diuretics
o Some used to relieve symptoms of BPH- increase urinary flow rate
o Example: “ Azosin” (doxazosin (Cardura)
o Adverse Effects:
Serious: hypotension (first dose) syncope
Common: dizziness
o Nursing implications: instruct pt. to lie down after taking first dose because
they may become dizzy
Beta-blockers “olol”: First-line treatment for heart failure & HTN
o Reduce BP by reducing heart rate through beta1 blockade (block receptors
for norepinhrine)
o Cause reduced secretion of renin
o Long-term use causes reduced peripheral vascular resistance
o Adverse Effects: orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia w/ reflex
tachycardia, sexual dysfunction in men, possible hypoglycemia or
hyperglycemia
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, “pril” Captopril
o Mechanism of Action:
Inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme, which is responsible for
converting angiotensin I (through the action of renin) to angiotensin
II
Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor and causes aldosterone
secretion from the adrenal glands
Result in decreased systemic vascular resistance (afterload),
vasodilation, and therefore decreased blood pressure
o Indications:
First-line treatment for heart failure & HTN
HF (either alone or in combination with diuretics or other drugs)
1
Slow progression of left ventricular hypertrophy after MI (cardio
protective)
Renal protective effects in patients with diabetes
Captopril and lisinopril can be used if a patient has liver dysfunction,
unlike other ACE inhibitors that are pro-drugs
*Pro-drugs are inactive in their administered form and must be
metabolized in the liver to an active form so as to be effective
o Adverse Effects: hyperkalemia & dry, nonproductive cough
o Serious drug interaction: NSAIDs
Angiotensin II receptor blocker “sartan” losartan (Dovan)
o Mechanism of Action:
Allow angiotensin I to be converted to angiotensin II, but block the
receptors that receive angiotensin II
Block vasoconstriction and release of aldosterone
Well tolerated, do not cause a dry cough
Indications: first-line treatment for heart failure & HTN
o Adverse Effects: URI, headache
May cause occasional dizziness, inability to sleep, diarrhea
Calcium channel blockers: Amlodipine “dipine” verapamil (calan),
diltiazem (cardizem)
o Mechanism of Action: cause smooth muscle relaxation by blocking the
binding of calcium to its receptors, preventing muscle contraction
o Adverse effect: constipation
High-fiber diet with plenty of fluids will help prevent constipation
o Indications: hypertension
Angina- ch. 23
Ischemia:
o Ischemic heart disease: Poor blood supply to the heart
muscle (Atherosclerosis, Coronary artery disease)
o Myocardial infarction (MI): Necrosis, or death, of cardiac
tissue, disabling or fatal
Therapeutic Objectives
o Minimize the frequency of attacks and decrease the
duration and intensity of anginal pain
o Improve the patient’s functional capacity
o Prevent or delay the worst possible outcome: MI
Cardiac glycosides: Digoxin
o Therapeutic level: between 0.5-2ng/mL
o Digoxin doses are held and the prescriber notified if the apical pulse is 60 beats/minute
o Negative chronotropic effect decreases HR
2
o Digoxin immune Fab (Digifab) is the antidote for a severe digoxin overdose
Required use of digitab when potassium level is above 5 mEq/L, severe sinus
bradycardia that does not respond to cardiac pacing, or an overdose of more than 10
mg of digoxin.
o Avoid bran muffins when taking digoxin
o Hypokalemia increases the chance of digitalis toxicity
Class III drugs: Amiodarone (ch. 25)
o Mechanism of action: prolonging action potential duration
o Indications: ventricular dysrhythmias
o Contraindication: hypersensitivity and bradycardia or AV block
Adverse effects: FDA black box warning: pulmonary toxicity, hepatotoxicity arrhythmia worsening-sinus
bradycardia, constipation, QT prolongation, hypotension, blue-gray coloring of the skin on the face, arms,
and neck
[Show More]






_2nd_E_Completed.png)