NR509 Shadow Health Physical Assessment Assignment Guidelines and Grading Rubric.
$ 11

NSG 5140 ADVANCED PATHOPHYSIOLOGY MIDTERM LATEST TEST EXAM REVIEW 2026 STUDY QUESTIONS WITH CORRECT VERIFIED ANSWERS 100% GUARANTEED PASS | RATED A+
$ 14.5

CPSGT AND RPSGT Exam Practice Questions (Polysomnography) 100% Correct
$ 10.5

Chapter 66: Shock, Sepsis, and Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th Edition
$ 6
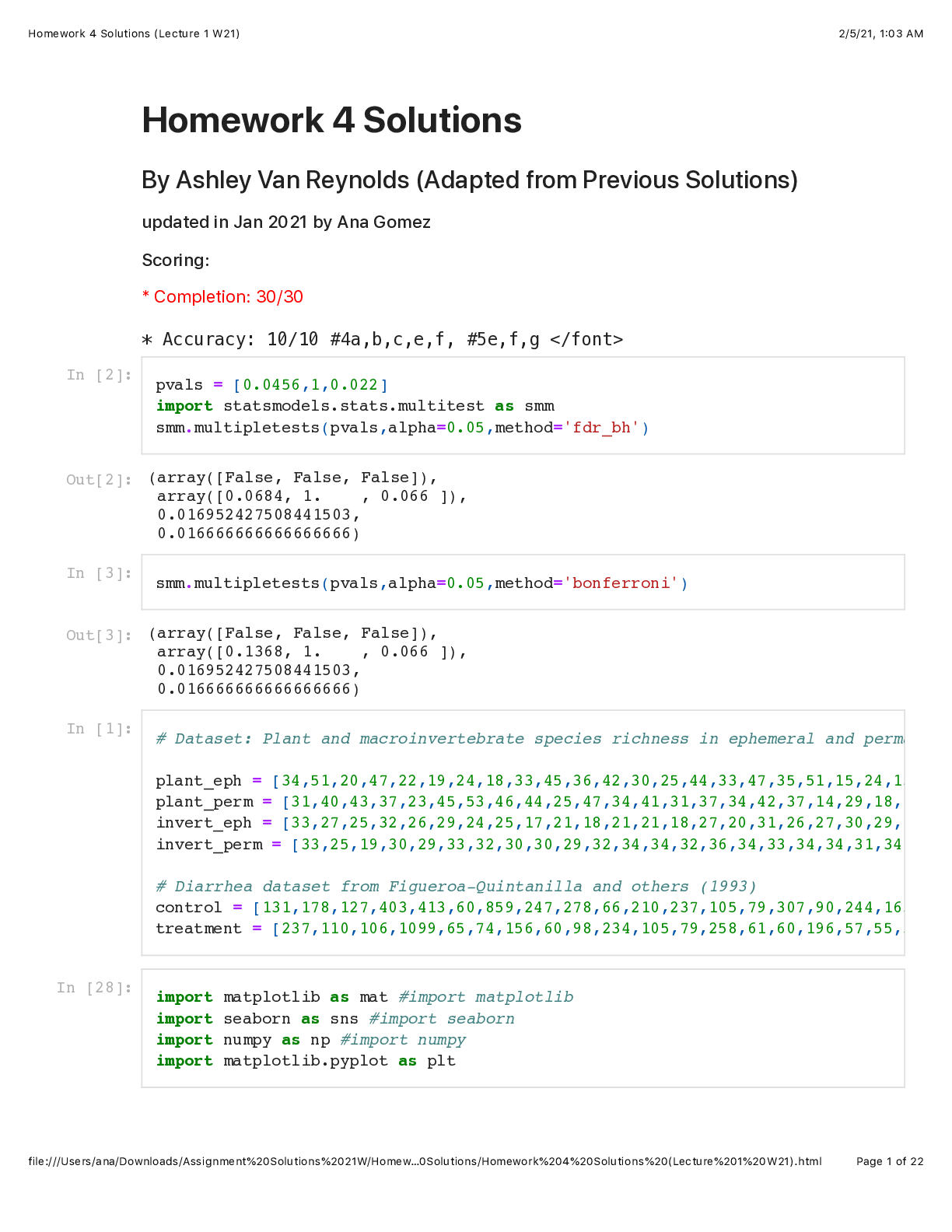
LS 40 (Life Science) Homework 4 Solutions (Lecture 1 W21)updated in Jan 2021
$ 13.5
 (1).png)
Comp 230 Quiz Week 6 (GRADED A) Questions and And Answer solutions | ALL CORRECT
$ 11

NCCER Electrical Level 3 Module 6: Distribution Equipment
$ 7.5

IT 336 INFORMATION ASSURANCE AND SECURITY REVIEW EXAM Q & A 2024IT 336 INFORMATION ASSURANCE AND SECURITY REVIEW EXAM Q & A 2024
$ 15

NR 328 – Pediatric Nursing MIDTERM EXAM 2 Questions and correct Answers (Verified Answers) 2025
$ 15

A-level FRENCH 7652/1 Paper 1 Listening, Reading and Writing Mark scheme June 2021 Version: 1.0 Final
$ 7

Nursing Informatics Concepts & Certification / Implementation Guide / 2025 Study Guide / Score 100% / Test Bank
$ 23

CST EXAM REVIEW basic science. Terms definition, question and answers, rated A
$ 5

[eBook][PDF] Children and Their Development, 7th (Global Edition) By Robert V. Kail
$ 14.5

RNSG1215 HA/EXAM 3/2022 Solved / RNSG 1215 Health Assessment Exam 3 Answered Spring 2022.
$ 18

WGU C182 Objective Assessment Questions And Answers Latest Update
$ 13.5

Nur 500 week_5_discussion
$ 9

RNSG 1363 Clinical Decision-Making Study Guide Graded A 2025