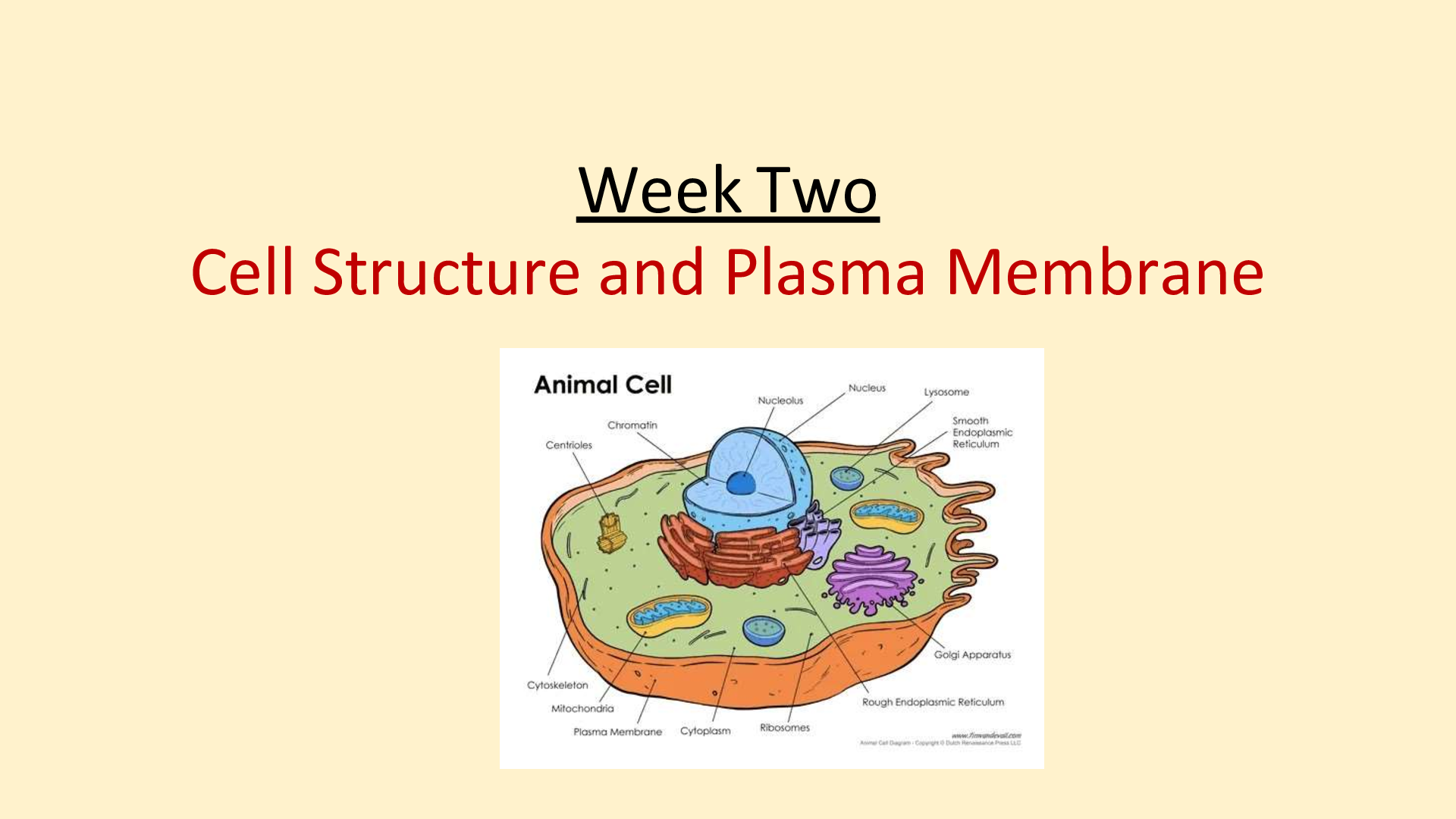
Week Two
Cell Structure and Plasma Membrane
History of Cells- 1680-1880’s
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek- developed first types of microscopes allowed observation
Robert Hooke- named “cells”
The Cell Theory:
1. All l
...
Week Two
Cell Structure and Plasma Membrane
History of Cells- 1680-1880’s
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek- developed first types of microscopes allowed observation
Robert Hooke- named “cells”
The Cell Theory:
1. All living things are composed of cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living things
3. All cells come from pre-existing cells
Clever and Quick You Tube about Cell History https:// www.youtube.com/watch?v=4OpBylwH9DU
Cell Types
• Prokaryotic Cell- simplest type of cell
• No nucleus or membrane bound organelles
• Ex: Bacteria
• Eukaryotic Cell- most complex
• Contains many membrane bound organelles like the nucleus
• Ex: Animals, plants, fungi and protists
Prokaryotic Cell Diagram
Cell Structures and their Function
• Cell (Plasma) Membrane: controls what goes in/out of cell
• Selectively permeable- lets some things in but not others
• Cell Wall: extra layer of protection found in all cells except
animal cells.
• consists of cellulose and proteins
• Nucleus: contains the chromosomes
• Nuclear Envelope: membrane with pores that controls what goes in/out of nucleus
• Nucleolus: small structure w/in the nucleus contains RNA – site of ribosome production
Animal and Plant Cells
Cell Structures and their Function cont…
• Chromatin/Chromosomes- DNA strands wrapped around a protein core- contains the genes
• Cytoplasm: a thick liquid material that contains organelles – always moving(streaming)
• Mitochondria: “powerhouse of the cell”
• Place where energy from food is stored ATP from cellular respiration
• Contains folds called Cristae to increase reaction efficiency
• Chloroplasts and Plastids: stores plant pigments like chlorophyll needed for photosynthesis
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts
Cell Structures and their Function cont…
• Ribosomes: tiny “dots” that are the site of protein synthesis- free floating or attached to ER
• Endoplasmic Reticulum: “ER” – complex network of tubes that connect the cell membrane with the nucleus
• Transports materials throughout the cell like a highway
• Two Types:
• Rough ER- walls covered in ribosomes
• Smooth ER- walls are smooth
• Golgi Apparatus(Bodies): modifies, packages and distributes the proteins made in ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Protein Pathway
Cell Structures and their Function cont…
• Lysosomes: “ clean-up crew- garbage collector”
• Structures that contain digesting enzymes and chemicals that capture and get rid of foreign materials, old organelles etc.
• Also are “Suicide Sacs”- they will release enzymes when cell dies
• Vacuoles and Vesicles: specific storage and delivery pouches for water, food, waste and proteins
• Cytoskeleton: variety of fibers that support and control movement of and w/in cell
• Microtubules: large tube-like structures form cilia and flagella as well as
Spindle fibers (Impt mitosis)
• Microfilaments: tiny fibers that move cytoplasm cause cytoplasmic streaming(moving organelles around cell)
Lysosomes
Cytoskeleton
Plant vs. Animal Cells
Plant vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells
• Cell wall
• Chloroplasts
• Large Central water vacuole
• Rectangular rigid shape
• No centrioles
Animal Cells
• No Cell Wall
• No Chloroplasts
• Smaller water vacuoles
• Irregular flexible shape
• Centrioles
Centrioles
Click on this link to watch a good review of Cell Structure Review
Cell or Plasma Membrane
• Phospholipid Bilayer with imbedded proteins
...................................................................................................CONTINUED................................................................................................
[Show More]


.png)





.png)

.png)