
WGU C204 (English Linguistics) Quiz 1 A+ Graded Western Governors University.
$ 12

Structural Pest Control Applicator's Training Program: General Category Manual Study Questions
$ 12

Oncology Board Review, Second Edition_ Blueprint Study Guide and Q&A
$ 16
.png)
PHI_445__Week_1_Quiz_1
$ 9.5
.png)
Mechanic Exam Questions and Answers Rated A
$ 10

AQA A-level FRENCH Paper 2 Writing June 2021 QP
$ 9.5

CNA STATE EXAM 2024 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS LATEST
$ 19

PHYS 1403 Lab 7: APPARENT & ABSOLUTE VISUAL MAGNITUDE Worksheet
$ 11

AngryBirdStressManagement “Don’t Get Angry” Angry Bird Bulletin Board: Stress Management Techniques & Tips
$ 16.5

[eBook] [PDF] Wind and Solar Energy Applications Technological Challenges and Advances By Satish Kumar Peddapelli, Peter Virtic
$ 30

C468 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS| GRADED A
$ 11

Case Notes/Answers Improving Last-Mile Productivity at Paack By Mihalis Markakis, Victor Martinez de Albeniz
$ 45

Early Childhood Education - NOCTI Review 1 (2022/2023) Already Graded A
$ 8

Criminology; Crim_Mid_Term_Notes latest with summary (100% well enlightened)
$ 8
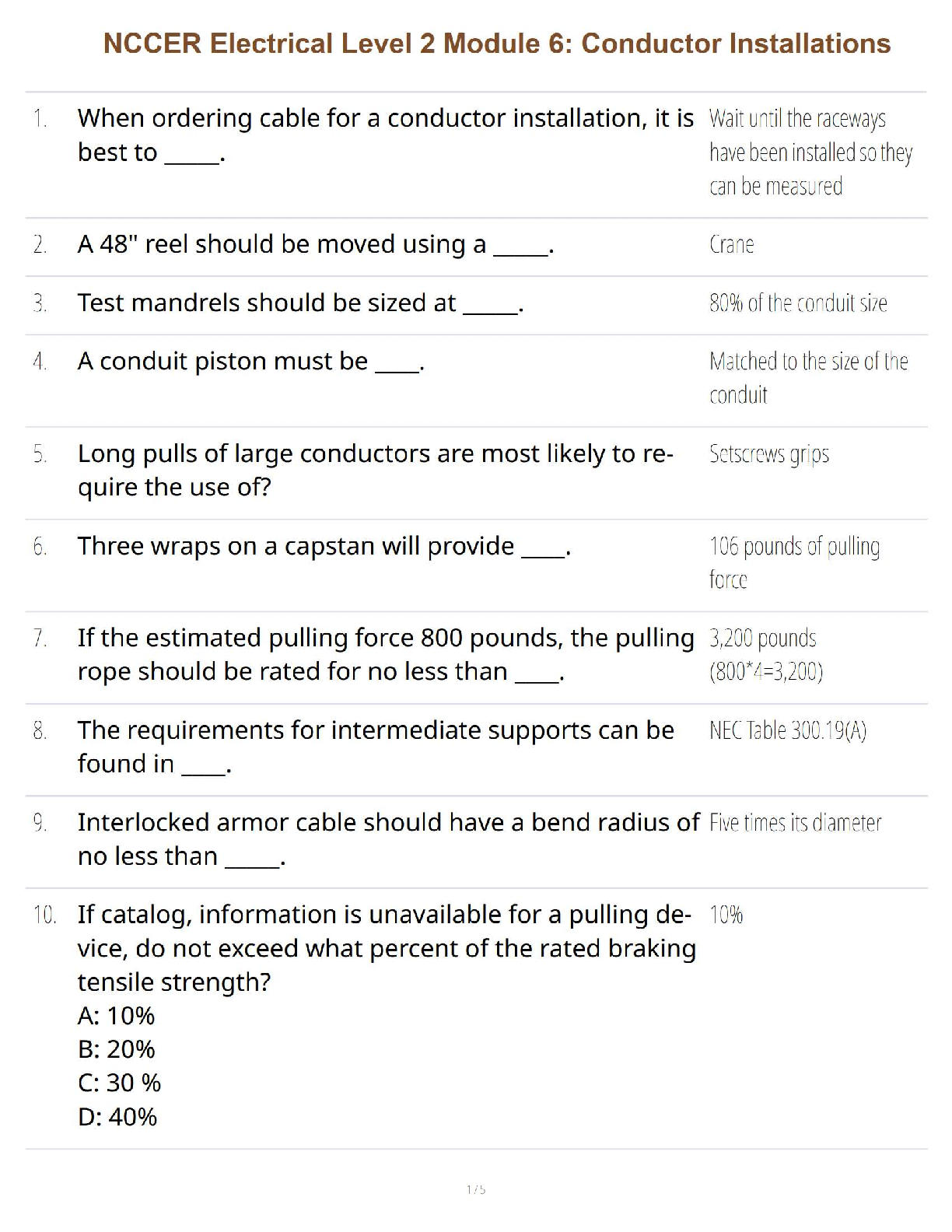
NCCER Electrical Level 2 Module 6: Conductor Installations
$ 7.5

TExES Core Subjects 4-8 Practice Exam Already Graded A
$ 17.5

Ferris State UniversityPOL INTERNATIOThe Long Walk to Freedom by Nelson Mandela
$ 11

Pilates BASI Written Exam – Verified Questions & Guaranteed Instructor Certification Success
$ 18.7

Sophia Learning - Art History I - Milestone Study Guide Revisions, 13 Updated Study Guide, Correctly Answered Questions, Test bank Questions and Answers with Explanations (latest Update), 100% Correct, Download to Score A
$ 35

NURSING CARE PLANS Guidelines for Individualizing , Client Care Across the Life Span 10th Edition 2019, Doenges, Moorhouse, Murr
$ 17

EMT READINESS EXAM 4 Questions and Answers (100 OUT OF 100) (Verified Answers)
$ 12

Confidence How To Sell Yourself Winning Techniques for Selling Yourself
$ 15

HESI A2 version 1 and 2 Exam 196 Questions with Verified Answers 2021 Updated,100% CORRECT
$ 9.5

ASE BRAKES A5 PRACTICE TEST EXAM RATED A 100% VERIFIED.
$ 13

CDA PRACTICE FOR COMING EXAM TRIAL QUESTIONS WITH 100 % SOCRED SOLUTION NEW UPDATED
$ 9.5
 Solved.png)
IHUMAN SCOTT BALDWIN (SEIZURE) STUDENT GUIDELINES TICKET TO ENTER FOR VIRTUAL SIMULATION
$ 10

The Handbook Of Evolutionary Psychology
$ 30

Ohio Lead Risk Assessor Exam – Verified Questions & Complete Certification Study Guide
$ 14.6

ILRHR 2600 Exam 3 Study Guide | 40 Questions with 100% Correct Answers | Updated | Download to score A+
$ 7

PHYSICS NEWTON'S LAWS SHORT NOTES
$ 10

CrossFit level 1 programming Guide with Verified Answers
$ 11

NACE CIP LEVEL 1 STUDY GUIDE QUESTIONS WITH CORRECT ANSWERS
$ 6

Nutritional Principles Study Guide Exam 1/GRADED A+ /Rasmussen College
$ 9.5
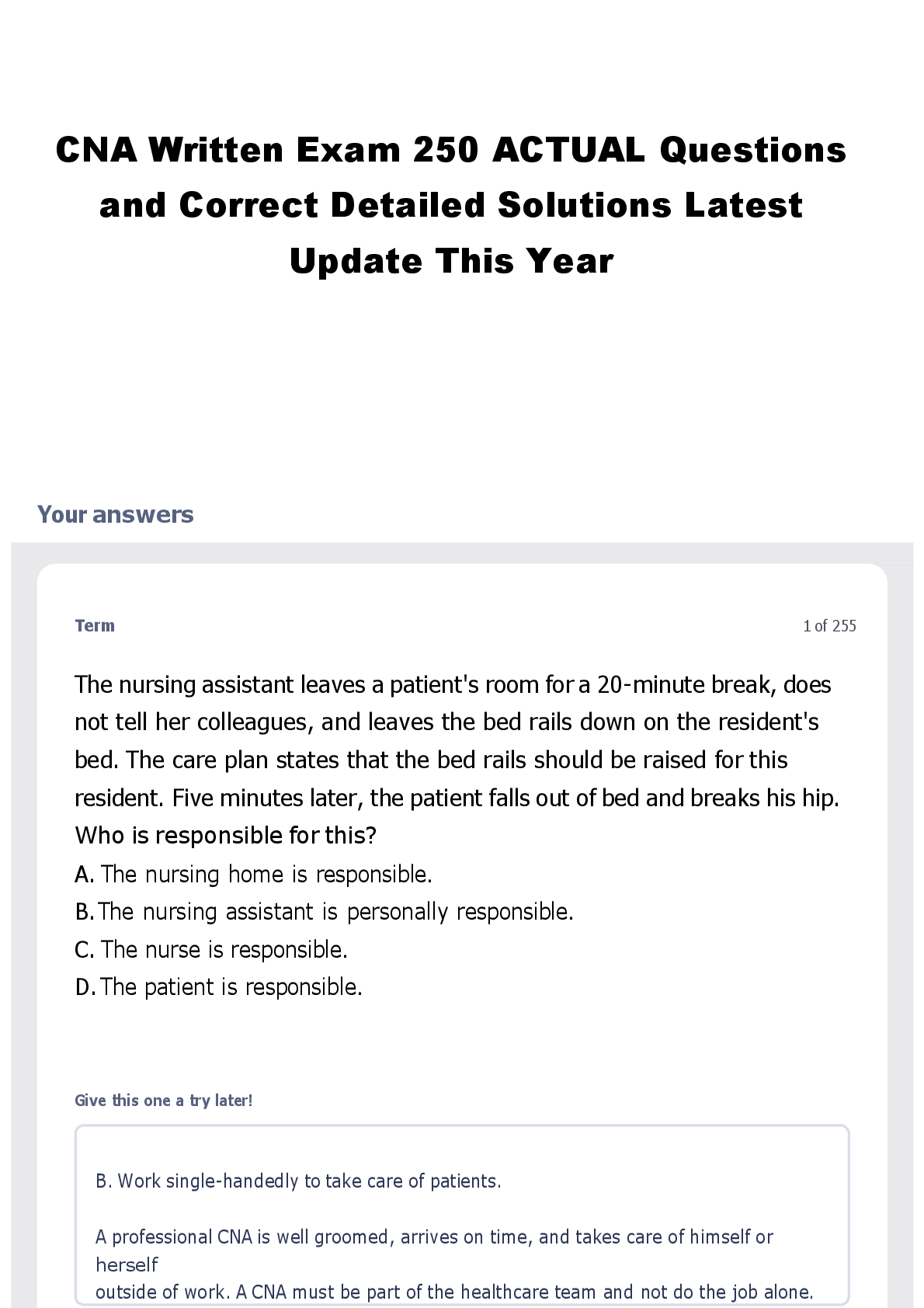
CNA Written Exam 250 ACTUAL Questions and Correct Detailed Solutions Latest Update This Year
$ 39.5

ATI PN LEADERSHIP MANAGEMENT PROCTORED EXAM (5 VERSIONS) (2020-2021) | COMPLETE DOCUMENTS (100% CORRECT)
$ 18

Fundamentals of instrumentation and control questions,. Graded A
$ 5

eBook Understanding Hypersonic Weapons. Managing the Allure and the Risk 1st Edition By Shannon Bugos, Kingston Reif
$ 29

Meaningful Use for Nurses: Implications & Recommendations Chamberlain College of Nursing NR-512: Nursing Informatics
$ 12
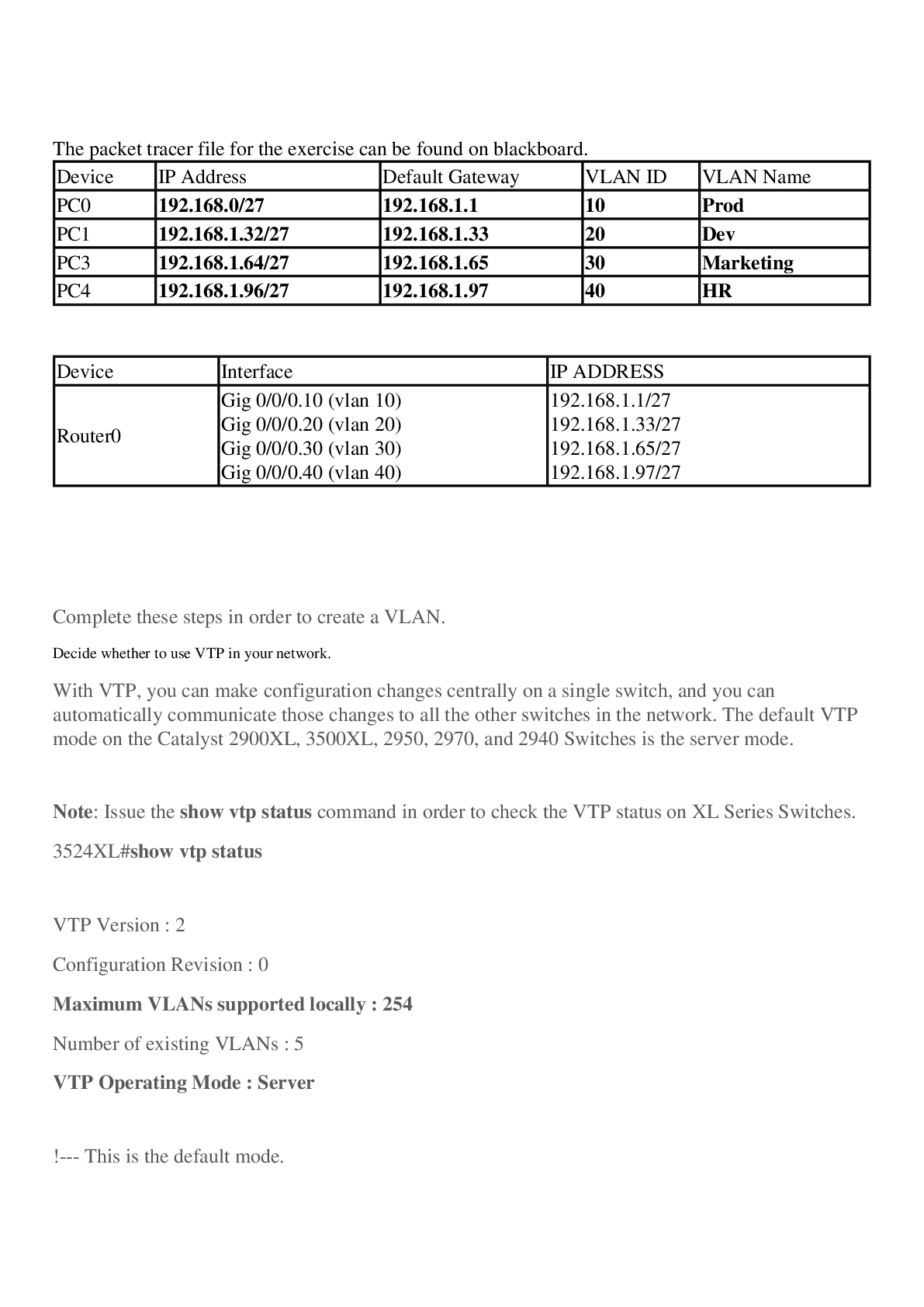
CISCO
$ 8
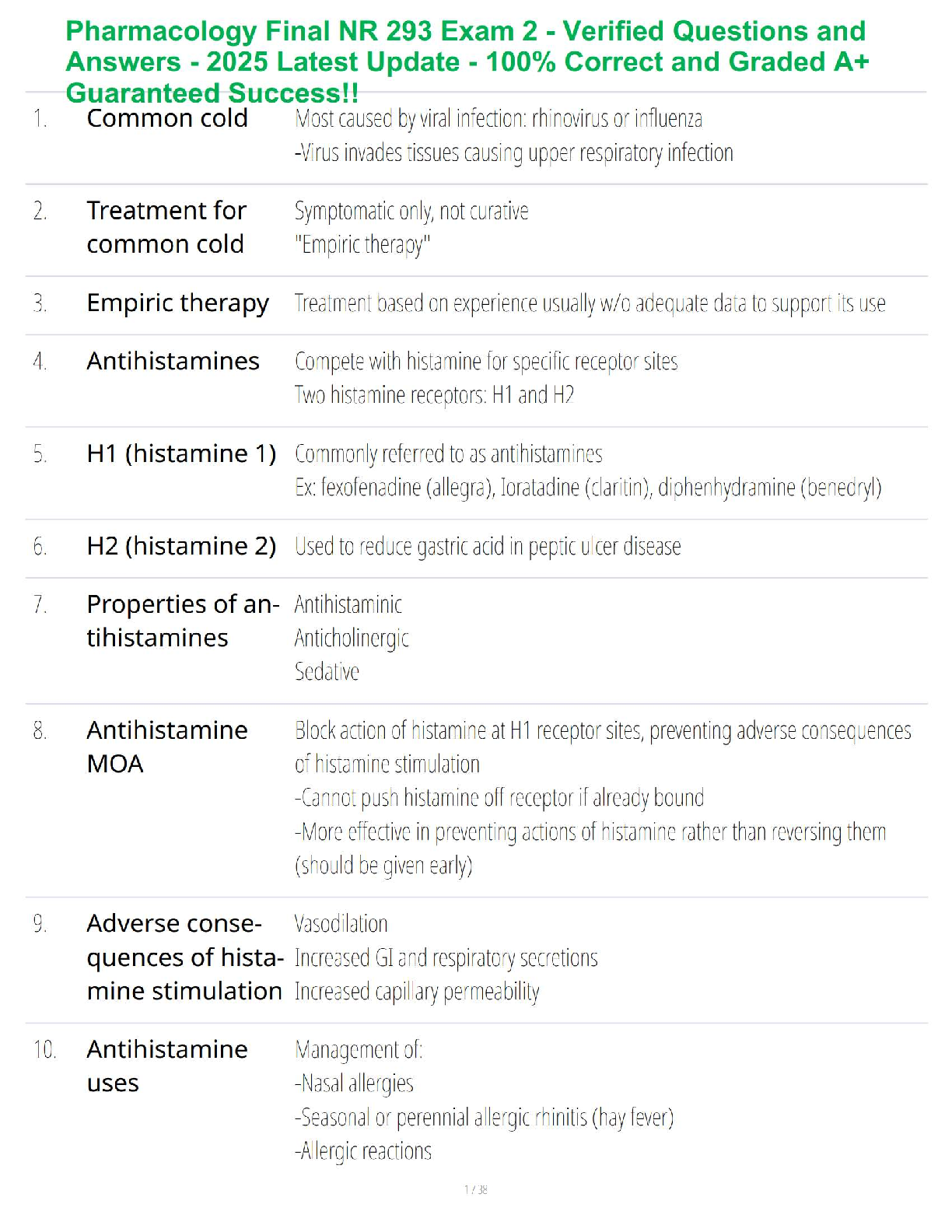
Pharmacology Final NR 293 Exam 1 - Verified Questions and Answers - 2025 Latest Update - 100% Correct and Graded A+ Guaranteed Success!!
$ 15.5
.png)
BPL 5100 GLO-BUS Industry 6, Golden Time Co SUMMARY OF DECISION MAKING
$ 7

Engineering & Technology Electrical Engineering Q1 a) Design a single-digit decade counter that counts from 0 to 9 and repeats. The single-digit decade counter should be built by a cascaded...
$ 8

CIS 524 - Term Paper - Crowdsourcing 2020
$ 30

ATI RN COMPREHENSIVE PREDICTOR 2023 BIOMECHANICS OF THE UPPER & LOWER LIMB-EXTREMITY AND BIOMECHANICS OF THE SPINE
$ 14

HUD Housing Counselor Certification Exam Guide 2025
$ 20

eBook PDF Commercial Refrigeration for Air Conditioning Technicians 3rd Edition By Dick Wirz
$ 30

(Intermediate HTML & CSS) CSS Functions Knowledge Assessment Guide 2024
$ 13

NICET FIRE ALARMS LEVEL 1 TEST LATEST 2025 WITH 130 QUESTIONS AND CORRECT VERIFIED ANSWERS/ NICET LEVEL 1 FIRE ALARMS EXAM 2025 (BRAND NEW!)
$ 15

Endocrine case study answers
$ 7

HRRB Exam Practice Questions 2022- 2023 – COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 9

MED SURG: AKI & CKD TEST 1-4 & STUDY GUIDE REVISIONS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS NEW 2024-2025
$ 19.5

SOLUTIONS MANUAL for Interplanetary Astrodynamics 1st Edition by David B. Spencer and Davide Conte ISBN-13 978-0367759704.
$ 22

eBook (EPUB) When the Moon Hits Your Eye 1st Edition By John Scalzi
$ 30

PDF(ebook) Computational Intelligence for Business Analytics,Witold Pedrycz ,Luis Martínez,1e
$ 27

NR-103 Week 2 Mindfulness Reflection | Download To Score An A



























