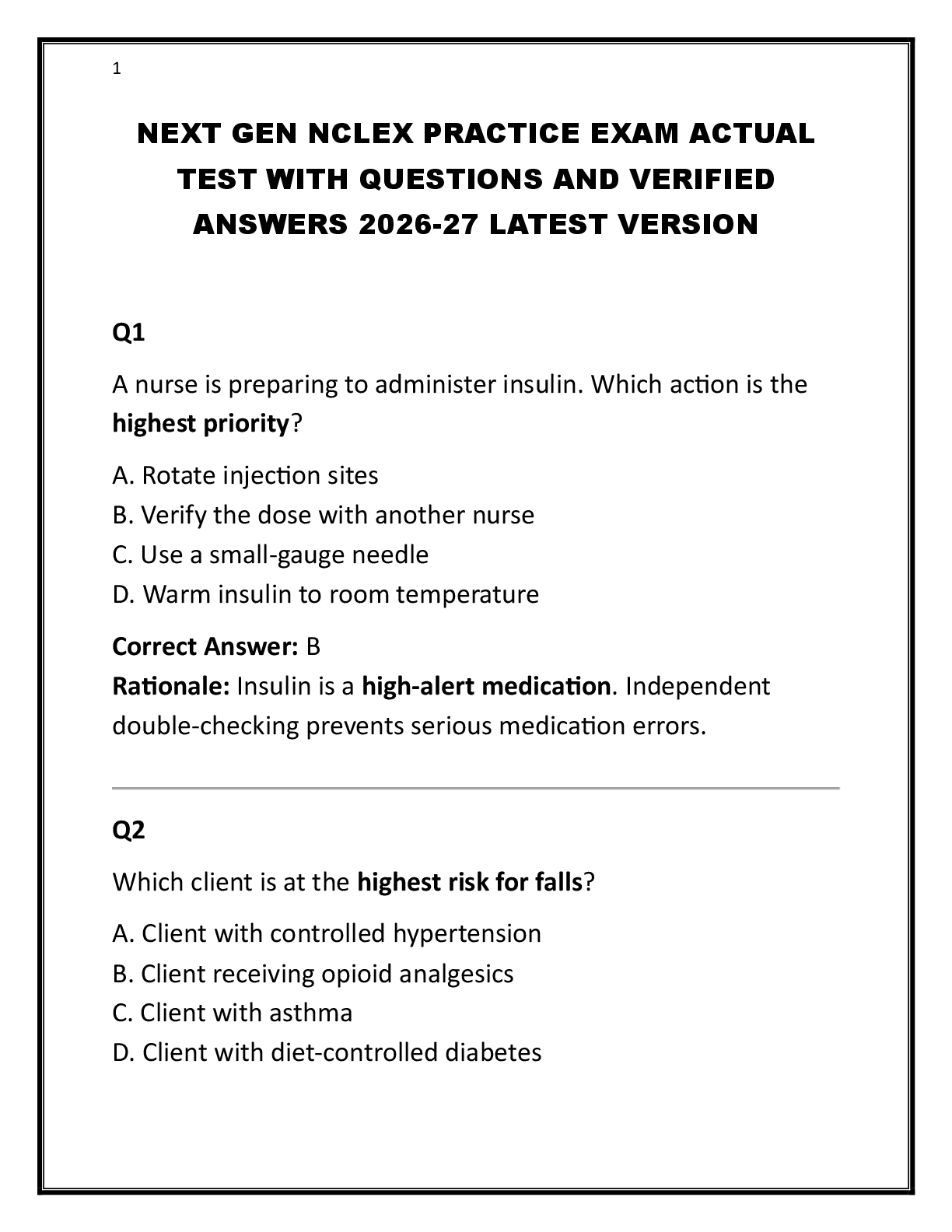
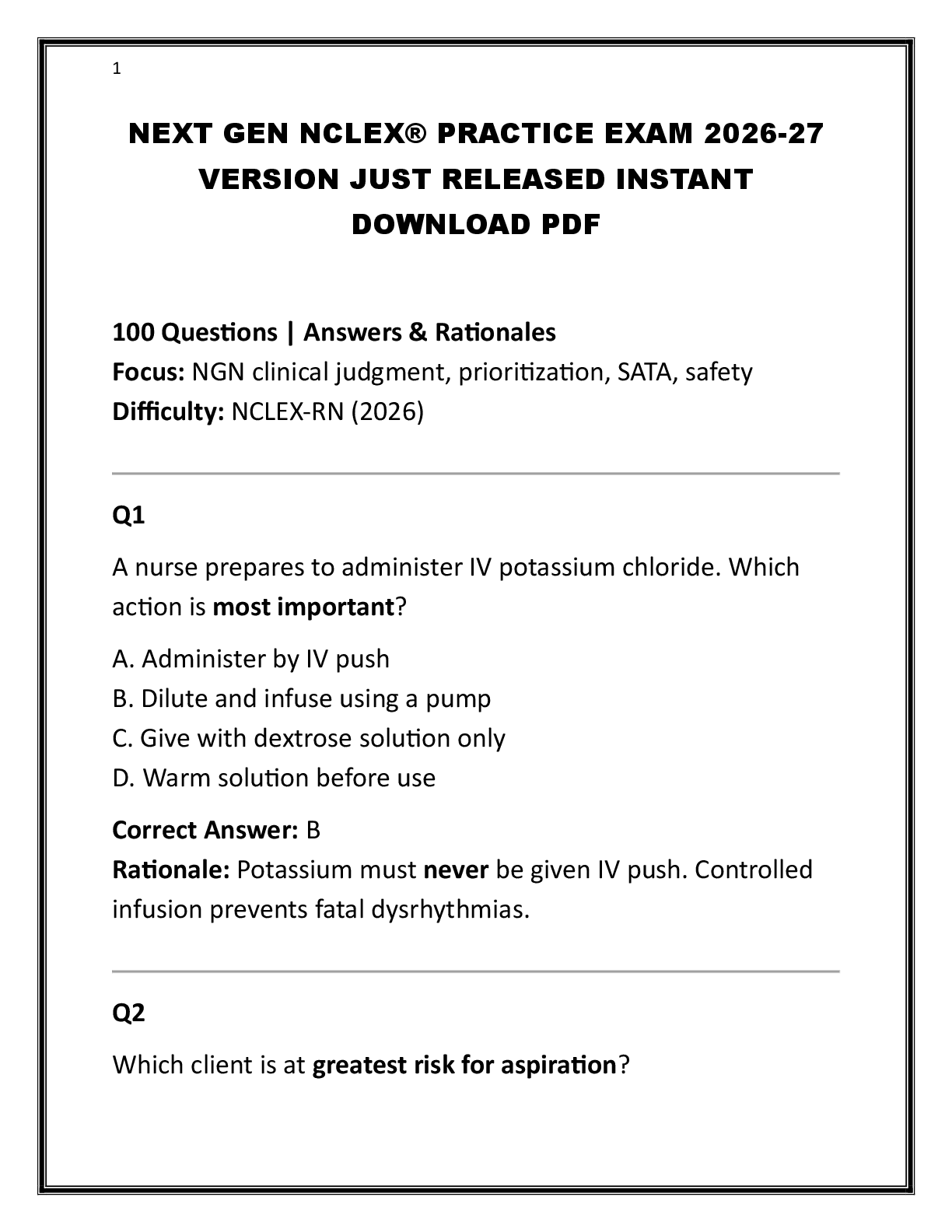
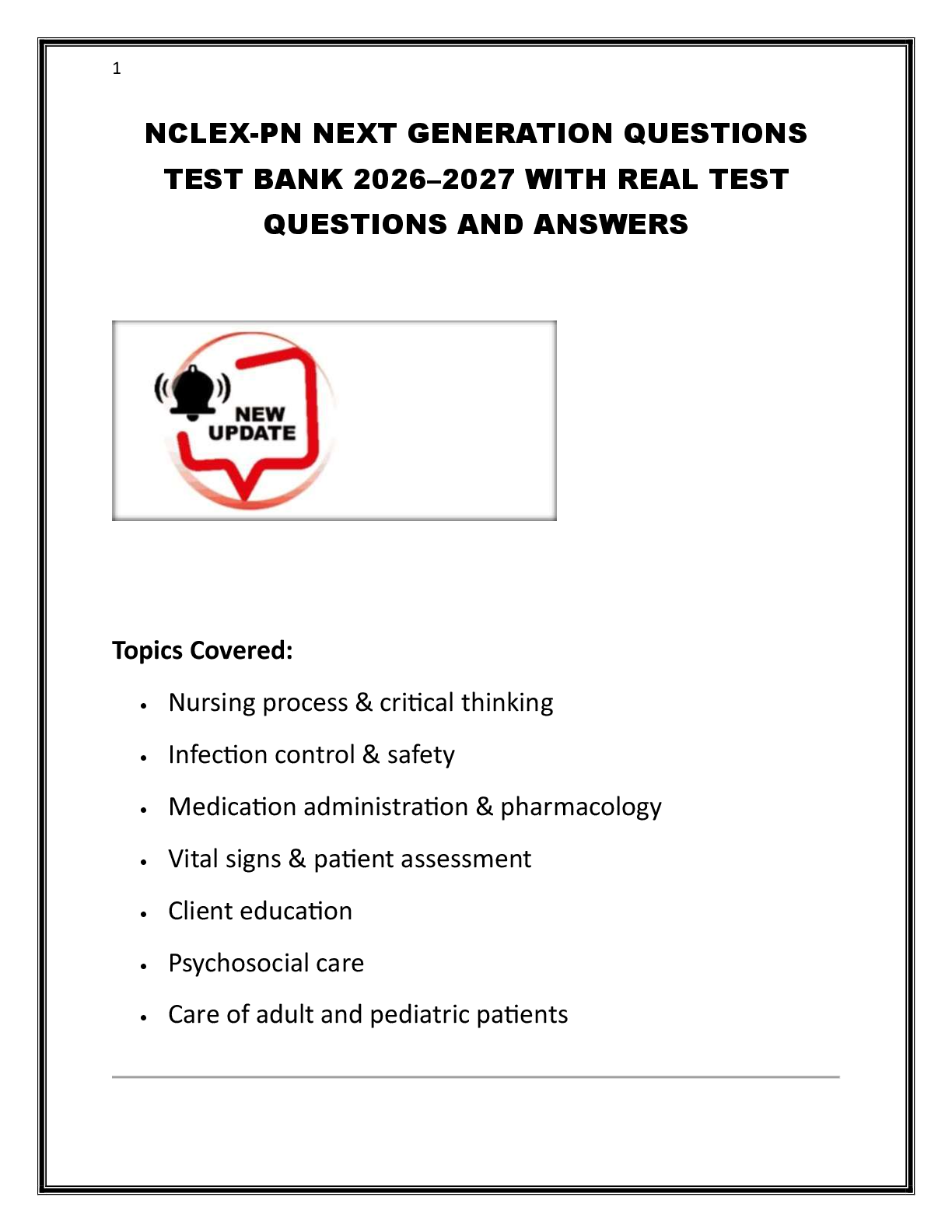
ATI PROCTORED EXAM PRACTICE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS A+ 2024
$ 12

BAOL 531Team 1 Roster Week 6 Assignment(Week 6 Assignment - Problems)
$ 11
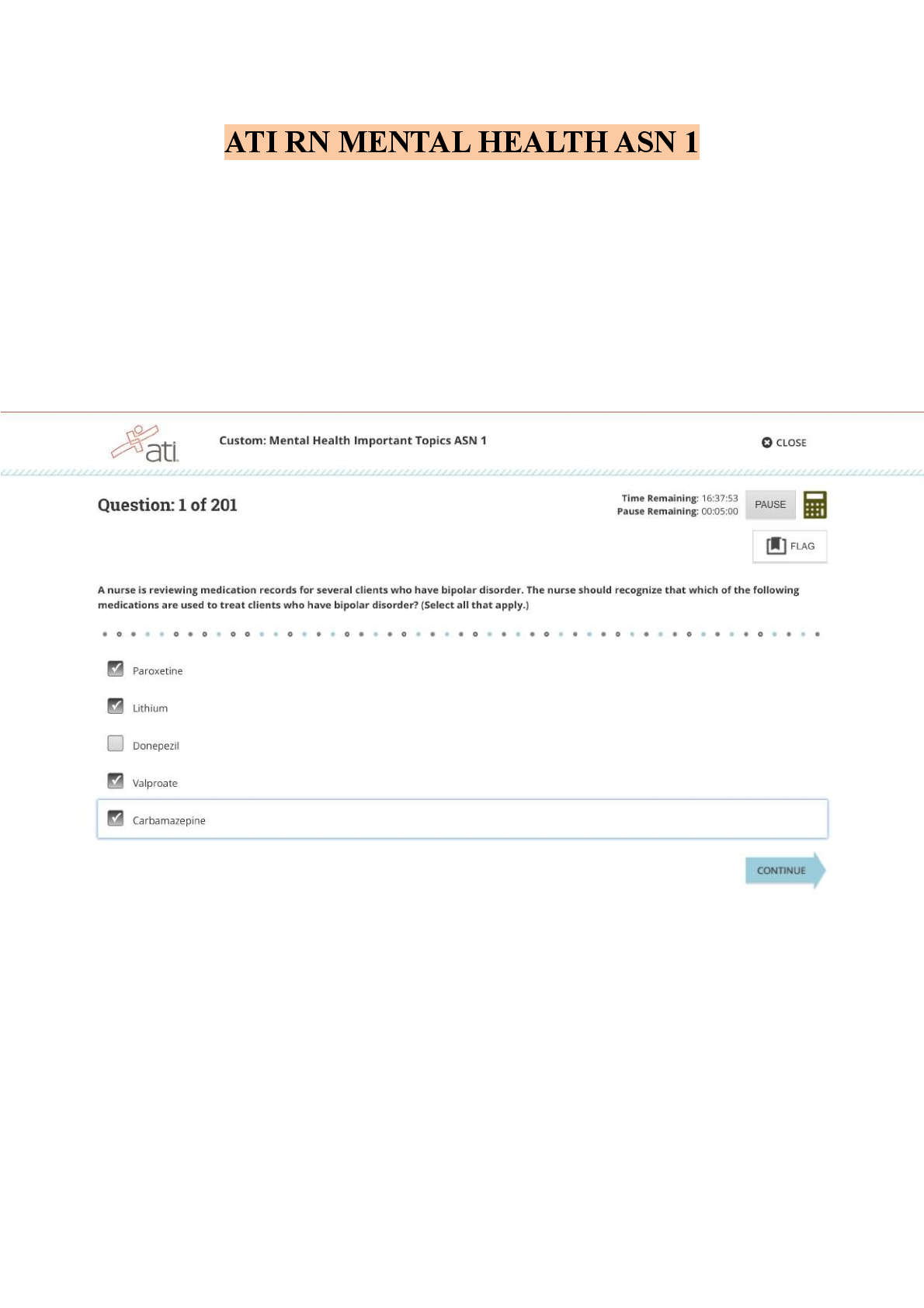
RN Mental Health CMS 2025 Exam Review 2025
$ 40

MATH 225N Week 6 Discussion 100% PASS
$ 7

NUR 550 Topic 4 DQ 1&2
$ 7

Test Bank for Cellular and Molecular Immunology 10th Edition Abbas
$ 12

STATS 139 Chapter 14 QUIZ - Optimization Modeling ;Applications MULTIPLE CHOICE( All answers correct)
$ 14

vSim for Nursing-Mental Health Case-Li Na Chen Part 1
$ 9

CHAPTER 1 STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEYVOCABULARY REVIEW
$ 12

Missouri State University, Springfield SPE 310 Chapter 7
$ 6

SALESFORCE CERTIFIED PARDOT CONSULTANT EXAM PRACTICE SOLUTION WITH ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 2022
$ 13

Clayton State University - SCI 1901FWho Killed Barry
$ 11

University of Maryland, University College STAT 200 Quiz 7.
$ 9

NURSING 7302 ADVANCED HEALTH ASSESSMENT OF THE NEONATE EXAM Q & A 2024
$ 11

NCLEX RN STUDY GUIDE - MED SURG.
$ 13.5

NURS 6550 Final Exam 2 | Walden University | Updated Fall 2024/2025 Question and Answers (Attempted Score {A+}
$ 12

NUR 513 Topic 4 Discussion Question 1/ COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 11
 Med Surg test questions Chapter 19 Postoperative Nursing Management.png)
Adult Nursing (NUR 105) Med Surg test questions Chapter 19 Postoperative Nursing Management
$ 12

ATI RN Medical Surgical Focus Review,Complete latest Summer 2022 solutions.
$ 6.5

NR 293 Week 8 Discussion: Glaucoma | GRADED A+ | Chamberlain College of Nursing
$ 9.5

HaDoop: What project was Hadoop originally a part of and what idea was that project based on?
$ 9

eBook [PDF] Crusading for Globalization US Multinationals and Their Opponents Since 1945 By Janick Marina Schaufelbuehl
$ 24

TX - SAE REAL ESTATE INVESTING PRACTICE EXAM Q & A 2024
$ 12

Mastering Anatomy & Physiology Lab Exam (Latest 2025/2026) | Verified Questions & 100% Correct Answers | A+ Guaranteed
$ 14.5

ATI RN Fundamentals Proctored Exam 2019 - 2020 Verified Q&A
$ 10

University of British Columbia BUSI 121 Homework Assignment 10 Answer Key.-VERIFIED BY EXPERTS-GRADED A+
$ 9

NURS 6551 Final Exam 5 with Answers