AQA GCSE PHYSICS 84632H Higher Tier Paper 2
$ 10
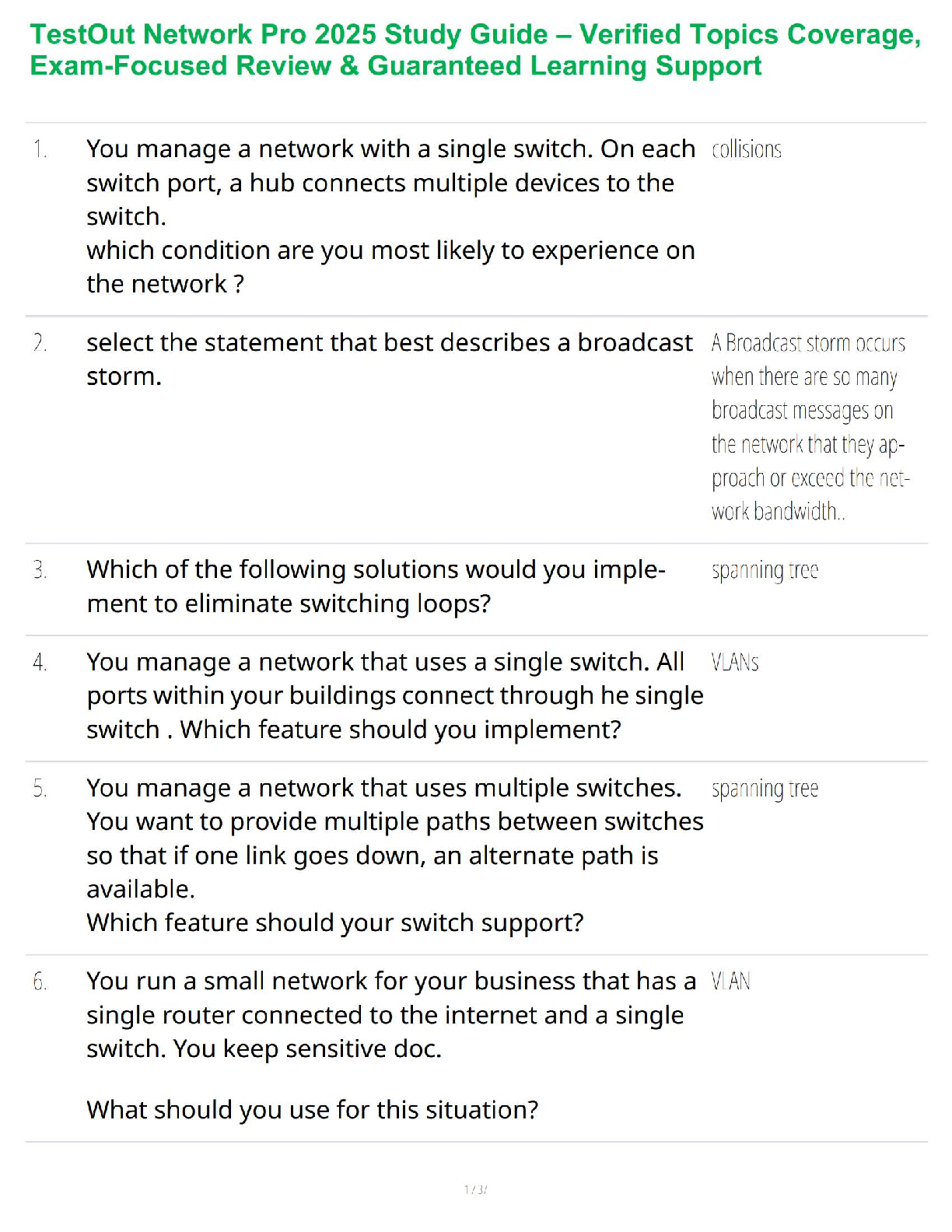
TestOut Network Pro 2025 Study Review Guide – Updated Networking Concepts Companion
$ 32

HESI HEALTH ASSESSMENT EXAM-with 100% verified solutions-2023-2024
$ 14

Test_bank_for_paramedic_care_principles_and_practice,_6th_edition (1)
$ 15

ALCPP CLC EXAM 1 PREP
$ 21

ISM 3541 Notes_for_exam_1Florida State University ISM 3541
$ 6

Incorporation of Management Theory into Practice.docx HCA- 465 Incorporation of Manage
$ 5

DAANCE ALL MODULES EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS WELL ANSWERED.
$ 13

American Red Cross Lifeguard Tests 2024! 100% CORRECT ANSWERS
$ 9.5

Prescotts Microbiology 10th Edition Willey Test Bank With Questions And Correct Answers ( 2022-2023)
$ 9

CSE (California Supplemental Exam) ARE
$ 10

(UF) EAB 6707 Applied Behavior I - Latest Finals Review Q & S 2024
$ 12
.png)
ServiceNow Certified System Administrator Practice Questions(QUESTIONS&ANSWERS)
$ 7
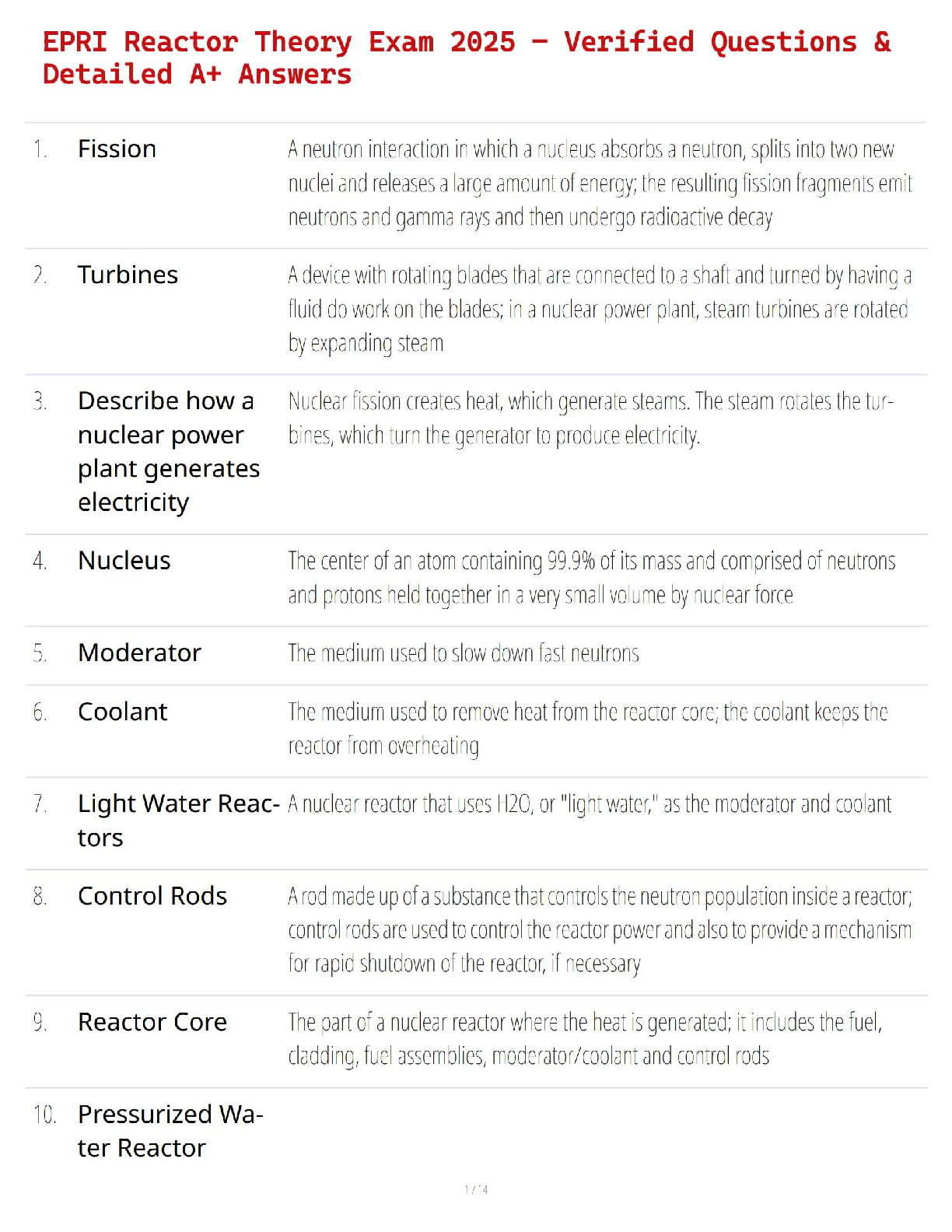
EPRI Reactor Theory Exam 2025 – Verified Questions & Detailed A+ Answers
$ 12

AQA GCSE English Language Paper 1: Explorations in creative reading and writing study guide 2020/21
$ 12

Test Bank for An Introduction to Brain and Behavior, 6th Edition by Macmillan A+ Latest
$ 19.5
Coding 1 Chapter 1 / Intro to Coding and Coding Professions / Chapter Review 2025 / Score 100% Study Guide & Test Bank
$ 17

ETHIC MILESTONE 4 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS LATEST 2021/2022,100% CORRECT
$ 15

375 Milestone 4
$ 10

Introduction to OSHA Study Guide
$ 8
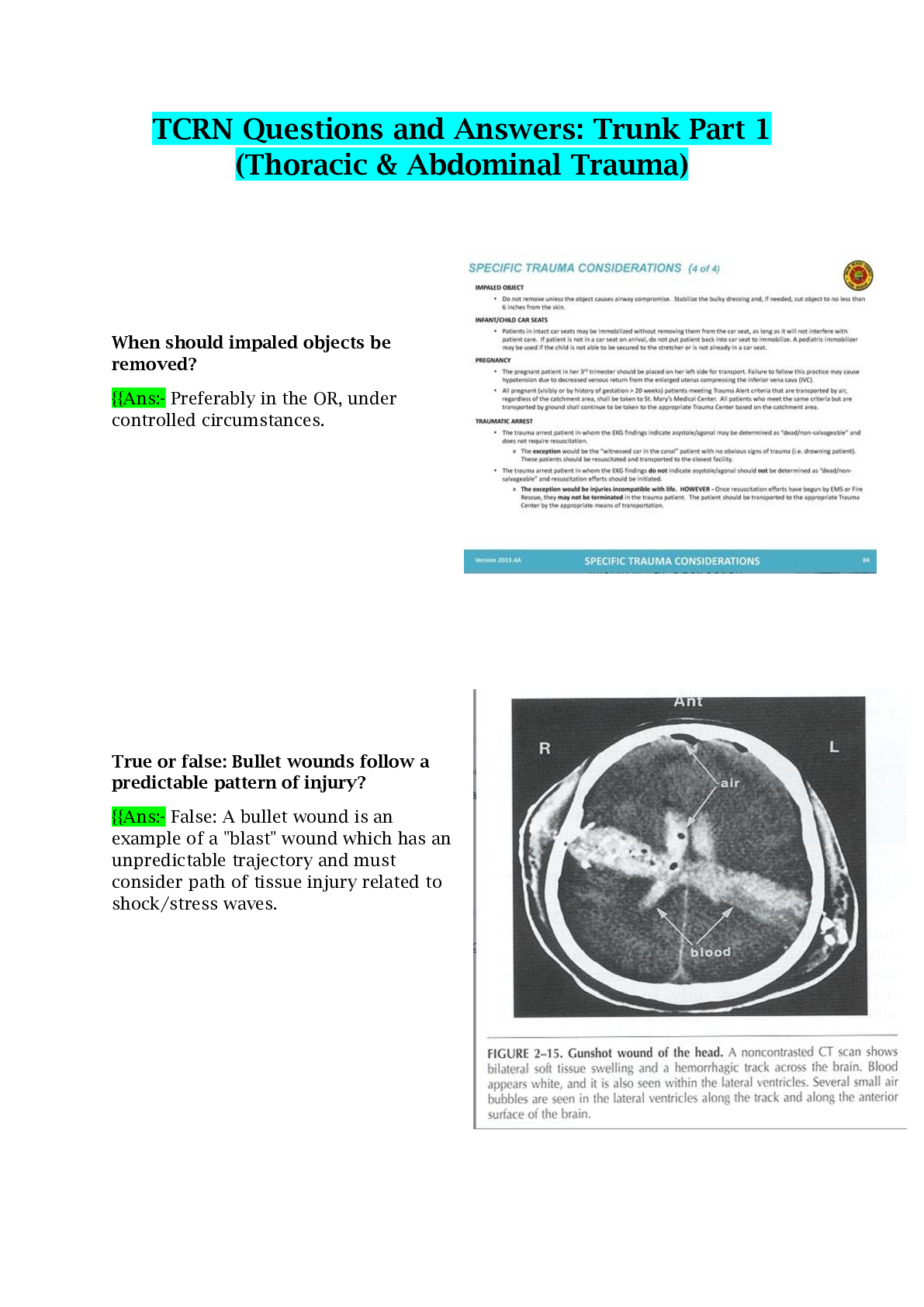
TCRN Questions and Answers: Trunk Part 1 (Thoracic & Abdominal Trauma)
$ 12

FINANCE 42014250 note. Chapter 3 Bonds and Loanable Funds
$ 6
.png)
WGU C779 Web DevelopmentFoundations Latest Version 2022 Rated A
$ 8

Vocabulary HESI Practice Exam - Questions and Answers
$ 15

eBook Hubris The American Origins of Russia's War against Ukraine 1st edition by Jonathan Haslam
$ 29

WGU C170 Data Management – Applications (MySQL) Project 2022
$ 7

ATI EXIT EXAM RN COMPREHENSIVE PREDICTOR 2025-2026 FORM A, B & C AND PRACTICE EXAMS AND RETAKE EXAM WITH NGN FORMAT NEWEST 2025 ACTUAL EXAM ALL QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS (VERIFIED ANSWERS) |ALREADY GRADED A+||NEWEST VERSIONS
$ 20

eBook for IM Entrepreneurship Successfully Launching New Ventures, 5th Edition By Bruce Barringer, Duane Ireland
$ 20

National University COM 103 Week Three Quiz 3 (All Answers are Correct)
$ 8

prestressed-concrete-design-lecture-notes
$ 13

MEDICAL SCIENCES REGULATIONS AND SCIENCES 2020/2021